Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Disain Amplifier RF (Bretchko Chapter 9) : Aspek2 Dasar
Hochgeladen von
ignatiusnickyOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Disain Amplifier RF (Bretchko Chapter 9) : Aspek2 Dasar
Hochgeladen von
ignatiusnickyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Disain Amplifier RF
[Bretchko Chapter 9]
Aspek2 Dasar
Disain Amplifier RF Semikonduktor
(November 2009)
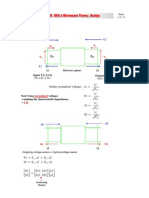
Rangkaian RF
Amplifier RF
Transducer Power Gain
Unilateral Transducer P. Gain
Unilateral Transducer P. Gain
Stability Circle
Amplifier beroperasi dengan bandwidth
tertentu
Impedansi kompleks dapat terbentuk dari
berbagai kombinasi real-imajiner
lingkaran
Sebagai konsekuensi, stabilitas juga
digambarkan dalamsebuat lingkaran
(circle) dengan pusat dan jari-jari tertentu
Input stability & output stability
Unconditional Stability
TUGAS
Membaca Chapter 9 Bretchko,
Mengerjakan ulang soal-soal contoh 9-1
sampai 9-18, bagi kelas menjadi 18 group.
Membuat atau menjalankan routin matlab
untuk menjawab soal-soal contoh
tersebut.
Mulai minggu yang akan datang dilakukan
demo untuk mengerjakan soal.
Ex. 9-1 Power relation
RF amplifier mempunyai S-parameter yang diukur pada
50 Ohm: s11=0.3-70, S21=3.585, S12=0.2-10
dan S22=0.4-45. Sumber berupa tegangan dengan
Vs= 50 volt dengan impedansi Zs=40 Ohm.
Outputnya mendrive antena dengan impedansi 75 Ohm.
Hitung:
Tranducer gain, unilateral transducer gain, available gain,
operating power gain
Power delivered to the load (PL), available power (PA) dan
inciden power Pinc
Ex. 9-3
Tentukan stability region dari BJ T
BFG505W dengan bias VCE=6 volt dan
Ic= 4mA. S-parameter diberikan pada
tabel berikut:
Matlab routine
%
% In this example we plot input and output stability circles
% for the BJ T whose S-parameters are measured at several
% frequencies. In this simulation we use the type BFG505W biased
% at Vce=6V and Ic=4mA
%
% Copyright (c) 1999 by P.Bretchko and R.Ludwig
% "RF Circuit Design: Theory and Practice"
%
close all; % close all opened graphs
clear all; % clear all variables
smith_chart; % create a Smith Chart
% f=500MHz
s11=0.384-j*0.584;
s12=0.029+j*0.031;
s21=-7.631+j*7.258;
s22=0.661-j*0.433;
s_param=[s11,s12;s21,s22]; % convert the S-parameters into matrix
notation
input_stability(s_param, 'r'); % plot input stability circle in red color
output_stability(s_param, 'b');% plot output stability circle in blue color
% f=750MHz
s11=0.114-j*0.551;
s12=0.044+j*0.029;
s21=-4.608+j*7.312;
s22=0.490-j*0.449;
s_param=[s11,s12;s21,s22];
input_stability(s_param, 'r');
output_stability(s_param, 'b');
% f=1000MHz
s11=-0.058-j*0.452;
s12=0.054+j*0.022;
s21=-2.642+j*6.641;
s22=0.379-j*0.424;
s_param=[s11,s12;s21,s22];
input_stability(s_param, 'r');
output_stability(s_param, 'b');
% f=1250MHz
s11=-0.160-j*0.343;
s12=0.059+j*0.015;
s21=-1.407+j*5.846;
s22=0.307-j*0.392;
s_param=[s11,s12;s21,s22];
input_stability(s_param, 'r');
output_stability(s_param, 'b');
Plot Input-output Stability
0
.
2
0
.
5
1
.
0
2
.
0
5
.
0
+0.2
-0.2
+0.5
-0.5
+1.0
-1.0
+2.0
-2.0
+5.0
-5.0
0.0
Ex-9-4
Carilah stability region dari transistor yang mempunyai
S-parameter yang diukur pada 50 Ohm: s11=0.7-70,
S12=0.2-10, S21=5.585 dan S22=0.7-45.
