Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lesson 10
Hochgeladen von
api-264511068Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lesson 10
Hochgeladen von
api-264511068Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
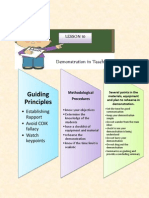
LESSON 10
DEMONSTRATION IN TEACHING
LESSON 10
ESTABLISHING RAPPORT
Greet your audience. Make
them feel at ease by your
warmth and sincerity. Simulate
their interest by making your
demonstration and yourself
interesting.
AVOID THE COLK
FALLACY
It is the assumption that what
is clear to the expert
demonstrator is also clearly
known to the person for whom
the message is extended.
WATCH FOR KEY
FORMATS
They are the ones at which an
error is likely to be made the
places at which many people
stumble and where the knacks
and tricks of the trade are
especially important.
MAKING THE MOST OF
COMMUNITY
RESOURCES AND FIELD
TRIPS
Make preliminary
contacts, a tour
arrangement with the
place to be visited
Make final
arrangements with the
school principal about
the details of the trip,
schedule,
transportation,
arrangements, finances,
and permission slips
from parents
Make a tentative route
plan, subject to later
alteration based on class
planning and objectives
Try to work out
mutually satisfactory
arrangements with
other teachers if the
trip will conflict with
their classes.
Prepare preliminary
lists of questions or
other materials
which will be helpful
in planning with the
students.
Discuss the objectives
and write them down.
LESSON 11
MAKING THE MOST OF COMMUNITY RESOURCES
AND FIELD TRIPS
LESSON 12
Transmit a wide range of
audio.
Bring models of
excellence to the viewer.
Bring the world of
reality to the home and
to the classroom through
a live broadcast or as
medicated through film
or videotape.
Make us see and hear
ourselves world events as
they happen
Be the most believable
news source.
Make some programs
understandable and
appealing to a wide
variety of age and
educational levels.
Become a great equalizer
of educational opportunity
because programs can be
presented over national
and regional networks.
Provide us with sounds and
sights not easily available
even to the viewer of a real
event through long shots,
close ups, zoom shots,
magnification and split
screen made possible by the
TV camera.
Can give opportunity to
teachers to view themselves
while they teach for purposes
of self-improvement
Can be both instructive and
enjoyable.
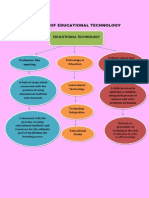
LESSON 13
TEACHING WITH VISUAL
SYMBOL
DRAWINGS
may not be real thing but better to
have a concrete visual aid than
nothing
avoid confusion, it is good our
drawing correctly represents the real
thing
CARTOONS
another useful visual symbol that can
bring novelty to our teaching
it tells the story metaphorically
STRIP
DRAWINGS
commonly called as comics or comic
strip
make use of strip that are educational
and entertaining at the same time
DIAGRAM
any drawing that shows arrangement
and relations as part of the whole
such as relative, value, origins and
development, chronological fluctuations,
distribution and etc.
c
ss
CHARTS
is a diagrammatic represenatations
of relationship among individual
whether as organization
examples of this are time chart,
comparison and contrast chart,
organizational, pareto and trend
chart
GRAPHS
examples of this are pine, bar , line
and pictorial graph
MAPS
representation of the surface of the
earth or some part of it
kinds of maps are physical, relief ,
commercial or economic and political
map.
LESSON 14
MAXIMAZING THE USE OF OVERHEAD PROJECTOR
CHALKBOARD
Write clearly and legibly on the board
It helps if you have a hard copy of your
chalkboard diagram or outline
Dont crowd your notes on the board
Make use of colored chalk to highlight key
points
Dont turn your back to your class while
you write the chalkboard
Provide the lines for your board if needed
with the grade level you teach
Make sure your board works are readable
in all sides of the room
Replace chalkboard with a detail concaved from
left to right to avoid glare
Write Please Save if there are board works for
tomorrow and cover with curtains
Make full use of the chalkboards
OVERHEAD PROJECTOR
(OHP)
Show pictures and diagrams using a
pointer on the transparency
You can use a marker or wax
based pencil to add details
You can control the rate or presenting
information by using progressive
disclosure technique
LESSON 15
students do not
learn by using
multimedia
produce by
others but can
learn by
creating it
themselves
working
together jointly
to accomplish a
common
intellectual
purpose
determining what
substantive content
would be included
is their projects as
well as the process
for producing
them
extend over a
significant time
seek to connect
students work in
school with the
wider world in
which students
live
address the
basic
knowledge
and skills of
all students
are expected
to acquire
PROJECT BASED LEARNING AND
MULTIMEDIA
Dimensions of Project Based Multimedia Learning
LESSON 17
ASSESSMENT IN A CONTRUCTIVIST,
TECHNOLOGY SUPPORTED LEARNING
Assessment in
a
constructivist,
technology
supported
learning
Complex learning cannot be assessed or
evaluated using any single measure. We must
examine both the processes and products of
students learning
Contructivist
classroom
Ideas were gripped on how we value it in our daily
life
Construction of ideas out from collected facts
occurs
Discourages memorization of facts
5 Es of Constructivism
ENGAGE
EXPLOR
E
EXPLAIN
ELABORA
TE
EVALUA
TE
LESSON 18
Rules and functions of an Educational Media
Center
-It functions as a vital instrument.
