Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
C 11 S 2
Hochgeladen von
api-261372832Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C 11 S 2
Hochgeladen von
api-261372832Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Motion
Section 2
Key Ideas
What changes when an object accelerates?
How do you calculate the acceleration of an
object moving in a straight line?
How can a graph be used to find acceleration?
Motion
Section 2
Bellringer
In your study of velocity, you learned it involves both the
speed of an object and the direction that the object is
traveling.
1. Which of the following examples shows a change in
velocity? Remember a change in velocity can be either a
change in speed or a change in the direction of motion.
Briefly explain your answers.
a. a car coming to a stop at a stop sign
b. a book sitting on a desk
c. a yo-yo in motion
d. a bicyclist making a left-hand turn at exactly 15 km/h
Motion
Section 2
Acceleration and Motion
What changes when an object accelerates?
When an object undergoes acceleration, its
velocity changes.
acceleration: the rate at which velocity changes over
time; an object accelerates if its speed, direction, or both
change
Motion
Section 2
Acceleration and Motion, continued
Acceleration can be a change in speed.
An increase or decrease in speed is an
acceleration.
Acceleration can also be a change in direction.
A motorcyclist who rides around the inside
of a large cage is constantly accelerating.
A person riding a Ferris wheel at an
amusement park is accelerating.
Swing Accident
The acceleration that occurs in circular motion
is known as centripetal acceleration.
Motion
Section 2
Calculating Acceleration
How do you calculate the acceleration of an object
moving in a straight line?
The average acceleration over a given time interval can
be calculated by dividing the change in the objects
velocity by the time over which the change occurs.
average acceleration
v f vi
t
final velocity - initial velocity
time
Motion
Section 2
Calculating Acceleration, continued
Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes.
If Acceleration is in the same direction as velocity,
then the object is speeding up. (++ or --)
If Acceleration is in the opposite direction as
velocity, then the object is slowing down. (+- or -+)
SI units of acceleration = meters per second per
second (m/s/s), or m/s2
Motion
Section 2
Visual Concept: Acceleration
Motion
Section 2
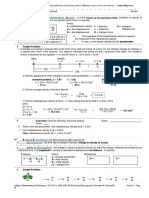
Math Skills
Acceleration
A flowerpot falls off a second-story windowsill. The
flowerpot starts from rest and hits the sidewalk 1.5 s
later with a velocity of 14.7 m/s. Find the average
acceleration of the flowerpot.
1. List the given and the unknown values.
Given:
time, t = 1.5 s
initial velocity, vi = 0 m/s
final velocity, vf = 14.7 m/s down
Unknown: acceleration, a = ? (m/s2 and direction)
Motion
Section 2
Math Skills, continued
2. Write the equation for acceleration.
final velocity initial velocity vf vi
acceleration =
= t
time
3. Insert the known values into the equation, and
solve.
v f vi
14.7 m/s 0 m/s
a
t
1.5 s
14.7 m/s
a
9.8 m/s 2 down
1.5 s
Motion
Practice Problems
Worksheet Examples
Section 2
Motion
Section 2
Table showing a bike trip
Time (s)
Velocity (m/s)
Distance this
interval
Total distance
13.00
13.00
13
13
13.00
13
26
13.00
13.00
Motion
Section 2
Total
Distance
(m)
Time (s)
Motion
Section 2
Velocity
(m/s)
Time (s)
Motion
Section 2
Answer the following
1. In past lessons we learned that on a distance
vs time graph the slope is the velocity.
Compare your graphs and write in the side
section whether you think you have proved or
disproved this and why.
2. Is the velocity changing on your graph?
3. So is there any acceleration?
Motion
Section 2
Graphing data about acceleration
Time (s)
Velocity (m/s)
Distance this
interval
Total distance
0.0
3.00
6.00
9.00
12.00
Motion
Section 2
Total
Distance
(m)
Time (s)
Motion
Section 2
Velocity
(m/s)
Time (s)
Motion
Section 2
Answer the following
1.
2.
3.
4.
In your distance vs time graph what is occuring to the
slope of the line as time passes?
