Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bio 100 Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-2698287760 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
88 Ansichten2 SeitenProkaryotic cells lack a nucleus and have DNA floating in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains the cell's DNA and internal compartments. All cells have a plasma membrane that regulates what enters and exits, and is made of phospholipids and proteins. Transport across the membrane can occur passively via diffusion or osmosis, or actively via transport proteins and ATP. Cells connect through tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. Eukaryotic cells have organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes that allow specialization of functions.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
bio 100 notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenProkaryotic cells lack a nucleus and have DNA floating in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains the cell's DNA and internal compartments. All cells have a plasma membrane that regulates what enters and exits, and is made of phospholipids and proteins. Transport across the membrane can occur passively via diffusion or osmosis, or actively via transport proteins and ATP. Cells connect through tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. Eukaryotic cells have organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes that allow specialization of functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
88 Ansichten2 SeitenBio 100 Notes
Hochgeladen von
api-269828776Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and have DNA floating in the cytoplasm, while eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that contains the cell's DNA and internal compartments. All cells have a plasma membrane that regulates what enters and exits, and is made of phospholipids and proteins. Transport across the membrane can occur passively via diffusion or osmosis, or actively via transport proteins and ATP. Cells connect through tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. Eukaryotic cells have organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes that allow specialization of functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Chapter #3: Cells
I.
II.
Prokaryotic Cells: Does not have a nucleus. DNA resides in the middle of the cell
Eukaryotic Cells:
i. Has a central control structure called a nucleus, containing the cells DNA
ii. About 10X larger
iii. Internal structure organized into compartments
I.
Plasma Membrane (all cells)
a. Take in nutrients
b. Dispose waste
c. Build molecules
d. Regulate heat
e. Regulate flow of materials
Structure consists of a Phospholipid bilayer: Contains membrane proteins
Receptor protein
Recognition proteins
Transport proteins
Enzymatic portions
Also contains carbohydrate chains (recognition), and cellulose (structure)
II.
Types of transport:
A. Passive:
1.
a.
b.
2.
a.
b.
Diffusion: Solvent dissolves in a solute, is randomly distributed
Simple diffusion passes through membrane
Facilitated: assisted by carrier molecule (transport proteins)
Osmosis: Water diffusing across a membrane:
Isotonic in balance
Hypotonic
a. Solute concentrations LOWER outside cell
b. Water diffuses into cell
c. Hypertonic
a. Solute concentration higher outside cell
b. Water diffuses out
B. Active transport:
1.
Primary: Uses energy directly from ATP
2.
Secondary: ???
C. Endocytosis:
1.
Phagocytosis cell engulfs a large particle (vesicle)
2.
Pinocytosis cells take in dissolved particles and liquid
3.
Receptor-mediated - receptor proteins bind to a specific particle, then engulf it
D. Exocytosis: - particles are packed in a vesicle. The vesicles outer shell fuses with the cell
membrane. The particles are expelled.
III.
Primary connections between cells:
A. Tight junctions continuous, water-tight seals
B. Desmosomes act like Velcro to fasten cells together
C. Gap junctions pores surrounded by special proteins that form an open channel between 2
cells
IV.
9 characteristics of eukaryotic cells:
A. Nucleus
1.
Largest, most prominent organelle
2.
2 functions:
a. Genetic control center
b. Storehouse for hereditary info
3.
Chromatin: thin fibers of DNA inside the nucleus
4.
Nucleolus
a. Area near the center or the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled
B. Cytoplasm
C. Cytoskeleton:
1.
Inner scaffolding
2.
Provides shape and support
3.
Controls traffic flow
4.
Enables movement
D. Cilia and Flagellum - control movement
E. Mitochondria: Energy converters
1.
Dual walls
2.
Endosymbiosis
F. Lysomes garbage disposals, contain digestive enzymes and acids
G. Rough endoplasmic reticulum Modifies proteins to be shipped to other locations, has
ribosomes
H. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Synthesizes lipids, detoxifies molecules, no ribosomes
I. Golgi Apparatus: processes products for distribution throughout the body (outside the cell)
V.
Plant cell walls: Provide additional support
A. Vacuoles: multipurpose storage sacs
1.
Nutrient storage
2.
Waste management
3.
Predator deterrence
4.
Sexual reproduction
5.
Physical support
B. Chloroplast:
1.
