Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Water Table Drainage
Hochgeladen von
Sandeep Vaishnav0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten2 SeitenWater Table Drainage
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenWater Table Drainage
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten2 SeitenWater Table Drainage
Hochgeladen von
Sandeep VaishnavWater Table Drainage
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Water-table drainage
LEARNING ELEMENT OBJECTIVE
When you have learned this learning element, you should be able to:
- describe in which cases water-table drainage is necessary.
DESCRIPTION AND FUNCTION
The function of water-table drainage is:
1. to intercept, collect and lead away any flow of subsurface water in the subgrade of the road;
2. to lower the water-table;
3. to drain water pockets.
Water-table drainage can consist of various types of ditches and canals, open or subsurface.
The design of these will vary from case to case, and it is the job of an engineer to design various types of water-table drainage.
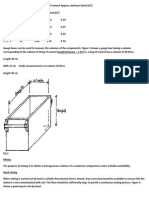
Embankment (valley crossing)
The most common method used is to build the road on an embankment so that the road base is elevated above the ground water
and the zone of capillary rise.
Fig 16
The zone of capillary rise can be reduced by placing a layer of porous material like hard core, gravel, sand, etc. at the bottom of the
fill. Another, but rarely used method, is to place an impervious membrane (plastic sheets) on the existing ground before the fill is
made.
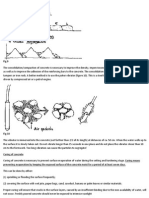
Drains (through swampy areas)
In order to lower a high water-table, drains are dug.
Fig 17
French drains
To drain water pockets French drains can be constructed.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Manning Equation For Discharge & Rating Puna-1Dokument30 SeitenManning Equation For Discharge & Rating Puna-1Sandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function and Composition of A Surface LayerDokument2 SeitenFunction and Composition of A Surface LayerSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Height of Colimation MethodDokument4 SeitenHeight of Colimation MethodSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTP Design 3.12 MLDDokument21 SeitenWTP Design 3.12 MLDSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravel, Sand and Fine Particles in A Soil SampleDokument3 SeitenGravel, Sand and Fine Particles in A Soil SampleSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- LE-4 The Manufacture of Concrete (Part2)Dokument4 SeitenLE-4 The Manufacture of Concrete (Part2)Sandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharges of Punatsangchhu River Near Taksha Parameters Computed DischargesDokument2 SeitenDischarges of Punatsangchhu River Near Taksha Parameters Computed DischargesSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final EmoDokument21 SeitenFinal EmoSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge KamechhuDokument1 SeiteDischarge KamechhuSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- LE-4 The Manufacture of Concrete (Part1)Dokument2 SeitenLE-4 The Manufacture of Concrete (Part1)Sandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- LE-5 Placing, Compacting and Curing of Concrete - 2Dokument1 SeiteLE-5 Placing, Compacting and Curing of Concrete - 2Sandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of DrainageDokument2 SeitenTypes of DrainageSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routine Maintenance Activities For RoadDokument1 SeiteRoutine Maintenance Activities For RoadSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- LE-5 Placing, Compacting and Curing of Concrete - 1Dokument1 SeiteLE-5 Placing, Compacting and Curing of Concrete - 1Sandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- AggregateDokument1 SeiteAggregateSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement of Soils by Mechanical MeansDokument3 SeitenImprovement of Soils by Mechanical MeansSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature, Definition and of Soil Mechanics PDFDokument1 SeiteNature, Definition and of Soil Mechanics PDFSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catchwater Drains and Scour ChecksDokument3 SeitenCatchwater Drains and Scour ChecksSandeep Vaishnav50% (2)
- Catchwater Drains and Scour ChecksDokument3 SeitenCatchwater Drains and Scour ChecksSandeep Vaishnav50% (2)
- Side Drains and Mitre Drains: Key Functions and Construction DimensionsDokument3 SeitenSide Drains and Mitre Drains: Key Functions and Construction DimensionsSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Field Tests To Determine Soil PropertiesDokument2 SeitenSimple Field Tests To Determine Soil PropertiesSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catchwater Drains and Scour ChecksDokument3 SeitenCatchwater Drains and Scour ChecksSandeep Vaishnav50% (2)
- Types of DrainageDokument2 SeitenTypes of DrainageSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Instruction For DrainageDokument4 SeitenField Instruction For DrainageSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- LE 5 CulvertsDokument3 SeitenLE 5 CulvertsSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catchwater Drains and Scour ChecksDokument3 SeitenCatchwater Drains and Scour ChecksSandeep Vaishnav50% (2)
- 4 Bridge DesignDokument7 Seiten4 Bridge DesignSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Cause Way DesignDokument7 Seiten2 - Cause Way DesignSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Culvert DesignDokument5 Seiten3 Culvert DesignSandeep VaishnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)