Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes1
Hochgeladen von
api-268533145Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes1
Hochgeladen von
api-268533145Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
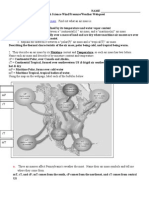
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
What is the relationship between craters, calderas, vents, and
magma?
Magma comes to Earths surface (lava). Lava erupts through an opening called a vent. At
the top of the volcano, around the vent, is a depression called a crater. If the crater is
larger than 1 km, than it becomes a caldera.
How does a crater lake form? (words and pictures)
A crater lake is formed when a side of the volcano collapses into the magma chamber
that once fueled the volcano.
What two factors does a volcanos appearance depend upon?
What characteristics vary among volcanoes?
The type of material that forms the volcano and the type of eruptions that occur. Shape,
size and composition.
Complete the following table in your notes:
Type of Volcano Materials &
Description
Sketch Example
Shield
Broad gently sloping
sides and a nearly
circular base
Mauna Loa
Cinder-Cone
Forms when
material ejected
high in the air, falls
back to Earth and
piles up around the
vent
Izalco
Composite
(Stratovolcano)
Forms when layers
of volcanic
fragments alternate
with lava
Mount St. Helens
And Mount Rainier
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
How do the volcanoes compare in terms of size and slope?
Shield volcanoes are the largest, and cinder-cone volcanoes are the smallest. Cinder-
cone volcanoes have the steepest slopes and shield volcanoes have the gentlest slopes.
Cinder-cone and composite volcanoes have a concave slope and shield volcanoes are
straight.
What factors cause differences in size and slope?
Different kinds of materials that make up each volcano, the vegetation that grows on
the volcanos slopes, local climate, and the eruptive history of the volcano.
What is tephra?
Rock fragments thrown into the air during a volcanic eruption.
What is a pyroclastic flow?
Rapidly moving volcanic material
Where are most volcanoes found?
At plate boundaries.
Use the maps provided to show: (1) the Circum Pacific Belt and the
Mediterranean Belt where convergent volcanism occur and (2) the
Hawaiian Emperor Volcanic Chain.
How do hotspots form?
When certain regions of Earths mantle gets unusually hot, it forms hot spots.
What do hotspots tell us about tectonic plates?
A trail of progressively older volcanoes forms as a plate moves over a hotspot.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Renewable Energy WebquestDokument3 SeitenRenewable Energy Webquestapi-269485108Noch keine Bewertungen
- APFC Accountancy Basic Study Material For APFCEPFO ExamDokument3 SeitenAPFC Accountancy Basic Study Material For APFCEPFO ExamIliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emilia Perroni-Play - Psychoanalytic Perspectives, Survival and Human Development-Routledge (2013) PDFDokument262 SeitenEmilia Perroni-Play - Psychoanalytic Perspectives, Survival and Human Development-Routledge (2013) PDFMihaela Ioana MoldovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Digest For Labor Relations 2Dokument40 SeitenCase Digest For Labor Relations 2zeigfred badanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lorax Truax QuestionsDokument2 SeitenLorax Truax Questionsapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Ees Post RefelctionDokument1 SeiteHonors Ees Post Refelctionapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wanted AliveDokument1 SeiteWanted Aliveapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Severe Weather WebquestDokument5 SeitenSevere Weather Webquestapi-2685331450% (2)
- Virtual Lab-Water QualityDokument6 SeitenVirtual Lab-Water Qualityapi-264220291Noch keine Bewertungen
- Webquest Climate ChangeDokument2 SeitenWebquest Climate Changeapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Freshwater Pollution Guided NotesDokument2 SeitenFreshwater Pollution Guided Notesapi-330462935Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Rain Virtual Lab WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAcid Rain Virtual Lab Worksheetapi-26475340350% (4)
- Climate NotesDokument2 SeitenClimate Notesapi-264874516Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Acid RainDokument1 SeiteWhat Is Acid Rainapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDokument2 SeitenAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- AirmassandfrontsawebquestDokument4 SeitenAirmassandfrontsawebquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- What-Is-A-Watershed-Webquest StudentworksheetDokument5 SeitenWhat-Is-A-Watershed-Webquest Studentworksheetapi-268533145100% (1)
- Water Cycle Webquest 2Dokument6 SeitenWater Cycle Webquest 2api-264756260Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nonrenwable ResourceDokument27 SeitenNonrenwable Resourceapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Waste Guided NotesDokument2 SeitenSolid Waste Guided Notesapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9-1 Surface WaterDokument38 Seiten9-1 Surface Waterapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Food Production in Europe WebquestDokument2 SeitenFood Production in Europe Webquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Meatrix MatthewDokument2 SeitenThe Meatrix Matthewapi-264886115Noch keine Bewertungen
