Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Key Topics For Mindmap
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed Zein Hendawy0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten1 SeiteKey Topics for Mindmap
Originaltitel
Key Topics for Mindmap
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenKey Topics for Mindmap
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten1 SeiteKey Topics For Mindmap
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed Zein HendawyKey Topics for Mindmap
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
P1.
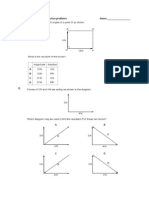
Physical quantities and units
1.1 Physical quantities
1.2 SI Units
1.3 Scalars and vectors
P2. Measurement techniques
2.1 Measurements
2.2 Errors and uncertainties
P3. Kinematics
3.1 Linear motion
3.2 Non-linear motion
P4. Dynamics
4.1 Newtons laws of motion
4.2 Linear momentum and its conservation
P5. Forces
5.1 Types of force
5.2 Equilibrium of forces
5.3 Centre of gravity
5.4 Turning effects of forces
P6. Work, energy, power
6.1 Energy conversion and conservation
6.2 Work
6.3 Potential energy, kinetic energy and
internal energy
6.4 Power
P7. Phases of matter
7.1 Density
7.2 Solids, liquids, gases
7.3 Pressure in fluids
7.4 Application of the kinetic theory
P8. Waves
8.1 Progressive waves
8.2 Transverse and longitudinal waves
8.3 Determination of speed, frequency and
wavelength
8.4 Electromagnetic spectrum
P9. Superposition
9.1 Diffraction
9.2 Interference
9.3 Two-source interference patterns
P10. Electric fields
10.1 Concept of an electric field
10.2 Uniform electric fields
P11. Current electricity
11.1 Electric current
11.2 Potential difference
11.3 Resistance
11.4 Sources of electromotive force
P12. Circuits
12.1 Practical circuits
12.2 Conservation of charge and energy
12.3 Use of the potential divider
P13. Physics of the atom
13.1 The nucleus
13.2 Isotopes
13.3 Nuclear processes
13.4 The nucleus of the atom: neutrons and
protons, isotopes, proton and nucleon
numbers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- IGCSE Physics Exam Revision NotesDokument34 SeitenIGCSE Physics Exam Revision NotesCoolman Poon88% (17)
- As Level Physics - Standing Waves ProblemsDokument5 SeitenAs Level Physics - Standing Waves ProblemsMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EverythingScience Grade10Dokument512 SeitenEverythingScience Grade10gnllindsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Reasons You Need A Strategy For Managing InformationDokument62 Seiten8 Reasons You Need A Strategy For Managing InformationjocimarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenMAINT OverviewManual ENG V080Dokument31 SeitenOpenMAINT OverviewManual ENG V080Mohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wasf Misr 2011Dokument664 SeitenWasf Misr 2011Mohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything Science Grade 11Dokument484 SeitenEverything Science Grade 11Mohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM025 EN 08-2014 IEC60034-30-1 - LowresDokument2 SeitenTM025 EN 08-2014 IEC60034-30-1 - LowresMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daihatsu Panel VanDokument8 SeitenDaihatsu Panel VanMohamed Zein Hendawy100% (1)
- Egypt Citizen Budget SummaryDokument2 SeitenEgypt Citizen Budget SummaryMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easter Assignment 2014 MEMODokument10 SeitenEaster Assignment 2014 MEMOMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics and Dynamics Assignment MEMODokument10 SeitenKinematics and Dynamics Assignment MEMOMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egypt Citizen BudgetDokument24 SeitenEgypt Citizen BudgetMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching As Physics Practical SkillsDokument86 SeitenTeaching As Physics Practical SkillsMohamed Zein Hendawy100% (2)
- Sam Gce MathematicsDokument97 SeitenSam Gce MathematicsShareef UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learner Guide For As and A Level Physics (Cambridge)Dokument41 SeitenLearner Guide For As and A Level Physics (Cambridge)Михаил ГоворовNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Level Physics - Vectors Practice ProblemsDokument4 SeitenAs Level Physics - Vectors Practice ProblemsMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Level Physics Momentum MEMO OLD IncompleteDokument3 SeitenAs Level Physics Momentum MEMO OLD IncompleteMohamed Zein Hendawy100% (1)
- Physics of The Atom - Practice ProblemsDokument8 SeitenPhysics of The Atom - Practice ProblemsMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Chapters in Tom DuncanDokument1 SeiteRevision Chapters in Tom DuncanMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Example ProblemsDokument7 SeitenDynamics Example ProblemsMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeinemannIGCSE Physics Chapter1Dokument11 SeitenHeinemannIGCSE Physics Chapter1Mohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving ODEs With Matlab Instructors Manual - L.F. ShampineDokument36 SeitenSolving ODEs With Matlab Instructors Manual - L.F. ShampineHermes®Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Summary Sheets For IGCSE Physical ScienceDokument9 SeitenRevision Summary Sheets For IGCSE Physical ScienceMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- After Ek HwanDokument1 SeiteAfter Ek HwanMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Case WhitepaperDokument7 SeitenBusiness Case WhitepaperMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 76 Egypts Muslim Brothers Confrontation or IntegrationDokument37 Seiten76 Egypts Muslim Brothers Confrontation or IntegrationMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Summary Sheets For IGCSE Physical ScienceDokument9 SeitenRevision Summary Sheets For IGCSE Physical ScienceMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Chow Technologies PresentationDokument41 SeitenDr. Chow Technologies PresentationMohamed Zein HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen