Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ati Summary
Hochgeladen von
Leah ElizabethOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ati Summary
Hochgeladen von
Leah ElizabethCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
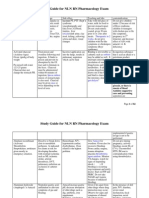
Priority:
o Airway
o Breathing
o Circulation
o Disability
o Safety
Urticaria
Dyspnea
Tinnitus
o May indicate ototoxicity
IV cefazolin
Salmeterol
o Long acting bronchodilator that prevents bronchospasm and
improves breathing
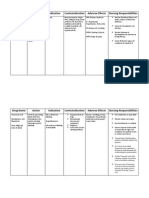
Oxybutynin
o anticholinergic
o Uses: urinary intolerance
o Teaching:
Symptoms patient should expect: blurred vision, dry mouth,
photophobia
Phenytonin
o Commonly causes gingival hyperplasia, therefore patient should let
dentist know he or she is taking the medication
Acetazolamide
o Chronic open angle glaucoma
o Adverse effects (instruct pt to monitor): Parenthesis (tingling of
fingers)
Oral Amoxiciilin
o If patient reports urticaria: may indicate allergic reaction and type of
antibiotic should be changed
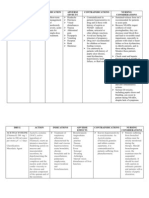
Clavulanate Potassium
Neostigmine
o Myasthenia gravis
o Adverse reaction: nausea
Warfarin
o Warfarin toxicity: Vitamin K (antidote)
Aspirin
o Long term therapy
S/s to notify provider: Hyperventilation
Valproic Acid
o Can cause liver failure
o Instruct clients to observe for s/s of liver failure: jaundice
Benztropine
o Anticholinergic agent
o Can develop tachycardia due to parasympathetic blockade of the heart
Tinnitus may indicate
Tuberculosis
o May be prescribed four-medication regimen including: isoniazid,
rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. This is done because the
combonation of medications eliminates resistant strains of TB, and it
can take up to six weeks to determine the sensitivity of the organism
to each medication.
Ferrous sulfate
o Take on empty stomach
o Antacids reduce absorption of iron
Chronic open angle glaucoma
Mannitol
o IV infusion 25% for one hour
The greatest risk to the patient taking IV Mannitol is
development of heart failure; therefore it is important to
instruct of s/s of heart failure: peripheral edema
Ketorolac
Oxybutynin
o Anticholinergic agent
o Side effects: dry mouth, blurred vision, photophobia
Doxycycline
o Tetracycline antibiotic
o Preg contraindicated; meds adverse effects on developing bones and
teeth
Magnesium sulfate IV infusion
o Uses: preterm labor
o Know s/s magnesium toxicity: decreased LOC
Magnesium toxicity results in CNS depression
Ceftazidime
o Cephalosporin antibiotic
o Severe penicillin allergy is a contraindication due to the potential for
cross sensitivity
o Monitor for anaphylaxis
Oral contraceptives
o Carbamazepine causes an accelerated inactivation of oral
contraceptives because of its action of hepatic medication-
metabolizing enzymes
Tamoxifin
o Anti-estrogen medication
o Treatment of breast cancer
o Expected adverse effects: hot flashes, bruising, menstrual
irregularities
Epoetin alfa
o Treat anemia
o If hematocrit rises too rapidly, hypertension and seizure can result, so
watch for increased BP
Fluoxetine
o Antidepressants
o Clients should not stop taking abruptly, should tape the dose or use an
antihistamine if gets rash
o Concurrent use of St. Johns Wort can increase the risk of serotonin
syndrome
o Suppresses platelet aggregation, which increases the risk of bleeding
when used concurrently with NSAIDS and anticoagulants. Therefore,
clients taking fluoxetine should avoid taking NSAIDS
Glargine
o Type one diabetes
o Solution clear
o Do not mix insulin glargine with any other insulins in same syringe,
because doing so can alter meds effects
Haloperidol
o Extrapyramidal symptom: akathisia
Clindamycin
o Can cause generalized muscle aches,
o Adverse effect: watery diarrhea because it can cause C-diff associated
diarrhea, which manifests as watery diarrhea. Without treatment, this
can be fatal.
Fluconazole
o (antifungal medication) effective in treating oropharyngeal and
systemic candidiasis
Methotrexate
o Immunosuppressant
o Can cause bone marrow suppression
Monitor and report indications of infection: fever, sore throat
Metoclopramide
o When used following surgery: Nurse should monitor for adverse
effects. Has multiple effects on CNS, including sedation.
Spacer minimizes the risk of candidiasis of mouth
Oprelvekin
o Thrombopoietic growth factor
o For management of adverse effects of chemotherapy
o Platelet count should be within expected range for medication to be
considered successful
Digoxin
o Signs of dig toxicity: yellow-tinged vision
Sucralfate
o Peptic ulcer disease
o Forms a protective barrier over ulcers
Atorvastatin
o Should be monitoring CK; mild injury, causing muscle weakness or
aches, develops in some clients taking statins, and this occasionally
progresses to myositis. Creatinine kinase levels rise in response to
enzymes released with muscle injury.
Chlordiazepoxide
o Acute alcohol withdrawal, should take to prevent delirum tremens
Morphine Sulfate
o Can cause bradycardia, Urinary retention
Tetracycline
o Take with food To reduce gastrointestinal distress
Furosemide
o Adverse effects: Dizziness, drop in blood pressure, hypokalemia,
urinary frequency, hyperglycemia
Ergotamine sublingual
o Take one tablet immediately after onset of aura or headache
Baclofen
o Nurse should document as a therapeutic outcome: decrease in flexor
and extensor spasticity
Prednisone
o Glucocorticoids
Adverse effects include osteoporosis which is monitored with
regularly scheduled bone density scans
Over the counter oral decongestions
o For nasal congestion
o Can constrict blood vessels
Enalapril
o Can develop hyperkalemia due to potassium retention by the kidneys
Albuterol
o Short acting beta 2 adrenergic agonist
o Causes bronchodilation and relieves bronchospasm during acute
asthma attacks
Metronidazole
o Combo with alcohol can cause a disulfiram-like reaction that can
include severe vomiting, hypotension, weakness
Hydromorphone
o Post op clients
Heparin infusion
o May indicate heparin-induced thrombocytopenia if low platelet count,
and it would be required to stop the medication
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
o Adverse effects: Vesicular, crusty rash, is a sign of johnsons syndrome
Indomethacin
o NSAID reduces pain and inflammation
Amphotericin B
o Intermittent IV bolus
o For histoplasmosis
o Adverse effects:fever
Diazepam
o Flumazenil is the reversal agent for benzodiazepine toxicity
Neostigmine is the reversal agent for neuromuscular blocker overdose
Atropine sulfate is the reversal agent for inhibitors overdose
Naloxone is the reversal agent for opioid toxicity
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level
o Most sensitve method for determining thyroid activity
Total t4 level
Total t3 level
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)
WBC
Hematocrit
Leukocyte
Erythrocyte
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCLEX Pharmacology LPDokument53 SeitenNCLEX Pharmacology LPSara Pirman100% (1)
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIVon EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- PHARMACOLOGYDokument69 SeitenPHARMACOLOGYKiran ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugQuiz 1bDokument4 SeitenDrugQuiz 1bDorothy ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Side Effects:: AtropineDokument7 SeitenSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CefuroximeDokument11 SeitenCefuroximeAlmira Ballesteros CestonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonVon EverandFast Facts: Ottimizzazione del trattamento delle fluttuazioni motorie nella malattia di ParkinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AminophyllineDokument9 SeitenAminophyllineZaira BataloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency DrugsDokument40 SeitenEmergency Drugsmattheus101Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATI Pharmacology Study Guide 2021Dokument41 SeitenATI Pharmacology Study Guide 2021Jennifer Weeks100% (2)