%
% This routine plots the input and output stability circles
% for a hypothetical transistor and whose S-parameters
% are defined in Exmaple 9-4
%
% Copyright (c) 1999 by P.Bretchko and R.Ludwig
% "RF Circuit Design: Theory and Practice"
%
close all; % close all opened graphs
clear all; % clear all variables
smith_chart; % create a Smith Chart
% S-parameters for the hypothetical transistor
s11=0.7*exp(j*(-70)/180*pi);
s12=0.2*exp(j*(-10)/180*pi);
s21=5.5*exp(j*(+85)/180*pi);
s22=0.7*exp(j*(-45)/180*pi);
s_param=[s11,s12;s21,s22];
[K,delta] =K_factor(s_param) % check stability
input_stability(s_param, 'r');
output_stability(s_param, 'b');
% print -deps 'fig9_9.eps'
Matlab result
0
.
2
0
.
5
1
.
0
2
.
0
5
.
0
+0.2
-0.2
+0.5
-0.5
+1.0
-1.0
+2.0
-2.0
+5.0
-5.0
0.0
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- RF Circuit Design - Theory and ApplicationsDokument653 SeitenRF Circuit Design - Theory and ApplicationsAyman Barakat94% (18)
- EDN Design Ideas 2005Dokument134 SeitenEDN Design Ideas 2005chag1956100% (2)
- VIDS Message Center Keypad Operator Instruction: D10R D11R D11R CDDokument24 SeitenVIDS Message Center Keypad Operator Instruction: D10R D11R D11R CDADJIMGARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Guidelines Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenDesign Guidelines Cheat SheetClaudio Lema FerrufinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kazrog True Iron User GuideDokument20 SeitenKazrog True Iron User GuideParsa ShomaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disain Amplifier RF (Bretchko Chapter 9) : Aspek2 DasarDokument43 SeitenDisain Amplifier RF (Bretchko Chapter 9) : Aspek2 DasarHyung NaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2315eng Digital ElectronicsDokument3 Seiten2315eng Digital ElectronicsHenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 4 Lab 4 - MOSFET AmplifierDokument22 SeitenFundamentals of Electrical Engineering 4 Lab 4 - MOSFET AmplifierGerson SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 2 (B) Aim: Study The Behavior of Circuit. TOOL: Multisim Simulator Circuit DiagramDokument5 SeitenExperiment No. 2 (B) Aim: Study The Behavior of Circuit. TOOL: Multisim Simulator Circuit DiagramKalyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab07B RC Frequency ResponseDokument5 SeitenLab07B RC Frequency ResponseNacho BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamplesDokument5 SeitenExamplesanjanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee312 Eee282 Lab7 Spring2015Dokument6 SeitenEee312 Eee282 Lab7 Spring2015vognarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece Software ReportDokument38 SeitenEce Software ReportWINORLOSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv CKT Technique Using GmIdDokument35 SeitenAdv CKT Technique Using GmIdnarashimarajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Two Stage Compensated Cmos Opamp-1Dokument3 SeitenDesign of Two Stage Compensated Cmos Opamp-1Varun AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-to-DC Power Converter by Rodney Yeu and Sudip Kundu ECE 345 Section H TA: Jon Wheeler 4/26/02 Project #34Dokument22 SeitenDC-to-DC Power Converter by Rodney Yeu and Sudip Kundu ECE 345 Section H TA: Jon Wheeler 4/26/02 Project #34Harkishen SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- GovindAgarwal Opt468bDokument203 SeitenGovindAgarwal Opt468bMatt ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDokument29 SeitenBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Report 8: Silicon Controlled RectifierDokument5 SeitenPractice Report 8: Silicon Controlled RectifierTecnicoItcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis Considerations of 4 GHZ Integrated Antenna With Negative Resis-Tance Oscillator S. H. IbrahimDokument21 SeitenDesign and Analysis Considerations of 4 GHZ Integrated Antenna With Negative Resis-Tance Oscillator S. H. IbrahimArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - OscillatorsDokument36 SeitenModule 3 - OscillatorsTanvi DeoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project PresentationDokument36 SeitenProject PresentationPrashant MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-Wise Eln QBDokument5 SeitenModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Circuits & Logic Design Laboratory: Lab ManualDokument61 SeitenElectronic Circuits & Logic Design Laboratory: Lab ManualSrihari Y.sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 RFDokument3 SeitenModule2 RFAshwini KothavaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 RF PDFDokument3 SeitenModule2 RF PDFashwini kothavaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes: (No. of Printed Pages-4) ES201 Enrol. No. (ET) End Semester Examination Nov.-Dec., 2016Dokument6 SeitenNotes: (No. of Printed Pages-4) ES201 Enrol. No. (ET) End Semester Examination Nov.