Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Homework 4
Hochgeladen von
Arthur DingCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Homework 4
Hochgeladen von
Arthur DingCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
AE 321
Homework 4
Due in class on September 27, 2013
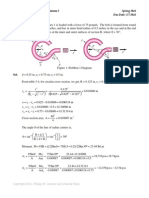
1. A metallic slab that is thin in z direction and has length and width equal to 2 in x and y
directions is subjected to tractions F, S, T (not to be determined) resulting at point A to the
stresses shown below.
(a) Determine the maximum shear stress on the x-y plane and the associated normal stresses and
draw the orientation of the element (square) they act.
(b) If this slab is made of an aluminum alloy with shear strength of 80 MPa, determine whether
the slab will fail (yield) or not.
60 MPa
20 MPa
90 MPa
A
y
x
O
T
F
S
F
S
T
2
2. The stress tensor at a point P in a material is given by:
o
ij
| |
=
3 1 1
1 0 2
1 2 0
(
(
(
KPa
(a) Find the principal stresses and principal directions of this stress tensor.
(b) Determine the magnitude and orientation of the absolute maximum shear stress at P.
3. The stress tensor at a point P referred to a (x, y, z) coordinate frame is:
120 40 30
150 20
100
ij
KPa o
(
(
( =
(
(
(a) Determine the stress components for a rotated frame (x, y, z) for which the matrix of
direction cosines is
o
ij
| |
=
1
2
3
2
0
3
2
1
2
0
0 0 1
(
(
(
(
(b) Compute the principal stresses using both the (x, y, z) and (x, y, z) axes as a basis.
(c) Find the orientation of the principal planes with respect to the (x, y, z) axes.
(d) Compute the stress invariants Q
i
for both frames (x, y, z) and (x, y, z) and verify that they
are equal.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #4: 1. First construct Mohr's circle. At stresses at the given element are σDokument8 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #4: 1. First construct Mohr's circle. At stresses at the given element are σArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 6 Solutions: (4 Points)Dokument7 SeitenHomework 6 Solutions: (4 Points)Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Dokument9 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #5: (5×5 25 POINTS)Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 Homework SolutionsDokument7 SeitenAE 321 Homework SolutionsArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 6Dokument1 SeiteHomework 6Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- (5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Dokument4 Seiten(5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE321 Homework SolutionsDokument13 SeitenAE321 Homework SolutionsArthur Ding100% (1)
- Homework 8Dokument3 SeitenHomework 8Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 5Dokument2 SeitenHomework 5Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σDokument6 SeitenSolutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #2Dokument7 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #2Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of MaterialsDokument282 SeitenMechanics of MaterialssydengineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Elastic FailureDokument6 SeitenTheories of Elastic FailurePrithvi ChilukuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrix Derivation of Spring FormulaDokument7 SeitenMatrix Derivation of Spring FormulanoormqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuum Mech ProblemsDokument85 SeitenContinuum Mech ProblemsDeepak Verma100% (1)
- Point Collocation Method Used in Solving Differential Equations in Boundary Value ProblemsDokument12 SeitenPoint Collocation Method Used in Solving Differential Equations in Boundary Value ProblemsSuddhasheel Basabi GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sol 4 Ma 1 C Prac 08Dokument5 SeitenSol 4 Ma 1 C Prac 08張芷瑕Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 SolutionDokument9 SeitenAssignment 3 SolutionMurat BayrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems in Unit - 1Dokument25 SeitenProblems in Unit - 1Prakasini SakthivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- As01 PDFDokument1 SeiteAs01 PDFAshutosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEMM Comp Dynamics Sp20Dokument5 SeitenSEMM Comp Dynamics Sp20RAFAELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Integral MCQ PDFDokument11 SeitenMathematics Integral MCQ PDFBilalAzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment #3 Solution - Spring 2014Dokument5 SeitenAssignment #3 Solution - Spring 2014Deepak KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics Response ForcesDokument4 SeitenStructural Dynamics Response ForcesMD NayeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium: Summing All Forces in The X Direction Where FX The Body Force Per Unit VolumeDokument6 SeitenEquilibrium: Summing All Forces in The X Direction Where FX The Body Force Per Unit Volumebadr amNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical ExamplesDokument20 SeitenNumerical ExampleslitrakhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 5Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 5Ansuman SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- SoMLec BeamDeflectionDokument16 SeitenSoMLec BeamDeflectionGibs RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics - Mock ExamDokument4 SeitenStructural Dynamics - Mock Examgen ridanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2014 15 CP2485 ASGN01 Friction With Answers Assignment 2Dokument6 SeitenFALLSEM2014 15 CP2485 ASGN01 Friction With Answers Assignment 2Chirag Sharma0% (1)
- Determinants Week 4 5Dokument47 SeitenDeterminants Week 4 5api-619738021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural dynamics problems and solutionsDokument8 SeitenStructural dynamics problems and solutionsamadeus135Noch keine Bewertungen
- Em 6.20Dokument3 SeitenEm 6.20sauciataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Stress ComponentsDokument8 Seiten3D Stress Componentsonnly1964Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - Types of Finite Elements - A4Dokument9 SeitenChapter 8 - Types of Finite Elements - A4GabrielPaintingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.5 Application of Multiple Integral)Dokument12 SeitenLecture Notes (Chapter 2.5 Application of Multiple Integral)shinee_jayasila2080Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of MaterialsDokument11 SeitenMechanics of MaterialsMagesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Analysis by Dr. Anita Pal Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics National Institute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209Dokument15 SeitenNumerical Analysis by Dr. Anita Pal Assistant Professor Department of Mathematics National Institute of Technology Durgapur Durgapur-713209KabirNoch keine Bewertungen
- A.MAULANA MALIK MH Dinamika Struktur c10Dokument6 SeitenA.MAULANA MALIK MH Dinamika Struktur c10Maulana MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Shear Deformations On The Elastic Critical Column LoadDokument5 SeitenThe Effect of Shear Deformations On The Elastic Critical Column Loadashok paul100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Airy Stress FunctionDokument19 SeitenChapter 5 Airy Stress FunctionGilang Farhan Ramadhan MulyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loaded Timoshenko BeamDokument9 SeitenLoaded Timoshenko Beamap scattolinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Stress Transformation in Shafts and BeamsDokument27 SeitenChapter 9: Stress Transformation in Shafts and BeamsYahia Raad Al-AniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch#5 CST Element PDFDokument17 SeitenCh#5 CST Element PDFAndre Sufadia SimorangkirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Questions 4523Dokument29 SeitenTutorial Questions 4523Toby Joseph ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05-Bar Element DuzeltilmisDokument56 Seiten05-Bar Element Duzeltilmismmk111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A: Piezoelectric Constitutive EquationsDokument6 SeitenAppendix A: Piezoelectric Constitutive EquationsAniruddh FaujdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buckling ExamplesDokument5 SeitenBuckling ExamplesSrivatsan SampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modal Analysis of Beams - An Experiment Symposium On Dynamic Problems of MechanicsDokument9 SeitenModal Analysis of Beams - An Experiment Symposium On Dynamic Problems of MechanicsnizamshahrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frame Analysis: Determine Natural Periods and Design Base Shear ForcesDokument6 SeitenFrame Analysis: Determine Natural Periods and Design Base Shear Forcesnial69100% (1)
- Sample - Solution Manual Metal Forming 4th Edition by William Hosford & Robert CaddellDokument24 SeitenSample - Solution Manual Metal Forming 4th Edition by William Hosford & Robert CaddellMaryam ʚiïɞNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Failure CriteriaDokument17 SeitenFatigue Failure CriteriaAmrMashhourNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1984 JN Reddy A Refined Nonlinear Theory of Plates With Transverse Shear Deformation IJSS 20Dokument16 Seiten1984 JN Reddy A Refined Nonlinear Theory of Plates With Transverse Shear Deformation IJSS 20fritz2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDokument9 SeitenPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toe QuestDokument4 SeitenToe Questrameshbabu_1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 2saurabhsryadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forces On DislocationsDokument24 SeitenForces On DislocationsArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAST - Lect22 Modal AnalysisDokument12 SeitenIAST - Lect22 Modal AnalysisArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #10Dokument6 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #10Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE321 Homework SolutionsDokument13 SeitenAE321 Homework SolutionsArthur Ding100% (1)
- (5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Dokument4 Seiten(5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE321 Homework 1 problemsDokument2 SeitenAE321 Homework 1 problemsArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #11Dokument6 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #11Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #8: Problem #1Dokument14 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #8: Problem #1Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σDokument6 SeitenSolutions of Homework 7: (A) Pressure at x=0, x=l resulting in uniform stress σArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 11Dokument2 SeitenHomework 11Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 - Solution of Homework #2Dokument7 SeitenAE 321 - Solution of Homework #2Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 10Dokument1 SeiteHomework 10Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- (5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Dokument4 Seiten(5 Points) : AE 321 - Solution of Homework #1Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 Homework 9 Due in Class On November 15, 2013: Problem 1Dokument2 SeitenAE 321 Homework 9 Due in Class On November 15, 2013: Problem 1Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 8Dokument3 SeitenHomework 8Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 5Dokument2 SeitenHomework 5Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE 321 Homework 7 Due in Class On November 1, 2013: Problem 1Dokument2 SeitenAE 321 Homework 7 Due in Class On November 1, 2013: Problem 1Arthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE321 Homework 1 problemsDokument2 SeitenAE321 Homework 1 problemsArthur DingNoch keine Bewertungen