-It reflects and supports the philosophy of the School.
-It shares and implements the school aims and
objectives
-It is involved in the teaching and learning process.
-It is a source center.
-It is a learning laboratory.
-It is a teaching agency.
-It is a service agency.
-It is a coordinating agency.
-A center for recreational reading, viewing, and
listening.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NescyDokument10 SeitenNescyapi-264509612Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 10: Demonstration in TeachingDokument11 SeitenLesson 10: Demonstration in Teachingapi-264468141Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptmap Momi ElibDokument9 SeitenConceptmap Momi Elibapi-264382729Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson10 EdtechDokument9 SeitenLesson10 Edtechapi-266582672Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptmap 2Dokument18 SeitenConceptmap 2api-264187866Noch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map FinalDokument19 SeitenConcept Map Finalapi-266353521Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elyn-Concept Map 2Dokument10 SeitenElyn-Concept Map 2api-266639833100% (1)
- Teaching Tools: B.Ed Course Code 8601 Unit: 9Dokument31 SeitenTeaching Tools: B.Ed Course Code 8601 Unit: 9muhammad zeshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information SheetDokument29 SeitenInformation SheetJohn Rey SR SoveranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm ModuleDokument8 SeitenMidterm ModuleMarjorie TrazonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M3, L1Dokument10 SeitenM3, L1Denosta Mercurio JonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eight Planet Model of The Solar SystemDokument22 SeitenEight Planet Model of The Solar SystemVictor Jose Valdehueza SomonodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sabah Pervaiz 826 Assigment No 2Dokument19 SeitenSabah Pervaiz 826 Assigment No 2kashafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Learning Cannot Be Assessed or Evaluated Using Any Single MeasureDokument4 SeitenComplex Learning Cannot Be Assessed or Evaluated Using Any Single MeasureJessa Mae David TuazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio Visual AidsDokument12 SeitenAudio Visual Aidsmonisha100% (1)
- SLIDE #1 - Understanding Blended LearningDokument9 SeitenSLIDE #1 - Understanding Blended LearningReaganRicafortNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thinking Skills - Geography and Sustainable DevelopmentVon EverandThinking Skills - Geography and Sustainable DevelopmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Educ 85 Reviewer: (GROUP1) Dale'S Cone of ExperienceDokument15 SeitenEduc 85 Reviewer: (GROUP1) Dale'S Cone of ExperienceMary Rose ManciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Display PolicyDokument4 SeitenDisplay PolicyJoshua JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories and Principles in The Use and Design of TechnologyDokument14 SeitenTheories and Principles in The Use and Design of Technologypenosajoy98Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Is Not Only A Job But Is A Way of LifeDokument22 SeitenTeaching Is Not Only A Job But Is A Way of LifeSahil NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19 innovative ways to promote creativity in the classroomDokument7 Seiten19 innovative ways to promote creativity in the classroomkankana borgohainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 ICT ResourcesDokument24 SeitenUnit 5 ICT ResourcesWAGAYEN , MarvenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Smart ClassDokument10 SeitenDigital Smart ClassDsquare solutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do's and Don'Ts of Demo-TeachingDokument5 SeitenDo's and Don'Ts of Demo-TeachingRegin PaildenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting Ready For Virtual StudioDokument26 SeitenGetting Ready For Virtual StudioRick LeBrasseurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Studio INFO For StudentsDokument14 SeitenVirtual Studio INFO For StudentsRick LeBrasseurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Visual AidsDokument4 SeitenThesis Visual Aidsmellisahedeensiouxfalls100% (2)