- Clinical Pharmacology Reviewer. RespiDokument4 SeitenClinical Pharmacology Reviewer. RespiSister RislyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensives:: Drug Endings & ClassificationDokument8 SeitenAntihypertensives:: Drug Endings & ClassificationAndres CardenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug AnalysisDokument3 SeitenDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicDokument13 SeitenPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathDokument4 SeitenRregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathHannah BuquironNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDokument3 SeitenName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nclex Pharm ReviewDokument10 SeitenNclex Pharm ReviewRuiqi YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug Studysachi yuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhenytoinDokument1 SeitePhenytoinJellie MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agranulocytosis An Adverse Effect of Allopurinol TDokument4 SeitenAgranulocytosis An Adverse Effect of Allopurinol TSYARIF HIDAYATULLAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDokument14 SeitenNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Investigations: QuinineDokument8 SeitenEssential Investigations: QuininemadhukarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrcpch-Pharma: Acute Aspirin OverdoseDokument15 SeitenMrcpch-Pharma: Acute Aspirin OverdoseRajiv KabadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDokument4 SeitenDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review NotesDokument82 SeitenReview Notesjames100% (2)
- Pharmacology ReviewDokument64 SeitenPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atropine Sulfate InjectionDokument4 SeitenAtropine Sulfate InjectionIrawanMarlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-4Dokument4 SeitenAmphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-4Vh TRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug StudyGail SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 40 Drugs and Nle FeedbacksDokument106 SeitenTop 40 Drugs and Nle FeedbacksGeraldin Buyagao Kinlijan100% (1)
- KidneyDokument5 SeitenKidneyAshish PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medications Sheet PreopDokument37 SeitenMedications Sheet Preopapi-503879428Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Room DrugsDokument20 SeitenEmergency Room DrugstsikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Dokument4 SeitenChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument2 SeitenDrugsMinyang ChowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument5 SeitenDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chief Complaint: Body WeaknessDokument13 SeitenChief Complaint: Body WeaknessJohn MaglinteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensives Summary Katzung PharmacologyDokument8 SeitenAntihypertensives Summary Katzung PharmacologyRobin TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineDokument8 SeitenDrug Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing Considerations Ketorolac TromethamineAiryn CanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument8 SeitenDrug Study Generic Name/ Trade Name Dosage/ Frequency Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTrojangBaboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDokument6 SeitenDr. Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKuyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epilepsy - DoneDokument6 SeitenEpilepsy - Doneemiliow_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- PharmacologyDokument116 SeitenPharmacologyDanica Chiara MotiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument22 SeitenDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- HyrdrocortisoneDokument7 SeitenHyrdrocortisoneRoseben SomidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- methotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1Dokument9 Seitenmethotrexate-Anti-Asthmatic Drugs Toxicity-1joonabil29Noch keine Bewertungen
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Dokument12 SeitenMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugDokument27 SeitenNon-Steroidal Anti - Inflammatory DrugMelissa SalayogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Ultimate Pre-Reg BNF NotesDokument29 SeitenUltimate Pre-Reg BNF NotesBob100% (7)
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDokument15 SeitenEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- Pharm PrepDokument3 SeitenPharm PrepAshley MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHN Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sandomigran PiDokument6 SeitenSandomigran PiNexi anessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peds Exam 1Dokument1 SeitePeds Exam 1Leah ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ob Study Guide #1Dokument10 SeitenOb Study Guide #1Leah ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrapartal PeriodDokument2 SeitenIntrapartal PeriodLeah ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ati #3Dokument8 SeitenAti #3Leah Elizabeth100% (8)
- 340 Final StudyDokument21 Seiten340 Final StudyLeah ElizabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Communication and The Therapeutic RelationshipDokument3 SeitenChapter 9: Communication and The Therapeutic RelationshipKINDATNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A: Sample Patient Profiles and Prescriptions: (For Pharmacist Use)Dokument6 SeitenAppendix A: Sample Patient Profiles and Prescriptions: (For Pharmacist Use)Cesly Jewel Acosta AvilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marri Laxman Reddy Institute of Pharmacy: Patient Medication History Interview FormDokument3 SeitenMarri Laxman Reddy Institute of Pharmacy: Patient Medication History Interview FormRaghu VenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 67166-Apvma Veterinary Medicines Technical Report TemplateDokument42 Seiten67166-Apvma Veterinary Medicines Technical Report Templateali aimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacy Management System Literature ReviewDokument8 SeitenPharmacy Management System Literature Reviewafdtywgdu100% (1)
- Internship Evaluation & Reporting: Part I. General Information - Student'S Input Student InfoDokument5 SeitenInternship Evaluation & Reporting: Part I. General Information - Student'S Input Student InfoLAZKILLERNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 M2 Professions and Professionalism PDFDokument16 SeitenL1 M2 Professions and Professionalism PDFprakashchittora6421Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality by Design (QBD)Dokument25 SeitenQuality by Design (QBD)Khrisna Whaty SilalahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uhc Irr DraftDokument107 SeitenUhc Irr Draftshenric16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case - Studies - in - Finance - Managing - For - Cor 2Dokument16 SeitenCase - Studies - in - Finance - Managing - For - Cor 2Taylor StephensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Mix On Betage Hilton Phrama ReportDokument21 SeitenMarketing Mix On Betage Hilton Phrama Reportmirza_2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fidelis Drug List 2018Dokument80 SeitenFidelis Drug List 2018Annie AnnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Jurisprudence HandoutsDokument13 SeitenNursing Jurisprudence HandoutsDENNIS N. MUÑOZ100% (3)
- UN PD CodesDokument38 SeitenUN PD CodesPraveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Hospital Community Pharmacy Assisting L3Dokument83 SeitenOS Hospital Community Pharmacy Assisting L3Max100% (3)
- Medications As Social Phenomena: Cite This PaperDokument31 SeitenMedications As Social Phenomena: Cite This PaperQwerty QwertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chip 2Dokument53 SeitenChip 2Bhavani BudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATB and Combined PillDokument8 SeitenATB and Combined PillDaniela SimõesNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Michael Yeadon WarningDokument14 SeitenDR Michael Yeadon WarningJerlyn MagraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The DoorDokument3 SeitenThe DoorAliah Necole EsquibelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abc Final PDFDokument542 SeitenAbc Final PDFBianca ParepeanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drotaverine: Solution For Injection - 40 MG / 2 MLDokument1 SeiteDrotaverine: Solution For Injection - 40 MG / 2 MLZarbakht AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication AdministrationDokument10 SeitenMedication AdministrationJemma NocalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSA MedsCheck GuidelinesDokument18 SeitenPSA MedsCheck GuidelinesRobbie WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year B. Tech. (Chemical Technology) (CR) (Semester - VII) Examination, November - 2017 Advanced Separation TechniquesDokument18 SeitenFinal Year B. Tech. (Chemical Technology) (CR) (Semester - VII) Examination, November - 2017 Advanced Separation TechniquesRANI KALASKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Success 4 Unit 3 & 4 Achievement TestDokument15 SeitenProject Success 4 Unit 3 & 4 Achievement TestPanjiHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of ChatGPT in MedicineDokument3 SeitenUses of ChatGPT in MedicineMiranda WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ksa and Uae 2020 AmroDokument131 SeitenKsa and Uae 2020 AmroamroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManufacturingUnits ListDokument47 SeitenManufacturingUnits ListMarketing DesignAccentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipls & AptsDokument84 SeitenIpls & AptsDesalegn TesfayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (30)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (81)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (60)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (170)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (46)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainVon EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (95)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesVon EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1412)