Site of photosynthesis
a. Thylakoids collect light for photosynthesis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AP Biology Review Sheet Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic (Other Living Things)Dokument4 SeitenAP Biology Review Sheet Prokaryotic Bacteria Eukaryotic (Other Living Things)api-286357921Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Intro To BiochemistryDokument4 Seiten1 - Intro To BiochemistryShardy Lyn RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 CellDokument94 SeitenChapter 3 Cellmohamedshilleh7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Cell OrganellesDokument11 SeitenNotes On Cell Organellesapi-241062194Noch keine Bewertungen
- AnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)Dokument7 SeitenAnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)HyvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells (10%) : I. Organelles I. Phospholipid BilayerDokument5 SeitenCells (10%) : I. Organelles I. Phospholipid Bilayerrashmi_harryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Reviewer 3 CellsDokument13 SeitenAnaphy Reviewer 3 CellsJohn Niño CasuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Science 9.2Dokument16 Seiten7 Science 9.2Rebecca LloydNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Cell StructureDokument5 SeitenI. Cell StructureAllyson CarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy Lecture Notes Update 2017Dokument58 SeitenHuman Anatomy Lecture Notes Update 2017RAGHVENDRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Parts and FunctionDokument29 SeitenCell Parts and Functionplayandhavefun23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio HMWRK Week 3Dokument3 SeitenBio HMWRK Week 3Oksana Kristina RootNoch keine Bewertungen
- CytologyDokument59 SeitenCytologyCla Nuval100% (1)
- Chapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1Dokument9 SeitenChapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1VeiliLookNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsDokument5 SeitenIB HL Biology Chapter 2 Notes CellsTiffani Choy100% (1)
- Biology AML NMAT ReviewerDokument15 SeitenBiology AML NMAT ReviewerJocelyn Mae CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blok The Grand Design of Human Body and The Cell As Biochemical MachineryDokument28 SeitenBlok The Grand Design of Human Body and The Cell As Biochemical MachineryChandra ShinodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Membranes: Structure/Function Diffusion and Osmosis Manufacture and Breakdown Energy, Support, and MovementDokument32 SeitenThe Cell Membranes: Structure/Function Diffusion and Osmosis Manufacture and Breakdown Energy, Support, and MovementehshonorsbioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure LectureDokument26 SeitenCell Structure Lecturedeepa gujjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLaboratory Actiivty 3 - Cellular Basis of LifeDokument5 SeitenDLaboratory Actiivty 3 - Cellular Basis of LifeSYDNEY JILL ACHAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesDokument37 SeitenBiology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesIanDiel ParagosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDokument7 SeitenNotes - Chapter 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationRogie P. BacosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Part of Study GuidesDokument11 Seiten1st Part of Study GuidesYaffaAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and Function: Biochemistry Jerrold T. Mangao, RN, MaedcDokument28 SeitenCell Structure and Function: Biochemistry Jerrold T. Mangao, RN, MaedcJerrold MangaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology ReviewerDokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology ReviewerJm Gutierrez50% (6)
- Building Your Own Fluid Mosiac Model of The Cell Membrane RESOURCESDokument16 SeitenBuilding Your Own Fluid Mosiac Model of The Cell Membrane RESOURCESVienne MonroidNoch keine Bewertungen
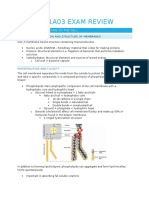
- Biology 1A03 Exam ReviewDokument69 SeitenBiology 1A03 Exam Review0xVi3tfireNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentDokument6 SeitenAP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentRobert Ladaga33% (3)
- NotesDokument4 SeitenNotesrickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Generalized Animal CellDokument35 SeitenThe Generalized Animal CellMelina MarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biol Worksheet 2013 Grade 11thDokument5 SeitenBiol Worksheet 2013 Grade 11thendalew damtieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells: DetailsDokument109 SeitenCells: DetailsAishwarya SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of The CellDokument17 SeitenStructure and Function of The CellIrene QuimsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Reviewer Cell Theory MicrosDokument28 SeitenBiology Reviewer Cell Theory MicrosNikko Pananganan DajaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology Outline - Chapter 4Dokument6 SeitenAP Biology Outline - Chapter 4Omar Lopez100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 CellsDokument9 SeitenCHAPTER 4 CellsNadeem IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Test Exervice M1Dokument10 SeitenCell Membrane Test Exervice M1joesmithmedina1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Act2 Bio SciDokument4 SeitenAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDokument27 SeitenAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Test 2Dokument2 SeitenBiology Test 2Rosa MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDokument53 SeitenSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIBAR, Justine - Biochem LE 1&2Dokument3 SeitenVIBAR, Justine - Biochem LE 1&2JustineNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 Final Exam 2nd QuarterDokument9 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 Final Exam 2nd Quarterjoei Arquero100% (1)
