Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
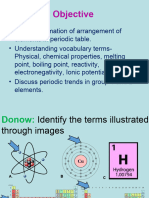
Most Reactive Most Reactive
Hochgeladen von
Kenth Roger A. MaquilingOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Most Reactive Most Reactive
Hochgeladen von
Kenth Roger A. MaquilingCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Most Reactive Potassium
Sodium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Tin
Lead
Hydrogen
Cooper
Silver
Gold
Least Reactive Platinum
Most Reactive Potassium
Sodium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Tin
Lead
Hydrogen
Cooper
Silver
Gold
Least Reactive Platinum
Most Reactive Potassium
Sodium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Tin
Lead
Hydrogen
Cooper
Silver
Gold
Least Reactive Platinum
Most Reactive Potassium
Sodium
Calcium
Magnesium
Aluminium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Tin
Lead
Hydrogen
Cooper
Silver
Gold
Least Reactive Platinum
Reactivity of
Elements
Lower then Higher: Play
Your Cards Right!
Submitted to: Mrs. Leonita Orozco
Submitted by; Kenth Roger Maquiling
Reactivity of Elements
Lower then Higher: Play your Cards Right!
Objective: To be able to determine the reactivity of the elements and learn how they
are known to be more reactive than the other.
Materials: Element Cards
Tape
A piece of short bond paper
Procedure:
1. The group will be given 14 cards, each containing an element.
2. A soon as the cards are given, (a) write the elements in an order of
decreasing reactivity.
3. Then (b) in an order of increasing reactivity, on the blank short bond paper.
Remember: Write the members on your group at the back of the page.
Evaluation:
1. The reactivity of an element or a metal depends on what?
2. In group 1A, does the reactivity increases or decreases? Support your
answer.
3. How about in group 7? Explain.
4. The farther from the nucleus an outer electron is, the ___________ it is to
break its attraction to the atomic nucleus.
5. How is the electronegativity of an element related to its reactivity?
Electronegativity is determined by what?
Conclusion:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- WS For PracticalDokument2 SeitenWS For PracticalRathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andrea, Roseline, Keely CH 5 Flame TestDokument7 SeitenAndrea, Roseline, Keely CH 5 Flame TestKeely Wu吳思穎Noch keine Bewertungen
- Redox Reaction Explanation: Zn Replaces Cu in CuSO4Dokument11 SeitenRedox Reaction Explanation: Zn Replaces Cu in CuSO4Logayne AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Bonding PresentationDokument21 SeitenIonic Bonding PresentationCheezy NachosNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 8 - Expt.6 - Voltaic CellDokument5 SeitenGROUP 8 - Expt.6 - Voltaic CellNicko CortoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms, Elements & the Periodic Table ActivityDokument2 SeitenAtoms, Elements & the Periodic Table ActivityMarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.6 Copper Plating and ElectrolysisDokument12 Seiten8.6 Copper Plating and ElectrolysisADITYA RAHMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 2 Online: Oxidation-Reduction Activity SeriesDokument12 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 2 Online: Oxidation-Reduction Activity SeriesirfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties Dobereiner Classification of ElementsDokument5 SeitenClassification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties Dobereiner Classification of ElementsVigneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Periodic Trends Updated 2023Dokument58 SeitenThe Periodic Trends Updated 2023stutireddy1912Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voltaic Cell - Yale UniversityDokument4 SeitenVoltaic Cell - Yale UniversityBelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonding: Unit 6 Honors Chemistry - 10 Grade Mr. Ali SaadDokument20 SeitenChemical Bonding: Unit 6 Honors Chemistry - 10 Grade Mr. Ali Saadapi-439932199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wesley Fink - Lemon Power Lab Write-UpDokument3 SeitenWesley Fink - Lemon Power Lab Write-Upapi-375163452Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2-Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDokument22 SeitenCh2-Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingSaif AlbaddawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science-9 Q2 M3 Wk3Dokument13 SeitenScience-9 Q2 M3 Wk3RILEY JASH GARCIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Melc No. 3: Explain How Ions Are Formed (S9Mt-Iie-F-16) : Alkaline Earth Metals Non-Metals ActinidesDokument11 SeitenMelc No. 3: Explain How Ions Are Formed (S9Mt-Iie-F-16) : Alkaline Earth Metals Non-Metals ActinidesAira RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Trends_0 (1)Dokument14 SeitenPeriodic Trends_0 (1)idontlike244Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 Grade 8 Atoms and The Periodic TableDokument49 SeitenWeek 5 Grade 8 Atoms and The Periodic TablemkraemerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table - Dr. MahbubDokument42 SeitenPeriodic Table - Dr. MahbubWREAK OFFICIALSNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionsDokument2 SeitenQuestionsNeema Lubin0% (1)