- Agents of Erosion and Mass MovementDokument1 SeiteAgents of Erosion and Mass Movementapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tragedy of The Bunnies Game 2Dokument2 SeitenTragedy of The Bunnies Game 2api-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Tetonics WebquestDokument12 SeitenPlate Tetonics Webquestapi-264090085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mining in My HouseDokument2 SeitenMining in My Houseapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Guided NotesDokument2 SeitenEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tides WebquestDokument2 SeitenTides Webquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tsunami WebquestDokument5 SeitenTsunami Webquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dirt On Soils WebquestDokument5 SeitenDirt On Soils Webquestapi-264873863Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rocks and Minerals WebquestDokument2 SeitenRocks and Minerals Webquestapi-264150929Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation of Activities UBCVDokument13 SeitenCompilation of Activities UBCVRenell Vincent RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 4Ps of Labor: Passenger, Passageway, Powers, and PlacentaDokument4 SeitenThe 4Ps of Labor: Passenger, Passageway, Powers, and PlacentaMENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On The Hells AngelsDokument6 SeitenResearch Paper On The Hells Angelsfvg2xg5r100% (1)
- Cost Accounting - LabourDokument7 SeitenCost Accounting - LabourSaad Khan YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Cover Letter For A Training ProgramDokument4 SeitenHow To Write A Cover Letter For A Training Programgyv0vipinem3100% (2)
- Westbourne Baptist Church NW CalgaryDokument4 SeitenWestbourne Baptist Church NW CalgaryBonnie BaldwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aditya Birla - FATCA and CRS - UBO - NON INDIVIDUALS PDFDokument2 SeitenAditya Birla - FATCA and CRS - UBO - NON INDIVIDUALS PDFHoaccounts AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Issues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianDokument22 SeitenIssues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianHarrish ZainurinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Level 1 2013-2014 Part 2Dokument54 SeitenGrammar Level 1 2013-2014 Part 2Temur SaidkhodjaevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lean Foundation TrainingDokument9 SeitenLean Foundation TrainingSaja Unķnøwñ ĞirłNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fernando Medical Enterprises, Inc. v. Wesleyan University Phils., Inc.Dokument10 SeitenFernando Medical Enterprises, Inc. v. Wesleyan University Phils., Inc.Clement del RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace & Aviation Job RolesDokument74 SeitenAerospace & Aviation Job RolesBharat JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM ........Dokument12 SeitenHRM ........Beenish AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evirtualguru Computerscience 43 PDFDokument8 SeitenEvirtualguru Computerscience 43 PDFJAGANNATH THAWAITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euro Tuner 1 2008 PDFDokument2 SeitenEuro Tuner 1 2008 PDFDarwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Solids Unit - I: Chadalawada Ramanamma Engineering CollegeDokument1 SeiteMechanics of Solids Unit - I: Chadalawada Ramanamma Engineering CollegeMITTA NARESH BABUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engaged Listening Worksheet 3 - 24Dokument3 SeitenEngaged Listening Worksheet 3 - 24John BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master ListDokument26 SeitenMaster ListNikhil BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life of a VoyageurDokument8 SeitenLife of a VoyageurBruce GuthrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terrestrial EcosystemDokument13 SeitenTerrestrial Ecosystemailene burceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ResearchDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Researchapi-385504653Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Dyspnoea - DR Yeat Choi LingDokument40 SeitenManagement of Dyspnoea - DR Yeat Choi Lingmalaysianhospicecouncil6240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amnesia: A Game of Remembering YourselfDokument11 SeitenAmnesia: A Game of Remembering YourselfNina JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Apostolic Church, Ghana English Assembly - Koforidua District Topic: Equipping The Saints For The MinistryDokument2 SeitenThe Apostolic Church, Ghana English Assembly - Koforidua District Topic: Equipping The Saints For The MinistryOfosu AnimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Notes - 1Dokument55 SeitenAccounting Notes - 1Rahim MashaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deforestation Contributes To Global Warming: Bruno GERVETDokument11 SeitenDeforestation Contributes To Global Warming: Bruno GERVETMajid JatoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - JTC Template On Project ProposalDokument10 Seiten04 - JTC Template On Project Proposalbakelm alqamisNoch keine Bewertungen