Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
U21919961 Investigation 7
Hochgeladen von
api-267804992Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
U21919961 Investigation 7
Hochgeladen von
api-267804992Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Erosion
What is soil erosion?
Soil erosion is the removal of material from one place and its transport towards another by the
action of wind or water
What causes soil erosion?
Increasing populations (Pimentel)
Loss of soil organic matter (Pimentel)
Overstocking and overgrazing
Inappropriate farming techniques
Lack of crop rotation
While a doubling of the population and a
moderate increase of livestock may still be
sustainable with other efforts performed,
unlimited growth will lead to an excessive
land resource overuse and an almost
irreversible ecological disaster within a
very few decades (Pimentel)
Population rates in regions where erosion is a serious problem, are greater than the
national average
Why is it a concern?
As the worlds population continues to grow, the amount of food production could be
under that of the population as increased soil erosion has slowed food production
(Brown)
Politics
Soil Conservation and Domestic Act of 1936:
President FDR signed legislation that allowed the U.S Government to pay farmers to cut
down on production to help conserve soil and help prevent erosion (Soil Conservation)
Rewarded farmers who planted crops to support the soil, rather than crops that were for
commercial use that exhausted the soil (Soil Conservation)
o This was difficult for many farmers to agree to as it was during the Great
Depression (Soil Conservation)
United States Department of Agriculture:
Soil division
o Responsible for formulating policy, collaborating with others at the international
and national level to carry out National Cooperative Soil
Survey (NCSS) activities (Natural Resources)
o The U.S Soil Conservation Service says that 158 million acres of the 413 million
acres need additional attention that what they are being given now
17 million of those acres are eroding so quickly that the Soil Conservation
Service recommends that it be shifted from continuous row cropping and
converted to woodland, grassland, or long term rotation (Brown).
o There are 141 million acres of cropland that are losing over five tons of soil a year
(Brown)
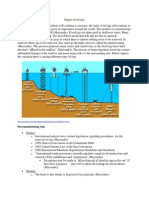
What is beach erosion?
Beach erosion is when the oceans waves and currents remove sand from a beach
(Coastal Change)
o This decreases the size of the beach
The sand is then carried out into the ocean, creating sandbars (Coastal Change)
Beach
serious
coastal
tourism is
Storms also
erosion is a
problem in
areas where
heavily relied on.
impact the rate
and extent of beach erosion.
Local Impacts
Beach renourishment projects are a costly and timely process, but many argue it is not a question
of if it should be done, but when. Here in Sarasota, we see this issue regarding Anna Maria
Island. In order to keep the beaches healthy and able to support the thousands of tourists who
visit the area for the beaches annually, the beaches must be built up.
Anna Maria renourishment project
$12 million project (Q&A)
Will involve pumping one million cubic yards of sand from offshore (Q&A)
The project is funded from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, FEMA (Federal
Emergency Management Agency), state of Florida and Manatee County (Q&A)
This adds, depending on the exact location, up to 200 feet of beach area and sand
(Q&A)
These beaches that are being renourished have a life of 6 to 8 years (Q&A)
Charlie Hunsicker, director of Manatee County's Parks and Natural Resources Department stated
that, Anna Maria Island is nourished on a periodic basis to replace sand lost to coastal erosion
for storm protection, sea turtle nesting and shorebird habitat and recreation (Q&A)
He also stated that, the Manatee County Shore Protection Project is a 50-year federally
authorized project that requires maintenance by periodic renourishment events every 10 years.
The most recent project was a storm damage repair project constructed in 2006 to re-establish the
10-year cycle after the impacts from the 2004-05 tropical storm season. Prior to that, the beach
was nourished in 2002 and 1992, representing the typical renourishment interval (Q&A)
Works Cited
Brown, L.R. "World Population Growth, Soil Erosion, and Food Security." World Population
Growth, Soil Erosion, and Food Security. | POPLINE.org. N.p., 27 Nov. 1981. Web. 18
Oct. 2014. <http://www.popline.org/node/395202>.
"Coastal Change Hazards: Hurricanes and Extreme Storms." Beach Erosion -. N.p., n.d. Web. 20
Oct. 2014. <http://coastal.er.usgs.gov/hurricanes/coastal-change/beach-erosion.php>.
