Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Project Pulmonary Artery
Hochgeladen von
Sirajus SalekinOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Project Pulmonary Artery
Hochgeladen von
Sirajus SalekinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Sirajul Salekin @01290031
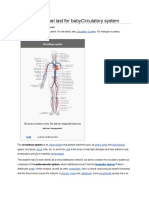
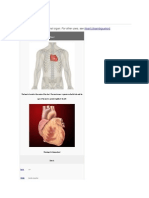
PULMONARY ARTERY
General Description:
The pulmonary arteries are blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the
lungs. It is one of the only arteries (other than the umbilical arteries in the fetus) that carry
deoxygenated blood.
In the human heart, main pulmonary artery begins at the base of the right ventricle. It is short
and wide - approximately 3.3 cm (1.5 inches) in length and 1.4 cm (0.65 inches) in diameter. It
then branches into two pulmonary arteries (left and right), which deliver de-oxygenated blood
to the corresponding lung.
Properties:
1. One of the most important parts of the whole heart anatomy
2. Maximum length in normal subject = 3.3 cm [1]
3. The normal mean pulmonary artery pressures is less than or equal to 18 mm Hg. [2]
4. Divided into the left pulmonary artery (LPA) and right pulmonary artery (RPA)
5. The RPA is longer than the LPA
Function:
1. Carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs.
2. Returns oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Dependency on external forces:
1. Presence of foreign substances in the pulmonary arteries blocks blood flow.
2. Blocking of blood flow increases the blood pressure in pulmonary artery.
References:
[1] Edwards PD, Bull RK, Coulden R. CT measurement of main pulmonary artery diameter. Br J
Radiol 1998;71:101820.
[2] Haimovici JBA, Trotman-Dickenson B, Halpern EF, et al. Relationship between pulmonary
artery diameter at computed tomography and pulmonary artery pressures at right-sided heart
catheterization. Acad Radiol 1997;4:32734.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartVon EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary CirculationDokument4 SeitenPulmonary CirculationDr Md Abedur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human HeartDokument6 SeitenHuman HeartVui SengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visceral Vascular Manipulation, 2011Dokument270 SeitenVisceral Vascular Manipulation, 2011kkalu_just_funky91% (11)
- Lecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceDokument29 SeitenLecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceAparmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System Q&A.Dokument77 SeitenCirculatory System Q&A.Alyasin FrougaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syok Hipovolemik EnglishDokument25 SeitenSyok Hipovolemik Englishatmarida 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseDokument10 SeitenA Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseBarben Balaquit100% (1)
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Dokument13 SeitenBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756Noch keine Bewertungen
- L2 PulmonaryCirculation PHAR6200 MMPH6172 173110Dokument85 SeitenL2 PulmonaryCirculation PHAR6200 MMPH6172 173110Rankie ChoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8Qghuzdwhu3K/Vlrorj/: 3-1 PurposeDokument54 Seiten8Qghuzdwhu3K/Vlrorj/: 3-1 PurposejaimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of The Cardiovascular SystemDokument5 SeitenComponents of The Cardiovascular SystemLorinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypertensionDokument9 SeitenHypertensionEdmr SlzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument24 SeitenCardiovascular SystemSurya VootlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elvina CH 2Dokument2 SeitenElvina CH 2Solomon Fallah Foa SandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note On Pressure Flow and ResistanceDokument43 SeitenNote On Pressure Flow and ResistanceSilver FestusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brevet Ch5 Circulation NotesDokument2 SeitenBrevet Ch5 Circulation Notesmajdkaraki9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio Physiol LectDokument20 SeitenCardio Physiol LectVivek ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Termpaper DPTDokument80 SeitenTermpaper DPTAsha jiluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanDokument4 SeitenLoreto, Bien BMG3FX/MWF/3:00-04:00 Lugo, Mariel Cabigao, JeanJean CabigaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDokument15 SeitenCardiovascular PhysiologyFARHAH BATRISYIA ABDUL RAHIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood VesselsDokument17 SeitenBlood VesselsLorraine OrugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem Peredaran DarahDokument4 SeitenSistem Peredaran DarahIndah SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument12 SeitenCirculatory SystemDipanshu JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Dokument9 SeitenBIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Jv Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics and The Cardiovascular System: October 2017Dokument30 