What does this tell you about the velocity of the bike
since slope = velocity?
Does your graph of the velocity vs time back up your
answer to #2?
Is the bike accelerating, decelerating, or staying at a
constant velocity?
Motion
Section 2
Graphing Accelerated Motion
How can a graph be used to find acceleration?
The slope of a straight line on a speed vs. time
graph is equal to the acceleration.
Motion
Section 2
Graphing Accelerated Motion, continued
Acceleration can also be
seen on a distance vs. time
graph.
The distance vs. time
graph is not a straight line
when the velocity is not
constant.
This curved line indicates
that the object is under
acceleration.
Motion
Section 2
Graphing Skills
Graphing Acceleration
A bus traveling on a straight road at 20 m/s uniformly
slows to a stop over 20 s. The bus remains stopped
for 20 s, then accelerates at a rate of 1.5 m/s2 for
10 s, and then continues at a constant speed. Graph
speed vs. time for 60 s. What is the buss final
speed?
1. Determine the x-axis and the y-axis of your graph.
The x-axis will indicate time, t, measured in s. The y-axis will
indicate speed, v, measured in m/s.
Motion
Section 2
Graphing Skills, continued
2. Starting from the origin, graph each section of the motion.
A. Draw and connect the first
two points:
t = 0 s, v = 20 m/s
t = 20 s, v = 0 m/s
B. Draw a horizontal line from t =
20 s to t = 40 s at v = 0 m/s.
C. Starting at t = 40 s and v = 0
m/s, draw a line with a slope
of 1.5 m/s2.
D. Draw a horizontal line from t =
50 s to t = 60 s at v = 15 m/s.
Motion
Section 2
Graphing Skills, continued
3. Read the graph to find the final speed.
At time, t = 60 s, the
speed is 15 m/s.
Motion
Crashes and safety
A common saying is:
Its not the crash that
hurts you, its the
sudden stop at the
end
Explain, relating to
acceleration, how
safety devices help
save injuries.
Give three examples
of car safety devices
and how they work in
terms of acceleration.
Section 2
Motion
Section 2
Egg Drop Safety
Today you will begin the planning of your egg safety
device. You need to complete the following by the end
of the day:
Get into your groups
Read the instructions and rules
Look over the materials you will be provided
Brainstorm for the best safety designs
Create detailed and annotated schematics of
your design (every aspect of it!)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Week 20Dokument1 SeiteWeek 20api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Week 14Dokument1 SeiteWeek 14api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Week 27Dokument1 SeiteWeek 27api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Week 26Dokument1 SeiteWeek 26api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Week 13Dokument1 SeiteWeek 13api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Week 17Dokument1 SeiteWeek 17api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Week 19Dokument1 SeiteWeek 19api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Week 19Dokument1 SeiteWeek 19api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Week 36Dokument1 SeiteWeek 36api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 16Dokument1 SeiteWeek 16api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Week 17Dokument1 SeiteWeek 17api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 30Dokument1 SeiteWeek 30api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Week 19Dokument1 SeiteWeek 19api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Week 36Dokument1 SeiteWeek 36api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Week 36Dokument1 SeiteWeek 36api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Week 16Dokument1 SeiteWeek 16api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Week 14Dokument1 SeiteWeek 14api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Week 15Dokument1 SeiteWeek 15api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12Dokument1 SeiteWeek 12api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 13Dokument1 SeiteWeek 13api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 14Dokument1 SeiteWeek 14api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 11Dokument1 SeiteWeek 11api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 30Dokument1 SeiteWeek 30api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Week 11Dokument1 SeiteWeek 11api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12Dokument1 SeiteWeek 12api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 13Dokument1 SeiteWeek 13api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 30Dokument1 SeiteWeek 30api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10Dokument1 SeiteWeek 10api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10Dokument1 SeiteWeek 10api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 30Dokument1 SeiteWeek 30api-261372832Noch keine Bewertungen