"Natural Resources Conservation Service." Soil Science Division. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Oct. 2014.
<http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/about/?cid=nrcs142p2_054335>.
Pimentel, David. "Soil Erosion: A Threat to Mankind." JSTOR 75.4 (1994): 1193. Web. 18 Oct.
2014. <http://www.jstor.org.ezproxy.lib.usf.edu/stable/1939447>.
"Soil Conservation in the New Deal Congress | US House of Representatives: History, Art &
Archives." Soil Conservation in the New Deal Congress. N.p., n.d. Web. 18 Oct. 2014.
http://history.house.gov/HistoricalHighlight/Detail/36550
"Q&A: Anna Maria Island Beach Renourishment." HeraldTribune.com. N.p., 8 Jan. 2014. Web.
21 Oct. 2014. <http://www.heraldtribune.com/article/20140108/ARTICLE/140109671>.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Water, Culture, and Power: Local Struggles In A Global ContextVon EverandWater, Culture, and Power: Local Struggles In A Global ContextNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Value of Coastal WetlandsDokument14 SeitenThe Value of Coastal WetlandsCayley CamarilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kong Lee - Human Impact On Beaches PDFDokument8 SeitenKong Lee - Human Impact On Beaches PDFNovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation and The National Parks Service: Anna 1Dokument11 SeitenConservation and The National Parks Service: Anna 1api-296746104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Resource DepletionDokument6 SeitenCauses of Resource DepletionGreenplanet CybercafeNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper FinalDokument10 SeitenWhite Paper Finalapi-609068180Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction 2Dokument12 SeitenIntroduction 2Jean Denis TavoueNoch keine Bewertungen
- IJRANSS - The Impact of Soil Erosion On Real Estate (Reviewed)Dokument6 SeitenIJRANSS - The Impact of Soil Erosion On Real Estate (Reviewed)Impact JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of An Agricultural Engineer in PDFDokument5 SeitenThe Role of An Agricultural Engineer in PDFTrisha Veronica AvengozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coastal Wetlands RestorationDokument21 SeitenCoastal Wetlands RestorationCarolina SchonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Clearing Final EssayDokument6 SeitenLand Clearing Final EssayChristie Lee WebbNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSDC Biorock Aff-2Dokument40 SeitenTSDC Biorock Aff-2Jose CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- SD Water Resources PDFDokument11 SeitenSD Water Resources PDFjayameenakshi mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of The Effects of Keta Sea Defence Project On The Livelihoods of The People in The Keta Municipality, Volta Region, GhanaDokument13 SeitenAssessment of The Effects of Keta Sea Defence Project On The Livelihoods of The People in The Keta Municipality, Volta Region, GhanaPremier PublishersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses of English in 2014Dokument11 SeitenTenses of English in 2014Aye XaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Losen K Final Nov 9Dokument9 SeitenLosen K Final Nov 9api-300198870Noch keine Bewertungen
- FinaldraftDokument5 SeitenFinaldraftapi-340244088Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coral Reef Destruction Because of Careless TourismDokument14 SeitenCoral Reef Destruction Because of Careless TourismKimberly CalimlimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter OneDokument8 SeitenChapter OneGreg EnyinnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working OutlineDokument7 SeitenWorking Outlineapi-383767685Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 Question Paper: Submitted By: Priyanka Roy B.SC Interior Design Guwahati College of Architecture and PlanningDokument21 Seiten2018 Question Paper: Submitted By: Priyanka Roy B.SC Interior Design Guwahati College of Architecture and PlanningSaurabh DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity in The Great Dismal Swamp-1Dokument3 SeitenBiodiversity in The Great Dismal Swamp-1jahiem.tidwellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Dams: Human and Environmental Benefits and CostsDokument28 SeitenLarge Dams: Human and Environmental Benefits and CostsKai Pascal AlibassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IssuebrieffinalDokument12 SeitenIssuebrieffinalapi-607306364Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coastal Erosion: Why in News?Dokument3 SeitenCoastal Erosion: Why in News?shraddhatiktok12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting The Impact of Sea-Level Rise On Caribbean Sea Turtle Nesting HabitatDokument10 SeitenPredicting The Impact of Sea-Level Rise On Caribbean Sea Turtle Nesting HabitatkhasanatunnajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Sea Mining in Cook IslandsDokument4 SeitenDeep Sea Mining in Cook IslandsAntoinette ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Fix Broken ChairDokument1 SeiteHow To Fix Broken ChairGuinerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ServiceresearchDokument3 SeitenServiceresearchapi-339981082Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coral ReefsDokument2 SeitenCoral Reefsafly YNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTP Assignment EssayDokument12 SeitenCTP Assignment EssayPrachi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading and SummarizingDokument5 SeitenReading and SummarizingBojana BorojevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- VA Report For The Municipality of San JoseDokument35 SeitenVA Report For The Municipality of San JoseRolly Balagon CaballeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Analysis of The Effects of Beach Replenishment On Intertidal SpeciesDokument9 SeitenAn Analysis of The Effects of Beach Replenishment On Intertidal Speciesapi-435915678Noch keine Bewertungen