SeitenPhysics and The Cardiovascular System: October 2017Ali HadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Circulatory SystemDokument16 SeitenHuman Circulatory SystemABDUL HANANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDokument13 SeitenCardio Respiratory Endurance Mam PascoDavid GoliathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical Root SyndromeDokument11 SeitenCervical Root SyndromeFadilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Heart ScienceDokument7 SeitenHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System - Lecture IIDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular System - Lecture IIpragantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Cardiovaskuler System: Institute of Health Science Pekanbaru Medical Center 2018Dokument7 SeitenPaper Cardiovaskuler System: Institute of Health Science Pekanbaru Medical Center 2018Rismala RANoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument11 SeitenCirculatory SystemAhmad S AlkarmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 ReviewerDokument7 SeitenScience 9 ReviewerArgie MabagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter # 33Dokument4 SeitenChapter # 33Lydia ValenciagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 103 Section 3 Circulatory, Respiratory & Excretory SystemDokument33 SeitenBio 103 Section 3 Circulatory, Respiratory & Excretory SystemMD Reyadus SalihenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeDokument9 SeitenThe Human Heart: Location, Size and ShapeL I G-Arijit HisabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2Dokument29 Seiten5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2uxdan154Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circulation and Cardiovascular SystemDokument12 SeitenCirculation and Cardiovascular SystemSatria MandalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Pathway: The Human Respiratory SystemDokument25 SeitenThe Pathway: The Human Respiratory SystemKenneth Decker PrietoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument21 SeitenCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDokument9 SeitenReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDan Ataniel EnsaladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Heart: Anatomy, Function & FactsDokument2 SeitenHuman Heart: Anatomy, Function & FactsFlorie Fe Rosario OrtegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory SystemDokument51 SeitenThe Circulatory SystemMohammed ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument9 SeitenPregnancy Induced HypertensionRiazell Antonio DungcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021Dokument5 SeitenCardiovascular System Lecture 1 2020 2021olawandeilo123Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemDokument8 SeitenHow Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemRoszana RafliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular SystemDrexel DalaygonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDokument7 SeitenPregnancy Induced HypertensionRalph Emerson RatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Anatomy Jeopardy GameDokument43 SeitenHeart Anatomy Jeopardy GameLaura HajdukiewiczNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3Dokument11 SeitenLec 3Mhmead AbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVSassignement 1 AnatomyDokument12 SeitenCVSassignement 1 AnatomyRista SimamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Function of The Left Atrium Is To Receive Blood From The Oxygen-Rich Lung and To Bring It Into The Left VentricleDokument3 SeitenThe Function of The Left Atrium Is To Receive Blood From The Oxygen-Rich Lung and To Bring It Into The Left VentricleAgung CahyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP AdhfDokument31 SeitenLP Adhften tenanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How The Heart WorksDokument6 SeitenHow The Heart Worksparveen bajajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Dokument10 SeitenLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart: This Article Is About The Internal Organ. For Other Uses, SeeDokument4 SeitenHeart: This Article Is About The Internal Organ. For Other Uses, Seemegawhat115Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideVon EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Old Algorithm New AlgorithmDokument3 SeitenOld Algorithm New AlgorithmSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE-3423 Signals and Systems I: Instructor: Dr. Artyom M. GrigoryanDokument12 SeitenEE-3423 Signals and Systems I: Instructor: Dr. Artyom M. GrigoryanSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amazon SDE Interview PrepDokument4 SeitenAmazon SDE Interview Prepkarunakarms8076100% (1)