- "A Good Demonstration Is Good Communication.": Demonstrations in TeachingDokument6 Seiten"A Good Demonstration Is Good Communication.": Demonstrations in TeachingSheena Oyon-oyon NotarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culminating Activity: Essential QuestionDokument5 SeitenCulminating Activity: Essential QuestionLAILANIE DELA PENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Literacy Skills: Media, Information and ICT LiteracyDokument12 SeitenDigital Literacy Skills: Media, Information and ICT LiteracyAlden Tagupa EscobidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eapp 12-Q3-M16Dokument15 SeitenEapp 12-Q3-M16Maya SweetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dales Cone of ExperienceDokument12 SeitenDales Cone of ExperienceRexson Dela Cruz TagubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. What Is Project-Based Multimedia Learning?Dokument7 SeitenChapter 1. What Is Project-Based Multimedia Learning?Romeo Balingao100% (1)
- k4 TheoriesDokument4 Seitenk4 TheoriesBobo YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team Legend ReportingDokument37 SeitenTeam Legend ReportingleahnmaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Selection Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenListening Selection Lesson Planfarid kefelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EED 2101 - Mid Term ExaminationDokument4 SeitenEED 2101 - Mid Term ExaminationJOMICA SANTOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orca Share Media1680593759018 7048921125824538377Dokument46 SeitenOrca Share Media1680593759018 7048921125824538377RedMoonLightNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLEARDokument33 SeitenTLEARrmnktmanangan28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Top Ten Academic StaffDokument2 SeitenInduction Top Ten Academic StaffLauraNoch keine Bewertungen
- JM S (Teaching Prof)Dokument12 SeitenJM S (Teaching Prof)Myrel Joy Fabiaña LucdayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Interactively With Electronic Whiteboards in Primary Phase - Becta Ict AdviceDokument36 SeitenTeaching Interactively With Electronic Whiteboards in Primary Phase - Becta Ict Adviceluiz carvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bpts Basic Productivity Tools Lesson Idea TemplateDokument3 SeitenBpts Basic Productivity Tools Lesson Idea Templateapi-678572474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mct31 Unit 1Dokument24 SeitenMct31 Unit 1Ndiphiwe MaliwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof Ed 4 MidtermDokument16 SeitenProf Ed 4 MidtermDojonel ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TananDokument9 SeitenTananapi-264308542Noch keine Bewertungen
- K To 12: An Answer To 21 Century Learners: Guide QuestionsDokument3 SeitenK To 12: An Answer To 21 Century Learners: Guide QuestionsAika Kate KuizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Create A 5 E Lesson Plan: 1. EngageDokument4 SeitenHow To Create A 5 E Lesson Plan: 1. EngageNormina Cagunan100% (1)
- Interactive Whiteboard Revolutionizes TeachingDokument3 SeitenInteractive Whiteboard Revolutionizes TeachingVanina DogaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening Selection Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenListening Selection Lesson Planfarid kefelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infografik DR ArumugumDokument8 SeitenInfografik DR ArumugumPhirexBlueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Digital and Digital Skills and Tools in Delivering Technology Enhanced LessonDokument3 SeitenNon-Digital and Digital Skills and Tools in Delivering Technology Enhanced LessonMa. Edessa Diona100% (1)
- I.C.T Primer Examen Parcial:: Word Cloud (Or Tag Cloud)Dokument8 SeitenI.C.T Primer Examen Parcial:: Word Cloud (Or Tag Cloud)Aldana CanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aflatoun Digital Learning CurriculumDokument308 SeitenAflatoun Digital Learning CurriculumemolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benigay Answerm10Dokument6 SeitenBenigay Answerm10juliet calingacion100% (5)
- LA - MANUAL-A4Low ResDokument36 SeitenLA - MANUAL-A4Low Resirma floresNoch keine Bewertungen
- S 2 - 21st Century Teaching (Edited)Dokument30 SeitenS 2 - 21st Century Teaching (Edited)Marlo Mel MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PortfolioDokument20 SeitenPortfolioJosé Puga MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2Dokument1 Seite2api-264511068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Davao Oriental State College of Science and TechnologyDokument3 SeitenDavao Oriental State College of Science and Technologyapi-264511068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1Dokument9 SeitenLesson 1api-264511068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coordinating SchoolnikkieDokument3 SeitenCoordinating Schoolnikkieapi-264511068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jemmima Akuffo Executive Assistant CV ATFUXDokument1 SeiteJemmima Akuffo Executive Assistant CV ATFUXJemima AkuffoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Correspondence-A Guide To Everyday Writing-Pearson ESL (2002)Dokument154 SeitenBusiness Correspondence-A Guide To Everyday Writing-Pearson ESL (2002)hilma suryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career Guidance Services GuideDokument11 SeitenCareer Guidance Services GuideCharles Ondieki100% (1)