- Article 77 - Coastline ErosionDokument5 SeitenArticle 77 - Coastline ErosionAniruddha SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Danielle Dyson Marine Conservation Ecology Case Study Paper 4 December 2020Dokument12 SeitenDanielle Dyson Marine Conservation Ecology Case Study Paper 4 December 2020api-456665119Noch keine Bewertungen
- SVT en Anglais 2ndeDokument4 SeitenSVT en Anglais 2ndeAndreea BerindeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Resources Agricultural and Environmental IssDokument11 SeitenWater Resources Agricultural and Environmental IssAlagos Emyrose Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper Soil ErosionDokument5 SeitenResearch Paper Soil Erosionzijkchbkf100% (3)
- Global Perspect6ive Individual ReportDokument11 SeitenGlobal Perspect6ive Individual Reportaiza abbassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringDokument47 SeitenIntroduction To Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringYashraj Singh BhadoriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Reclamation ArticleDokument2 SeitenLand Reclamation ArticleEminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joseph Sherick Case StudyDokument16 SeitenJoseph Sherick Case Studyapi-711051659Noch keine Bewertungen
- 14 - Rocky Intertidal Shores Prognosis For The Future Pp. 209-225Dokument18 Seiten14 - Rocky Intertidal Shores Prognosis For The Future Pp. 209-225Soma GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topics Question:: Number of Words: 1173Dokument5 SeitenTopics Question:: Number of Words: 1173Neha Lal100% (1)
- Seagrasses-A Unique Group of Flowering Plants That: Seagrasses As Ecological Service Providers and Biological SentinelsDokument5 SeitenSeagrasses-A Unique Group of Flowering Plants That: Seagrasses As Ecological Service Providers and Biological SentinelsNanggala AryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth's Natural Resources and Human ImpactsDokument22 SeitenEarth's Natural Resources and Human ImpactsanimaksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wilf Dustin Loi FinalDokument10 SeitenWilf Dustin Loi Finalapi-700336808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Watersheds and Wetlands Week7Dokument4 SeitenWatersheds and Wetlands Week7Thalia SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Philippine Frestwater Resources. Strategies For Sustainable Development Rafael D. Guerrero III - Agricultural Sciences 1997Dokument6 Seiten3 - Philippine Frestwater Resources. Strategies For Sustainable Development Rafael D. Guerrero III - Agricultural Sciences 1997Gabrielle PingolNoch keine Bewertungen
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Above PictureDokument16 Seiten© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Above PictureAlisha ChopraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background StudyDokument3 SeitenBackground StudyABM EXODUS SET A MITZI CLOUD CANSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Islands White Paper - Copy 2Dokument7 SeitenIslands White Paper - Copy 2api-711033918Noch keine Bewertungen
- INTRODUCTIONDokument9 SeitenINTRODUCTIONAlusine TommyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection From Coastal ErosionDokument30 SeitenProtection From Coastal ErosionArunrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection From Coastal ErosionDokument30 SeitenProtection From Coastal ErosionHaryo ArmonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap9 Marine PollutionDokument30 SeitenChap9 Marine PollutionDwiMariaUlfahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaterResources AgriculturalDokument10 SeitenWaterResources AgriculturalCông AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- U21919961 Investigation 10Dokument4 SeitenU21919961 Investigation 10api-267804992Noch keine Bewertungen
- U21919961 Investigation 9Dokument4 SeitenU21919961 Investigation 9api-267804992Noch keine Bewertungen
- U21919961 Investigation 5Dokument6 SeitenU21919961 Investigation 5api-267804992Noch keine Bewertungen
- U21919961 Investigation 2Dokument5 SeitenU21919961 Investigation 2api-267804992Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Forestry ProjectDokument23 SeitenAnalog Forestry Projectquick1411Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atlantic Canada Hunter Education Part BDokument100 SeitenAtlantic Canada Hunter Education Part BRodrigo Magaldi100% (1)
- B.sc. Hons. ZoologyDokument110 SeitenB.sc. Hons. ZoologyHarsh Dalal0% (1)