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1Dokument7 SeitenScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Properties Unit 4 Notes on Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsDokument4 SeitenMaterial Properties Unit 4 Notes on Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsSAP BWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good MorningDokument17 SeitenGood MorningRyan SacoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tania Melendez-Lainez - Reactivity LabDokument3 SeitenTania Melendez-Lainez - Reactivity LabTania Melendez-LainezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - The Solid State: Page No 4Dokument29 SeitenChapter 1 - The Solid State: Page No 4shivansh gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flame TestDokument32 SeitenFlame TestElisa EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Law Notes Answer Key PDFDokument9 SeitenPeriodic Law Notes Answer Key PDFamalieroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exploration: Electron ConfigurationDokument9 SeitenStudent Exploration: Electron ConfigurationJohn Hudson Student - SandersonHS0% (1)
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1Dokument7 SeitenScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 1 Validated 1MYLENE B. ZABALLERONoch keine Bewertungen
- EE138 Chapter 4-SlidesDokument10 SeitenEE138 Chapter 4-SlidesWenhaoShiNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII Chemistry CH#1 Notes (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)Dokument25 SeitenXII Chemistry CH#1 Notes (Sir Nasim Zulfiqar)haideralihulioNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII Chemistry 2023 (Complete Notes) - 1Dokument201 SeitenXII Chemistry 2023 (Complete Notes) - 1anzalabdullatif2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics STREAM Club - Activity 1 - April 2021Dokument3 SeitenPhysics STREAM Club - Activity 1 - April 2021Paige Azizan SawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment Date Title Purpose: Shanique ThomasDokument4 SeitenExperiment Date Title Purpose: Shanique Thomasshanique thomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lemon PowerDokument2 SeitenLemon Powerapi-385956544Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kecenderungan Sifat Periodik 2018Dokument45 SeitenKecenderungan Sifat Periodik 2018Maulina SurindriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flame Test Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenFlame Test Lab ReportJohn Carlo Almero0% (1)
- Atoms, Electrons & Energy Levels: Electrons Are The Bonds That Hold The World Together!Dokument41 SeitenAtoms, Electrons & Energy Levels: Electrons Are The Bonds That Hold The World Together!cmillica1176100% (3)
- Thermochemistry LabDokument16 SeitenThermochemistry Labapi-342506583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flinn Lab 1: Atomic Structure & Periodic Trends: Observe Part 1Dokument7 SeitenFlinn Lab 1: Atomic Structure & Periodic Trends: Observe Part 1Angelo RayesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Metals ExperimentDokument15 SeitenProperties of Metals ExperimentSamVicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions Periodic Table of Elements Get The Table Organized in TimeDokument3 SeitenQuestions Periodic Table of Elements Get The Table Organized in TimeJonathan ApiladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Grade Electric Circuits LessonDokument14 Seiten4th Grade Electric Circuits Lesson4Be BraveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrolysis: of Molten Ionic CompoundsDokument16 SeitenElectrolysis: of Molten Ionic CompoundsHafiz Abdul RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QTR 1 Module 5 Metals & NonmetalsDokument12 SeitenQTR 1 Module 5 Metals & NonmetalsNick BantoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- KT Term Classification of ElementsDokument6 SeitenKT Term Classification of ElementsAnkit TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- COURSES > PHYSICS GUEST SITE > CONTROL PANEL > 2ND SEM. QUIZZES > PREVIEW ASSESSMENT Q01Dokument97 SeitenCOURSES > PHYSICS GUEST SITE > CONTROL PANEL > 2ND SEM. QUIZZES > PREVIEW ASSESSMENT Q01agil syahrirNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 BondingDokument48 SeitenCH 2 BondingMusab Abdrabbuh100% (1)
- Periodic TrendsDokument30 SeitenPeriodic TrendsRobert obispoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument24 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesMadhan chakravarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSSM Topic 5Dokument18 SeitenTSSM Topic 5sudotesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital Diagrams Valance Electrons Electron Dot StructuresDokument20 SeitenOrbital Diagrams Valance Electrons Electron Dot StructuresKieth ObaobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure & Interatomic BondingDokument25 SeitenAtomic Structure & Interatomic BondingusercmdmcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kids Science ExperimentsDokument2 SeitenKids Science ExperimentsAkihilesh Singh Thakur100% (1)