- Online Learning NewsletterDokument164 SeitenOnline Learning Newslettertino3528Noch keine Bewertungen
- Making Wise Decisions During Uncertain TimesDokument5 SeitenMaking Wise Decisions During Uncertain TimesCrystal SnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Home Learning Plans for Grade 3Dokument17 SeitenWeekly Home Learning Plans for Grade 3Cy DacerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Eka Mayang SariDokument2 SeitenCV Eka Mayang SariAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Personal LetterDokument7 SeitenChapter 6 Personal LetterDewi UmbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CoachingDokument38 SeitenCoachingLab-lab Santiago100% (1)
- Sabeniano - Final ResearchDokument30 SeitenSabeniano - Final Researchcrizzy olayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjectivism and RelativismDokument3 SeitenSubjectivism and RelativismAlaka RajeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Outline - GLSCM - SCND - MBA (Global) May 16Dokument14 SeitenSubject Outline - GLSCM - SCND - MBA (Global) May 16Siddharth GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think Win WinDokument4 SeitenThink Win WinLim BunkimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selecting and Defining Target Behaviors: Cooper, Heron, and Heward All Rights ReservedDokument40 SeitenSelecting and Defining Target Behaviors: Cooper, Heron, and Heward All Rights ReservedSantiagoTrujilloLemusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wilgress John 22141789 Educ 5464 Program Virtual MuseumDokument10 SeitenWilgress John 22141789 Educ 5464 Program Virtual Museumapi-352302857Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Information SystemDokument55 SeitenAccounting Information SystemRodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature - Reader-Functional English - U1&U2 PDFDokument40 SeitenLiterature - Reader-Functional English - U1&U2 PDFvar6212Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anagement Ystem Esults-Ased Erformance: PortfolioDokument32 SeitenAnagement Ystem Esults-Ased Erformance: PortfolioFactura Neil50% (2)
- Stage Gate ModelDokument3 SeitenStage Gate ModelEnrico Mella100% (1)
- Contemporary Philippine Arts RegionsDokument3 SeitenContemporary Philippine Arts RegionsBei CabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action ResearchDokument14 SeitenAction ResearchAnonymous zneVs6bqJMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeroom Guidance SF9 & SF10 AttachmentDokument2 SeitenHomeroom Guidance SF9 & SF10 AttachmentCharity S. Jaya - AgbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AERO2379 & AERO2350 Lecture 5 Prezzi Style - 24 Mar 2020-1Dokument71 SeitenAERO2379 & AERO2350 Lecture 5 Prezzi Style - 24 Mar 2020-1samala sonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management: Analyzing Consumer MarketsDokument45 SeitenMarketing Management: Analyzing Consumer Marketsabhaydimapur007Noch keine Bewertungen
- American SpeechDokument10 SeitenAmerican SpeechCamille CampomanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasb Conference - Sup EvaluationDokument34 SeitenNasb Conference - Sup Evaluationapi-32275271Noch keine Bewertungen
- BRANIGAN - Eduard - A Point of View in The CinemaDokument6 SeitenBRANIGAN - Eduard - A Point of View in The CinemaSonia RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Analysis and Job DescriptionDokument16 SeitenJob Analysis and Job DescriptionAbhishek AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rysemus 25 CommProgramDokument11 SeitenRysemus 25 CommProgramKimberly RysemusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Commerce (Computer Application) (B.C.C.A.) Semester-I (C.B.C.S.) Examination ENGLISH-I (Communication Skills) Compulsory Paper-1Dokument4 SeitenBachelor of Commerce (Computer Application) (B.C.C.A.) Semester-I (C.B.C.S.) Examination ENGLISH-I (Communication Skills) Compulsory Paper-1Harsh VardhanNoch keine Bewertungen