-Dec., 2016Ryash ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ade Question BankDokument7 SeitenAde Question BankSonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsDokument9 SeitenDepartment of Electrical Engineering EE363: Power ElectronicsAbrahan ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor Device Simulation & Process Modelling LabDokument19 SeitenSemiconductor Device Simulation & Process Modelling LabAasif KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor: Penguat Daya Dan Perancangan Penguat Klas A (Amplifier Design)Dokument66 SeitenTransistor: Penguat Daya Dan Perancangan Penguat Klas A (Amplifier Design)Adri Muhaimin AfifNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEPT. of Computer Science Engineering SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203Dokument6 SeitenDEPT. of Computer Science Engineering SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203yash rawat (RA1911031010029)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product Profile: NPN 9 GHZ Wideband TransistorDokument14 SeitenProduct Profile: NPN 9 GHZ Wideband TransistorIelupokkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Engineering Design Exercise 2015Dokument30 SeitenRadio Engineering Design Exercise 2015Sadiqur Rahaman Sumon100% (2)
- Design and Analysis of An Equal Split Wilkinson Power DividerDokument11 SeitenDesign and Analysis of An Equal Split Wilkinson Power DividerLucky AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Objective: To Design Microwave AmplifierDokument3 SeitenCourse Objective: To Design Microwave AmplifierAshwini KothavaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation Analysis of Lighting Switching Impulse VoltagesDokument13 SeitenSimulation Analysis of Lighting Switching Impulse Voltagespeppeto373137Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 4single Stage IC Amplifier (For IT Class)Dokument85 SeitenChapter - 4single Stage IC Amplifier (For IT Class)Rajesh BathijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - Experiment Diode j09Dokument19 Seiten01 - Experiment Diode j09Ahmed Sobhy KhattabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elx 311 Chap 7 SlidesDokument23 SeitenElx 311 Chap 7 SlidesDaniyar SeytenovNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC1256-Lab ManualDokument67 SeitenEC1256-Lab Manualjeyaganesh86% (7)
- S-55.3120 Passive Filters, Exercise Problems: © H © H © H © H R RDokument7 SeitenS-55.3120 Passive Filters, Exercise Problems: © H © H © H © H R Rtamann2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Varactor SPICE ModelsDokument5 SeitenVaractor SPICE ModelsswatagodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Shift OscillatorDokument31 SeitenPhase Shift OscillatorArjob MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 2 Marks QuestionsDokument13 SeitenEc2251: Electronic Circuits Ii Sem / Year: Iv/ Ii Unit I Feedback Amplifiers 2 Marks QuestionsSumathy SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung Plasma Training ManualDokument57 SeitenSamsung Plasma Training ManualevaristoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung Plasma Training ManualDokument57 SeitenSamsung Plasma Training ManualDamiao100% (1)
- Electronic Circuit Analysis July 2023Dokument8 SeitenElectronic Circuit Analysis July 2023raj3roy4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 10 OpticalDokument4 SeitenExpt 10 OpticalSastry KalavakolanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Wave Shaping: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokument0 SeitenLinear Wave Shaping: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringanishadandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillators-RC Phaseshift & Wein BridgeDokument4 SeitenOscillators-RC Phaseshift & Wein BridgeKrishnachandran RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workshop 02Dokument5 SeitenWorkshop 02Damith ErangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02b Rfamp PDFDokument18 Seiten02b Rfamp PDFHassan Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8. Converter Transfer Functions: 8.1. Review of Bode PlotsDokument103 SeitenChapter 8. Converter Transfer Functions: 8.1. Review of Bode Plotsbojan 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillator DesignDokument56 SeitenOscillator DesignHanggaKusumaYusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eetop - CN MMIC DesignDokument207 SeitenEetop - CN MMIC DesignA Mohan BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 8-Electrooptic Devices PDFDokument34 SeitenCH 8-Electrooptic Devices PDFMahavir ChavdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorVon Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Instrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualVon EverandInstrumentation and Test Gear Circuits ManualBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Variable Length CodesDokument5 SeitenVariable Length CodesignatiusnickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog TelevisionDokument16 SeitenAnalog TelevisionignatiusnickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP338Plus AusDokument6 SeitenGP338Plus AusAbhishek RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM338 398 BrochureDokument6 SeitenGM338 398 BrochureMutahirrasoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-Parameters 5 Maret 2013Dokument11 SeitenS-Parameters 5 Maret 2013ignatiusnickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-Parameters 5 Maret 2013Dokument11 SeitenS-Parameters 5 Maret 2013ignatiusnickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Config Item Creation Flow2Dokument1 SeiteConfig Item Creation Flow2sen2985100% (1)
- Granqvist Svec PEVoC6 MicrophonesDokument14 SeitenGranqvist Svec PEVoC6 MicrophonesBeverly PamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-5 RES500-Academic Writing and Research Skills 1 Semester (2019-2020)Dokument5 SeitenAssignment-5 RES500-Academic Writing and Research Skills 1 Semester (2019-2020)Fatima WassliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 4Dokument32 SeitenTest 4Santosh JagtapNoch keine Bewertungen
- AXIS Camera Station S1148 Recorder: User ManualDokument39 SeitenAXIS Camera Station S1148 Recorder: User ManualfguerreroaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Config Cisco 881 Isla PartidaDokument4 SeitenConfig Cisco 881 Isla PartidaJohan Frederick FoitzickNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL Server Installation and ConfigurationDokument52 SeitenSQL Server Installation and ConfigurationAshish ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- USBDF01W5 (SMD UD1 Sot323-5l)Dokument11 SeitenUSBDF01W5 (SMD UD1 Sot323-5l)VasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Info Rma Tion: Software ManualDokument32 SeitenFor Info Rma Tion: Software Manualm0n g3yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google File System (GFS)Dokument18 SeitenGoogle File System (GFS)Mohit GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- "A Study of Online Trading and Stock Broking": A Project Report OnDokument85 Seiten"A Study of Online Trading and Stock Broking": A Project Report OnShubha DevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kozinets Gretzel 2020 Commentary Artificial Intelligence The Marketer S DilemmaDokument4 SeitenKozinets Gretzel 2020 Commentary Artificial Intelligence The Marketer S DilemmalionelfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sqlmap Cheatsheet v1.0-SBDDokument2 SeitenSqlmap Cheatsheet v1.0-SBDtalsxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Durbin LevinsonDokument7 SeitenDurbin LevinsonNguyễn Thành AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SPSSDokument4 SeitenWhat Is SPSSElla Marie BaricuatroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parallelized Deep Neural NetworksDokument34 SeitenParallelized Deep Neural NetworksLance LegelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firmware Functional Description MPH-04, MPB-04, MPD-04 R911315485 - 02 PDFDokument914 SeitenFirmware Functional Description MPH-04, MPB-04, MPD-04 R911315485 - 02 PDFCristopher EntenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malvika Joglekar: Profile SummaryDokument3 SeitenMalvika Joglekar: Profile SummaryVipin HandigundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 2: Chapter 1-IntroductionDokument26 SeitenPart 2: Chapter 1-IntroductionSeif AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- RIF150 MiniMag Flowmeter Manual ENGDokument34 SeitenRIF150 MiniMag Flowmeter Manual ENGIvo Tadej GrmajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video Cassette Recorder: Instruction ManualDokument24 SeitenVideo Cassette Recorder: Instruction ManualPaweł MyczkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elt Test Set (Ets) Operation Manual 570-1000 Revision ADokument28 SeitenElt Test Set (Ets) Operation Manual 570-1000 Revision Anixon_b_2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Declaration of XXXXXXXXX.: (Redacted) Location in The United States of AmericaDokument17 SeitenDeclaration of XXXXXXXXX.: (Redacted) Location in The United States of AmericaEnwardCZorhanz94% (31)
- NTA UGC NET Electronic Science SyllabusDokument3 SeitenNTA UGC NET Electronic Science Syllabusgrk.elrNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFM PCV Pricing and Revenue ManagemetDokument6 SeitenRFM PCV Pricing and Revenue ManagemetLoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- P780Dokument50 SeitenP780Shailesh BhanushaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAN Signaling Analysis Guide (RAN10.0 - 02)Dokument245 SeitenRAN Signaling Analysis Guide (RAN10.0 - 02)Juan Camilo GalvisNoch keine Bewertungen