- HW 2Dokument1 SeiteHW 2Sirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level Set Methods in Medical Image Analysis: Segmentation: Nikos ParagiosDokument92 SeitenLevel Set Methods in Medical Image Analysis: Segmentation: Nikos ParagiosSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Processing Codes For Different AlgorithmsDokument17 SeitenImage Processing Codes For Different AlgorithmsSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample ProposalDokument2 SeitenSample ProposalSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Time-Domain Ab Initio Perspective: Photoinduced Electron Transfer at Molecule-Semiconductor InterfacesDokument33 SeitenA Time-Domain Ab Initio Perspective: Photoinduced Electron Transfer at Molecule-Semiconductor InterfacesSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Processing and Data Analysis-The Multiscale ApproachDokument315 SeitenImage Processing and Data Analysis-The Multiscale ApproachSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motor Drives - Modeling Analysis and Control KrishnanDokument652 SeitenElectric Motor Drives - Modeling Analysis and Control KrishnanSirajus Salekin100% (1)
- Learning Hessian Matrix PDFDokument100 SeitenLearning Hessian Matrix PDFSirajus SalekinNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Security Notes International Security NotesDokument34 SeitenInternational Security Notes International Security NotesBEeNaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19c Upgrade Oracle Database Manually From 12C To 19CDokument26 Seiten19c Upgrade Oracle Database Manually From 12C To 19Cjanmarkowski23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Repair Manual (2017)Dokument59 SeitenConcrete Repair Manual (2017)Fernando EscriváNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Lesson 2Dokument31 SeitenModule 1 Lesson 2Angela Rose BanastasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Futures Volume 1 Issue 3 1969 (Doi 10.1016/0016-3287 (69) 90026-3) Dennis Livingston - Science Fiction As A Source of Forecast MaterialDokument7 SeitenFutures Volume 1 Issue 3 1969 (Doi 10.1016/0016-3287 (69) 90026-3) Dennis Livingston - Science Fiction As A Source of Forecast MaterialManticora VenerabilisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Convection Transfer EquationsDokument9 SeitenConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresDokument67 SeitenCSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresJellyn BaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft PDFDokument166 SeitenDraft PDFashwaq000111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exotic DVM 11 3 CompleteDokument12 SeitenExotic DVM 11 3 CompleteLuc CardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Management TY BSC ITDokument57 SeitenProject Management TY BSC ITdarshan130275% (12)
- User Manual PM3250Dokument80 SeitenUser Manual PM3250otavioalcaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 788 ManualDokument16 Seiten788 Manualn0rdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Beckers World of The Cell 9th Edition Hardin Solutions Manual PDFDokument35 SeitenDwnload Full Beckers World of The Cell 9th Edition Hardin Solutions Manual PDFgebbielean1237100% (12)
- Chapter 1Dokument6 SeitenChapter 1Grandmaster MeowNoch keine Bewertungen
- FpsecrashlogDokument19 SeitenFpsecrashlogtim lokNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVOM ManualDokument2 SeitenEVOM ManualHouston WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- DION IMPACT 9102 SeriesDokument5 SeitenDION IMPACT 9102 SeriesLENEEVERSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous Little Red Book SummaryDokument6 SeitenFamous Little Red Book SummaryMatt MurdockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1Dokument11 SeitenSteel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dominion Wargame RulesDokument301 SeitenDominion Wargame Rules4544juutf100% (4)
- Syllabus PDFDokument3 SeitenSyllabus PDFBibin Raj B SNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Based INSET Interim EvaluationDokument8 SeitenSchool Based INSET Interim Evaluationprinces arcangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signature Object Detection Based On YOLOv3Dokument4 SeitenSignature Object Detection Based On YOLOv3Lý Khánh NhưNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practising Modern English For Life Sciences Students Caiet Exercitii-1Dokument77 SeitenPractising Modern English For Life Sciences Students Caiet Exercitii-1Robert BobiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soujanya Reddy (New)Dokument6 SeitenSoujanya Reddy (New)durgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDokument181 SeitenModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pantalla MTA 100Dokument84 SeitenPantalla MTA 100dariocontrolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLG418 (Dcec) PM 201409022-EnDokument1.143 SeitenCLG418 (Dcec) PM 201409022-EnMauricio WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gomez-Acevedo 2010 Neotropical Mutualism Between Acacia and Pseudomyrmex Phylogeny and Divergence TimesDokument16 SeitenGomez-Acevedo 2010 Neotropical Mutualism Between Acacia and Pseudomyrmex Phylogeny and Divergence TimesTheChaoticFlameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Dokument3 SeitenSwitching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Jerry Fourier KemeNoch keine Bewertungen