- Radio Activity and ParticlesDokument34 SeitenRadio Activity and ParticlesKiron SheiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Periodic Law NotesDokument36 SeitenThe Periodic Law NotesAref DahabrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 2, Wk.2-M2Dokument29 SeitenScience: Quarter 2, Wk.2-M2Sir Miguel MalvarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Help Sheet 5a - Atomic Structure & PeriodicityDokument4 SeitenHelp Sheet 5a - Atomic Structure & PeriodicityAdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Activity-Sheet-ModularDokument6 SeitenScience Activity-Sheet-ModularNathea Jehiel Santa AnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Csomes DNADokument6 Seiten9 Csomes DNAKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure 30ml Egg White in A Beaker Prepare 30 of Whole MilkDokument1 SeiteMeasure 30ml Egg White in A Beaker Prepare 30 of Whole MilkKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stored SamplesDokument2 SeitenStored SamplesKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Flow in Pipes: Laminar vs Turbulent Flow and Head LossesDokument34 SeitenFluid Flow in Pipes: Laminar vs Turbulent Flow and Head LossesKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beer NotesDokument5 SeitenBeer NotesKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3 2Dokument6 SeitenExperiment 3 2Kenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urine Analysis: Physical & Microscopic ExamDokument7 SeitenUrine Analysis: Physical & Microscopic ExamKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stewed Chicken With Hunt's Pork & BeansDokument1 SeiteStewed Chicken With Hunt's Pork & BeansKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 4Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 4Kenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems (LT1)Dokument1 SeitePractice Problems (LT1)Kenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Vision: The Association of Biological Engineers and Biotechnologists (BIOLOGIC) Will Aspire To Promote BiologicalDokument6 SeitenOur Vision: The Association of Biological Engineers and Biotechnologists (BIOLOGIC) Will Aspire To Promote BiologicalKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiDokument1 SeiteExperiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Sheet: CHM 115 Analytical Chemistry Lecture 2Dokument1 SeiteSummary Sheet: CHM 115 Analytical Chemistry Lecture 2Kenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Tests: Experiment 1 Preliminary Tests and Solubility Classification of Organic CompoundsDokument1 SeitePreliminary Tests: Experiment 1 Preliminary Tests and Solubility Classification of Organic CompoundsKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO24P Practice Problem: Prepared By: HscabreraDokument1 SeiteBIO24P Practice Problem: Prepared By: HscabreraKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 5: pGLO™ Bacterial Transformation: Schematic DiagramDokument1 SeiteExperiment 5: pGLO™ Bacterial Transformation: Schematic DiagramKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiDokument1 SeiteExperiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiDokument1 SeiteExperiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiDokument1 SeiteExperiment 10: Isomerization of An Alkene Schematic Diagram: Group IiiKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- TaxonomyDokument7 SeitenTaxonomyKenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 5Dokument1 SeiteExperiment 5Kenth Roger A. MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rich Man and The Poor ManDokument1 SeiteThe Rich Man and The Poor ManInah Kristine AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsVon EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeVon EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionVon EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsVon EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableVon EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilVon EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksVon EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingVon EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolVon EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsVon EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (90)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryVon EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementVon EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableVon EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionVon EverandThe History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)