- 1 CellsDokument9 Seiten1 CellsmeerzasarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined KBB BiologyDokument97 SeitenCombined KBB BiologyTsering LamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology Is The Study of TissuesDokument87 SeitenHistology Is The Study of TissuesElena ArvanitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsDokument7 SeitenModule 3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsJade Lagada PagariganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teas NotesDokument31 SeitenTeas NotesjanettNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 BioDokument5 SeitenCH 6 BioedwarddameNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 5 MembranesDokument7 SeitenCHAPTER 5 MembranesNadeem IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural OrganizationDokument18 SeitenStructural OrganizationMSANITYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes: CellsDokument5 SeitenBiology Notes: CellsDaniel BalurisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Outline: ELL Tructure and UnctionDokument5 SeitenChapter Outline: ELL Tructure and Unctionrommel benamir100% (1)
- Transport of Substances Through Cell MembranesDokument34 SeitenTransport of Substances Through Cell MembranesSanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cheat SheetDokument5 SeitenCell Cheat SheetAJ Coots100% (2)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokument6 SeitenProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJam MoralejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Across Plasma Membrane PDFDokument2 SeitenTransport Across Plasma Membrane PDFTracie Curry100% (1)
- (John F. Moulder) PHI Handbook of XRay Photoelectron SpectrosDokument192 Seiten(John F. Moulder) PHI Handbook of XRay Photoelectron SpectrosCamilo CorredorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbanions Carbocations and CarboradicalsDokument21 SeitenCarbanions Carbocations and CarboradicalsAnaAmaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coding in Communication System: Channel Coding) Will Be AddressedDokument5 SeitenCoding in Communication System: Channel Coding) Will Be AddressedDuge PlakolliNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCS800 Firmware Manual EnglishDokument298 SeitenDCS800 Firmware Manual EnglishMadson FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rsa Netwitness Logs and Packets: Server, Dac and San HW SpecificationsDokument10 SeitenRsa Netwitness Logs and Packets: Server, Dac and San HW SpecificationsfunyiroemberNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Virtual Reality Simulation in Surgical Training in The Light of COVID-19 PandemicDokument13 SeitenThe Role of Virtual Reality Simulation in Surgical Training in The Light of COVID-19 PandemicIván Hernández FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTTS Corporate BrochureDokument20 SeitenLTTS Corporate BrochureshountyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Steam GenerationDokument23 SeitenChapter 1 - Steam GenerationAzhan FikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjectives 4Dokument34 SeitenAdjectives 4Delia Bolasoc100% (1)
- Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenLab Reportivan glenn baldomerostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensor Gaurd Installation and Maintenance ManualDokument57 SeitenSensor Gaurd Installation and Maintenance ManualCapacitacion TodocatNoch keine Bewertungen
- The C Puzzle BookDokument93 SeitenThe C Puzzle Bookabhijeetnayak67% (3)
- Lecture-V Reaction and Separation SystemDokument54 SeitenLecture-V Reaction and Separation SystemErmias AbelnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioTime 8.5 User ManualDokument144 SeitenBioTime 8.5 User ManualKashif Adeel50% (2)
- Thermal Analysis and Compensation of A Double Column Machining CentreDokument9 SeitenThermal Analysis and Compensation of A Double Column Machining CentreShamanth CNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mathematical Society of Serbia - 60 YearsDokument23 SeitenThe Mathematical Society of Serbia - 60 YearsBranko Ma Branko TadicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm rp - Nguyễn Phú Minh Nhật - 20202795Dokument1 SeiteMidterm rp - Nguyễn Phú Minh Nhật - 20202795Minh Nhật100% (1)
- Standard Test Method For Density and Void Content of Freshly Mixed Pervious ConcreteDokument4 SeitenStandard Test Method For Density and Void Content of Freshly Mixed Pervious ConcreteManaswini VadlamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Yogurt Production Line Simulation Using Arena SoftwareDokument8 SeitenEvaluation of Yogurt Production Line Simulation Using Arena Softwareg defNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Life Prediction - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDokument14 SeitenFatigue Life Prediction - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsMohamed AlaaElDinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionsDokument8 SeitenSolutionsJavid BalakishiyevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake EnginneringDokument11 SeitenEarthquake EnginneringkkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inform: Extending PhoenicsDokument42 SeitenInform: Extending PhoenicsrsigorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbott 2021 ApJL 915 L5Dokument24 SeitenAbbott 2021 ApJL 915 L5Manju SanthakumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Control SystemDokument34 SeitenDigital Control SystemLaxman Koirala100% (3)
- Final Formula SheetDokument1 SeiteFinal Formula SheetFaryalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bluetooth PresentationDokument18 SeitenBluetooth Presentationarjun_rathore8178Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cortec, VpCI-371 Application GuideDokument2 SeitenCortec, VpCI-371 Application Guidemonserrat PereaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cobol Language Fundamentals: Structured COBOL Programming, Stern & Stern, 9th Ed ItionDokument53 SeitenCobol Language Fundamentals: Structured COBOL Programming, Stern & Stern, 9th Ed ItionAsk NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mac Keyboard ShortcutsDokument16 SeitenMac Keyboard ShortcutsSaira FazalNoch keine Bewertungen