Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Metallurgical Testing
Hochgeladen von
Jitendra KumarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Metallurgical Testing
Hochgeladen von
Jitendra KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Metallurgical Testing
Non-Destructive Testing
This is carried out on components rather than on test pieces, they are designed to indicate flaws occurring
due or after manufacture. They give no indication of the mechanical properties of the material.
Surface flaws may be detected by visual means aided by dye penetrant or magnetic crack
detection. Internal flaws may be detected by X-ray or ultrasonic testing.
In addition to this there are special equipment able to eam machine finish.
Liquid Penetrant Methods
The surface is first cleaned using an volatile cleaner and degreaser. ! fluorescent dye is then applied and a
certain time allowed for it to enter any flaws under capillary action. "sing the cleaning spray, the surface
is then wiped clean. !n ultra violet light is shone on the surface, any flaws showing up as the dye
fluoresce.
The more commonly used #ye penetrant method is similar in application. The surface is
cleaned an d the low viscosity penetrant sprayed on. !fter a set time the surface is again cleaned. !
developer is then used which coats the surface in a fine white chalky dust he dye seeps out and stains the
developer typically a red colour.
$oth these methods are based loosely on the old paraffin and chalk method.
Magnetic crack detection
! component is place between two poles of a magnet The lines of magnetism concentrate around flaws.
%agnetic particles are then applied, in a light oil or dry sprayed, onto the surface where they indicate the
lines of magnetism and any anomalies. This method of testing a has a few limitations. &irstly it cannot be
used on materials which cannot be magnetised such as austenitic steel and non-ferrous metals. Secondly
it would not detect a crack which ran parallel to the lines of magnetism.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Brochure o Pumps Deepwell Gas CarriersDokument4 SeitenBrochure o Pumps Deepwell Gas CarriersJohn MarxisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen AnalysersDokument2 SeitenOxygen AnalysersJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pilgrim NutDokument2 SeitenPilgrim NutJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallel Operation of GeneratorsDokument5 SeitenParallel Operation of GeneratorsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Ship Steam Plan1Dokument3 SeitenMotor Ship Steam Plan1Jitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
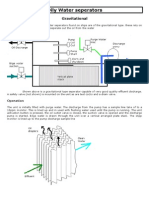
- Oily Water SeperatorsDokument2 SeitenOily Water SeperatorsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation of A Centrifugal Oil PurifersDokument3 SeitenOperation of A Centrifugal Oil PurifersJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Microbiological AttackDokument10 SeitenOverview of Microbiological AttackJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
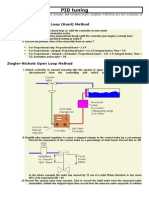
- PID TuningDokument4 SeitenPID TuningJitendra Kumar100% (1)
- Overall Arrangement: Description of The Salient PartsDokument6 SeitenOverall Arrangement: Description of The Salient PartsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Increasing Propulsive EfficiencyDokument6 SeitenIncreasing Propulsive EfficiencyJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molybdenum DiSulphideDokument1 SeiteMolybdenum DiSulphideJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil WhirlDokument2 SeitenOil WhirlJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Distribution and Factors in Journal BearingsDokument2 SeitenOil Distribution and Factors in Journal BearingsAnkit DedhiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbes of Microbiological Attac1Dokument3 SeitenMicrobes of Microbiological Attac1Jitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Ship Steam Plant ControlDokument1 SeiteMotor Ship Steam Plant ControlJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tooth Design: Forces Acting On Spur GearsDokument77 SeitenTooth Design: Forces Acting On Spur GearsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navigation LightingDokument1 SeiteNavigation LightingJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marpol 73Dokument12 SeitenMarpol 73Jitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical GovernorsDokument1 SeiteMechanical GovernorsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbes of Microbiological Attac1Dokument3 SeitenMicrobes of Microbiological Attac1Jitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Used in Ships Sea Water SystemsDokument1 SeiteMaterials Used in Ships Sea Water SystemsAnkit DedhiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
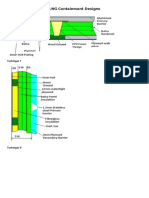
- LNG Containment DesignsDokument3 SeitenLNG Containment DesignsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LNG Reliquifactio1Dokument1 SeiteLNG Reliquifactio1Jitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquified Gas CargoesDokument2 SeitenLiquified Gas CargoesJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lifting Using Accessories: Calculation of LoadDokument2 SeitenLifting Using Accessories: Calculation of LoadJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lube Oil Requirements For Diesel EnginesDokument3 SeitenLube Oil Requirements For Diesel EnginesJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Sulphur FuelsDokument1 SeiteLow Sulphur FuelsJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jacket Water SystemDokument2 SeitenJacket Water SystemJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)