- hw7 ch8Dokument8 Seitenhw7 ch8faisalphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Lecture Problems On DynamicsDokument37 SeitenLecture Problems On DynamicsCha Castillo100% (1)
- Safety Gear TestingDokument17 SeitenSafety Gear TestingFERNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quickcheck Questions: Motion in One DimensionDokument57 SeitenQuickcheck Questions: Motion in One DimensionArda ÇekmeceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emf Type 2 Part 2 of 2 EngDokument19 SeitenEmf Type 2 Part 2 of 2 EngRavi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS ART INTEGRATION PROJECT ON ELECTROSTATICSDokument16 SeitenPHYSICS ART INTEGRATION PROJECT ON ELECTROSTATICSCHIEF VISHAAL 45Noch keine Bewertungen
- XI-Physics ASSIGNMENTS - (Motion in One Dimension)Dokument5 SeitenXI-Physics ASSIGNMENTS - (Motion in One Dimension)RecoDex GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- element of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringDokument10 Seitenelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringelement of electrical engineeeringrathorsumit2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Division of Bohol Science 8 Quarter 1 - Week 3 (Day 1) : S8FE-Ia-16)Dokument4 SeitenDivision of Bohol Science 8 Quarter 1 - Week 3 (Day 1) : S8FE-Ia-16)Johndion A. RulomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion and UAMDokument42 SeitenProjectile Motion and UAMChelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Physics: Mechanical Waves (3 Hours)Dokument11 SeitenPhysics: Mechanical Waves (3 Hours)Nur Farhana SuhaimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Institute: Type (I) : Very Short Answer Type Questions: (01 Mark Each) 1Dokument63 SeitenOne Institute: Type (I) : Very Short Answer Type Questions: (01 Mark Each) 1saghir merajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics - Chapter 18 (Beer7)Dokument31 SeitenDynamics - Chapter 18 (Beer7)api-3709496100% (1)
- Exam 1Dokument6 SeitenExam 1api-375738241Noch keine Bewertungen
- SOAL QUARTER FINAL AND SEMIFINAL PHYSICS PROBLEMSDokument6 SeitenSOAL QUARTER FINAL AND SEMIFINAL PHYSICS PROBLEMSFebryn NgkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Example ProblemsDokument38 SeitenDynamics Example ProblemsMatt JohansenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSICS FOR HEALTH SCIENCE ActivitiesDokument10 SeitenPHYSICS FOR HEALTH SCIENCE ActivitiesMyrel Joy Fabiaña LucdayNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Tech. Degree Examination Civil, EEE, ME & AE: (April-18) (EME-102)Dokument5 SeitenB.Tech. Degree Examination Civil, EEE, ME & AE: (April-18) (EME-102)Maheshpoetry teluguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science1 PDFDokument20 SeitenScience1 PDFFact HubzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision: DC circuits, electric charge, rotational motion, and wavesDokument1 SeiteRevision: DC circuits, electric charge, rotational motion, and wavesanuelisajoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Phy: Chapter Motion Sample QuestionsDokument9 SeitenClass 9 Phy: Chapter Motion Sample QuestionsXâlmañ KháñNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYSIC3Dokument47 SeitenPHYSIC3Sofië0% (1)
- Angular Momentum - Physics F111 BITS PilaniDokument66 SeitenAngular Momentum - Physics F111 BITS PilaniHarsh Hirani100% (1)
- Tutorial 8Dokument5 SeitenTutorial 8Aina AqilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory Project: Self Inductance of A CoilDokument10 SeitenPhysics Investigatory Project: Self Inductance of A CoildevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics Force and Acceleration Part 1Dokument13 SeitenKinetics Force and Acceleration Part 1Ian De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEWTON'S LAWS TESTDokument3 SeitenNEWTON'S LAWS TESTVarun SethNoch keine Bewertungen
- UEMX 1943 Dynamics Tutorial 1 Kinematics and Newton's LawsDokument5 SeitenUEMX 1943 Dynamics Tutorial 1 Kinematics and Newton's LawsChee HoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FreefallDokument9 SeitenFreefallSer RhoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton'S Laws of MotionDokument10 SeitenNewton'S Laws of MotionsaylalisaNoch keine Bewertungen