- Fields of Physical GeographyDokument5 SeitenFields of Physical GeographyTrisha Ace Betita ElisesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Infectious Diseases of PlantsDokument11 SeitenEmerging Infectious Diseases of PlantsNichita Alina GabrielaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystems 190902121239Dokument47 SeitenEcosystems 190902121239Haries SukandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub-Branches: Physical Geography (Also Known As Physiography) Is One of The Two MajorDokument3 SeitenSub-Branches: Physical Geography (Also Known As Physiography) Is One of The Two MajorShamoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tomato Seedlings WebDokument20 SeitenTomato Seedlings WebBesim SalkićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cretaceous Oceanography and ForaminiferaDokument29 SeitenCretaceous Oceanography and ForaminiferadzzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- കസ്തൂരി രംഗന് സമിതി സമര്പ്പിച്ച റിപ്പോര്ട്ട്- ഒന്നാം ഭാഗംDokument407 Seitenകസ്തൂരി രംഗന് സമിതി സമര്പ്പിച്ച റിപ്പോര്ട്ട്- ഒന്നാം ഭാഗംIndiavision LiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminarski Rad CajkoDokument8 SeitenSeminarski Rad CajkoZarko StankovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco KidsDokument11 SeitenEco KidsJosphine Mundava MaringaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Modelling To Predict Plant Growth in Terms Light Exposure and Leaf AreaDokument3 SeitenMathematical Modelling To Predict Plant Growth in Terms Light Exposure and Leaf AreaPremier PublishersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant EcologyDokument22 SeitenPlant EcologyAtika ZulfiqarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter, Energy and Life in EcosystemDokument10 SeitenMatter, Energy and Life in EcosystemLouis Fetilo FabunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco SystemDokument32 SeitenEco SystemIravati RayNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Cycle of MatterDokument28 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Cycle of MatterRamil NacarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENVR E-101: Sustainability & Environmental Management: InstructorDokument27 SeitenENVR E-101: Sustainability & Environmental Management: InstructorBrian MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDokument12 Seiten09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDhiraj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of SpeciesDokument35 SeitenDefinition of Speciesmastermind20130% (1)
- Payton The MetropolisDokument6 SeitenPayton The MetropolisDenis GachevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystems of The OceanDokument17 SeitenEcosystems of The OceanUyul EverywhereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Study Guide 21 PDFDokument1 SeiteAnswer Key Study Guide 21 PDF24 Madyson BourneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Laws: Presented by Shashikant S NehulDokument10 SeitenEnvironmental Laws: Presented by Shashikant S NehulDevank RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seeds DisperselDokument9 SeitenSeeds DispersellovleshrubyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS Agriculture and ForestryDokument14 SeitenCSS Agriculture and ForestryM Faadi MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ackerman 1963 Where Is A Research FrontierDokument13 SeitenAckerman 1963 Where Is A Research FrontierMatt TenneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystem - Meaning and StructureDokument11 SeitenEcosystem - Meaning and StructureParveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenLab Reportapi-329606080Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies PDFDokument6 SeitenMultidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies PDFanu100% (1)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessVon EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldVon EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (597)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesVon EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionVon EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (812)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseVon EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (69)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogVon EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsVon EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (65)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersVon EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorVon EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (137)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutVon EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (142)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildVon EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (44)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterVon EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsVon EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (13)
- The Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Von EverandThe Best American Science And Nature Writing 2021Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignVon EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeVon EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (19)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (35)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsVon EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (223)