Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry Science Fair Year 09
Hochgeladen von
Nkemzi Elias Nzetengenle0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
6 Ansichten4 SeitenModel to measure energy in a fuel is called a calorimeter. Kerosene in this case is used as the fuel.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenModel to measure energy in a fuel is called a calorimeter. Kerosene in this case is used as the fuel.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
6 Ansichten4 SeitenChemistry Science Fair Year 09
Hochgeladen von
Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleModel to measure energy in a fuel is called a calorimeter. Kerosene in this case is used as the fuel.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
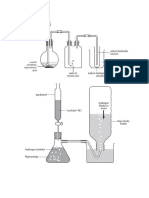
Model to measure energy in a fuel
Measuring energy in a fuel
The device used to measure energy
in a fuel is called a calorimeter.
Experiment:
Aim: Designing a model to measure
the energy in a fuel
Requirements: Mayonaise bottle (as
spirit lamp), beaker, water, wooden
clamp and stand, thermometer
(0.1), plastic lid, kerosene (in place
of spirit), cut off container (as
draught shield), piece of cloth (as
wick)
Set-up:
Clamp
and
stand
lid
kerosene
Mayonaise bottle (as burner)
Water
Flame
Piece of
clot
!eaker (as Calorimeter)
"ermometer
Cut off container
Procedure:
- Pour an amount of water (e.g. 100cm
3
) into
the beaker and record its temerature.
- !eigh the sirit burner containing the fuel
(kerosene in this case) and record its mass
- "ight the burner so that the burning fuel
heats the water.
- !hen the temerature has risen by about
10 #$ ut out the burner flame$ record the
temerature of the water and then reweigh
the burner and fuel immediately.
- The amount of fuel burnt is found by
subtracting the mass of the burner and fuel
after the e%eriment from the mass of the
burner and fuel before the e%eriment.
- The rise in temerature is found by
subtracting the temerature of the water at
the beginning of the e%eriment from the
temerature of the water at the end of the
e%eriment.
- The energy released by burning the mass
of the fuel is indicated by the rise in
temerature of water.
As an important note, the essential
measurements carried out are #
- "e mass of te fuel burnt
- "e temperature rise of $ater
- "e mass of $ater used% &t is needless
$ei'in' $ater since density of $ater is
(')cm
*
% "is means tat (++cm
*
of $ater
$ei' (++'%
Data collected
Mass of $ater equal to ,olume of $ater used - (++'%
&nitial temperature of $ater - "
(
.C
/i'est temperature of $ater - "
.C
Mass of burner0 $ick and kerosene at te start - m
(
'
Mass of burner0 $ick and kerosene at te end - m
1
'
Analysis of data
Mass of $ater (m) - (++ '%
Specific eat capacity of $ater (c) - 2%13'
-(
4
-(
%
"emperature rise (5") - "
6 "
i
- (+.C
5/ - mc5" - (++ 7 2%1 7 (+ - 21++3
Mass of kerosene burnt - m
(
6 m
1
- m
k
%
Conclusion
The energy released by burning a
certain mass of kerosene (m
k
) is
&'00(.
)asses of different fuels to roduce
the same temerature (10.C) can then
be comared. The smaller the mass
burnt to roduce a temerature change
of 10.C0 the better the fuel.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- ISUZU 4HK1 6HK1 Type Engine PDFDokument48 SeitenISUZU 4HK1 6HK1 Type Engine PDFЙОРДАН ГЕОРГИЕВ90% (21)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- E-Trike Presentation For DOE-VFO, 06-19-12Dokument37 SeitenE-Trike Presentation For DOE-VFO, 06-19-12kapedong100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Opel Omega B CodesDokument12 SeitenOpel Omega B CodesRazvan Secarianu100% (5)
- 1100 Series VistaDokument64 Seiten1100 Series VistaJesus Neto100% (5)
- API RP 500 - Recommended Practice For ClaDokument6 SeitenAPI RP 500 - Recommended Practice For ClaRoberto VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drilling Supervisor Engineer Operations in Houston TX Resume John FaselerDokument1 SeiteDrilling Supervisor Engineer Operations in Houston TX Resume John FaselerJohn FaselerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai Engine Catalog PDFDokument12 SeitenHyundai Engine Catalog PDFahmed67% (3)
- Manual Taller Outlook (Dierre) 125 Efi (Idioma Ingles)Dokument173 SeitenManual Taller Outlook (Dierre) 125 Efi (Idioma Ingles)Cordobessa89% (9)
- Oi 2Dokument122 SeitenOi 2Emmanuele Tiria Garzón100% (1)
- Flame Tests, Atomic Spectra & Applications Activity C12!2!02 & 03Dokument11 SeitenFlame Tests, Atomic Spectra & Applications Activity C12!2!02 & 03Nurul Hana OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manhour NSRPDokument10 SeitenManhour NSRPvazzoleralex6884Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae (Rotating Equip. Maint. Engineer)Dokument2 SeitenCurriculum Vitae (Rotating Equip. Maint. Engineer)amro32150% (2)
- Flares in Refineries and Chemical Plants - Industry Standards and US Emissions RegulationsDokument31 SeitenFlares in Refineries and Chemical Plants - Industry Standards and US Emissions Regulationsnasirmuzaffar100% (3)
- Fire ProtectionDokument203 SeitenFire ProtectionSela MandianganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of Analysis: Quality ControlDokument2 SeitenCertificate of Analysis: Quality ControlASHOK KUMAR LENKANoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Dokument2 SeitenActivity Sheet-02 (Plum Pudding Model of The Atom)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallic ObjectsDokument1 SeiteMetallic ObjectsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 QuestionsDokument20 SeitenTopic 2 QuestionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox Equations To Be BalancedDokument1 SeiteRedox Equations To Be BalancedNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallic ObjectsDokument1 SeiteMetallic ObjectsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIXTURESDokument13 SeitenMIXTURESNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet-09 (Symbols and Atomic Numbers of The 1st 20 Elements)Dokument2 SeitenActivity Sheet-09 (Symbols and Atomic Numbers of The 1st 20 Elements)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDokument4 SeitenSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet-03 (Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment)Dokument2 SeitenActivity Sheet-03 (Rutherford Gold Foil Experiment)Nkemzi Elias Nzetengenle100% (1)
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDokument6 SeitenStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDokument6 SeitenStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersDokument6 SeitenStereochemistry Hopefully Made Simpler: StereoisomersNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Dokument3 Seiten2-Test For Ions (Qualitative Analysis)Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEST Rate and EnergeticsDokument1 SeiteTEST Rate and EnergeticsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form Three ChemitryDokument1 SeiteForm Three ChemitryNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDokument4 SeitenSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- HL Practice Questions On PeriodicityDokument5 SeitenHL Practice Questions On PeriodicityNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoalo 07Dokument5 SeitenStereoalo 07Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate and Rate ConstantDokument1 SeiteRate and Rate ConstantNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of ReactionsDokument21 SeitenRate of ReactionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorption Spectra of Complex IonsDokument2 SeitenAbsorption Spectra of Complex IonsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- T3HQDokument9 SeitenT3HQNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- StereochemistryDokument6 SeitenStereochemistryNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stereoalo 07Dokument5 SeitenStereoalo 07Nkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility of S-Block CompoundsDokument4 SeitenSolubility of S-Block CompoundsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SetupsDokument5 SeitenChemistry SetupsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic QuestionsDokument22 SeitenAtomic QuestionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 2HQDokument5 SeitenChemistry 2HQVongai Christine MlamboNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Soap and Detergent Cleaansing ActivityDokument8 Seiten2 Soap and Detergent Cleaansing ActivityhudahilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self-Study Guide # 6 For 10 GradeDokument8 SeitenSelf-Study Guide # 6 For 10 GradeJuandi CordobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Ignition Systems: CM WP ME HA AP LG EP CS IN EL AV TO PS BVDokument1 SeiteElectronic Ignition Systems: CM WP ME HA AP LG EP CS IN EL AV TO PS BVRaju GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ksi KRR Operators ManualDokument69 SeitenKsi KRR Operators ManualAeres707Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 6 Log Interpretation Hakeem DahoDokument6 SeitenPaper 6 Log Interpretation Hakeem DahoSadiq JalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 0literservicemanual2Dokument191 Seiten3 0literservicemanual2Stuart BradleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toro Weed EaterDokument23 SeitenToro Weed EaterTamara Takano100% (1)
- Tata Motors - Cars - UtilityDokument4 SeitenTata Motors - Cars - UtilityAdarsh JalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibro-Hydro Brick Block-Semi AutoDokument3 SeitenVibro-Hydro Brick Block-Semi Autosteelage11Noch keine Bewertungen
- I Beth09gb - e Tdmas4000tec PDFDokument12 SeitenI Beth09gb - e Tdmas4000tec PDFhaerulamriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intensifying Multiphase Reactions and Reactors: Strategies and ExamplesDokument16 SeitenIntensifying Multiphase Reactions and Reactors: Strategies and ExamplesMuhammad Arsalan AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- E12028 PDFDokument6 SeitenE12028 PDFZamir Andres SencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Population Census of Cambodia 2008 Final Census Results Figures at A GlanceDokument4 SeitenGeneral Population Census of Cambodia 2008 Final Census Results Figures at A Glanceanh00Noch keine Bewertungen
- DifferenceDokument3 SeitenDifferencehp rocksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Env Impact Assessment KelticPetroDokument249 SeitenEnv Impact Assessment KelticPetrorome_n21Noch keine Bewertungen
- ICDA - MX Line - MRPL - Multiphase Flow Modeling Report Draft 1.0Dokument16 SeitenICDA - MX Line - MRPL - Multiphase Flow Modeling Report Draft 1.0Anonymous AtAGVssJNoch keine Bewertungen