Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Storage HWK
Hochgeladen von
api-266837147Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Storage HWK
Hochgeladen von
api-266837147Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Storage
Devices
In this section, fill in the information below about each method of storage. Include relevant diagrams under each
heading. Delete this red text when youre done.
Magnetic Storage
Definition/Characteristics: Magnetic storage media and devices store data in the form of small magnetic dots.
How it works: These store data on Iron Oxide which is known to us as rust. The dots are manipulated using magnetic
fields which are created electromagnets.
Examples of Devices/Media: Examples of devices are hard disk drives, portable/external hard disk drives and
magnetic tapes.
Solid State
Definition/Characteristics: Solid state means that there are no moving parts on this storage therefore there is no
tape or no spinning disks.
How it works: It is a non volatile storage and this means its rewritable.
Examples of Devices/Media: Solid state drives, memory cards, USB sticks
Optical
Definition/Characteristics: Information is stored on reflective discs
How it works: The storage is kept on a disk that is bumps or flat and then it is read using a laser.
Examples of Devices/Media: CD, DVD or Blu ray
Advantages and Disadvantages
Fill in the table below. Use the internet to help you. Delete this red text when youre done.
Type of Storage
Hard Disk Drive
Typical Size
Uses
Advantages
Disadvantages
1-4 tb
It stores data by
using rapidly
rotating disks.
It stores its data
even when the
computer is
turned off.
Relatively cheap
and quick.
Moving parts
could wear out or
damage and loose
data. Regular
crashes can
damage the disks.
2 tb
They do not need
a power source
and very large
amounts of data
can be stored.
It is portable.
It can break and
because it
portable it is
easily damaged.
6-8 TB
Used for server
backups.
It holds extremely
large amounts of
data.
It is slow to read
and write data.
Portable HDD
Magnetic Tape
Reliable.
32- 64 GB
Memory Stick
32- 64 GB
Flash memory
card
Usually used for
storing personal
files and
transferring them.
Large amounts of
storage in a very
small size.
Limited life
spams.
Usually used to
store photo
graphs or videos
on a camera.
Large amounts of
storage space.
Easily lost or
damaged.
Easily lost or left
behind.
Storage Methods
Youve looked a lot at storage methods and what storage devices are used for. But you havent looked at how the
data is actually stored and accessed on a device.
Answer the following questions:
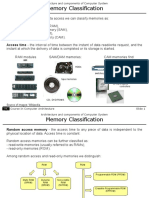
1. What is SEQUENTIAL storage/Access? Whereas Random access memory can be accessed randomly this data
is read in a data sequence.
2. Give one storage device/media that uses the sequential method of file storage. Hard disks and magnetic
tapes.
3. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of sequential method of file storage. One advantage of this
method is it is done systematically and in an order but one disadvantage it can only be used for permanent
storage whereas RAM is temporary.
4. What is Random Access? The process of accessing information directly rather than a fixed sequence.
5. Give one storage device/media that uses the Random Access method of storage, A CD
6. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of the Random Access method of storage One advantage of
Random Access is that it is very fast but a disadvantage is that it is volatile.
Backup
What is the definition of Backup?
What is the difference between Backup and Backing Storage?
Give two reasons why backups should be used/made
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Spreadsheets Lesson 1Dokument6 SeitenSpreadsheets Lesson 1api-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Flat File and Relational DatabasesDokument1 SeiteFlat File and Relational Databasesapi-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Database Key Words and The Primary KeyDokument2 SeitenDatabase Key Words and The Primary Keyapi-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Questions and Answers AssessmentDokument2 SeitenQuestions and Answers Assessmentapi-266658213Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- What Are Data TypesDokument7 SeitenWhat Are Data Typesapi-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Network Scenario SheetDokument3 SeitenNetwork Scenario Sheetapi-266862390Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Section 2 and 3 Merged FeedbackDokument2 SeitenSection 2 and 3 Merged Feedbackapi-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Input DevicesDokument4 SeitenInput Devicesapi-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Feed Back Section 1Dokument2 SeitenFeed Back Section 1api-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- Input Devices Exam QuestionsDokument4 SeitenInput Devices Exam Questionsapi-266837147Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Yr 10 - Recording AssignmentDokument3 SeitenYr 10 - Recording Assignmentapi-271072076Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Ism Practical FileDokument62 SeitenIsm Practical FilePriya AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Explosives Rules, 2010 PDFDokument203 SeitenExplosives Rules, 2010 PDFAhmed MujtabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- HP 1040 (E) DVD Drive Manual - EnglishDokument2 SeitenHP 1040 (E) DVD Drive Manual - EnglishMaster ChiefNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- 3par Customer Training Inform (T and F Class) GOOD DocumentDokument30 Seiten3par Customer Training Inform (T and F Class) GOOD DocumentAmrit Chhetri67% (3)
- SNIA Enterprise TCO Calculator Rev 1 4Dokument5 SeitenSNIA Enterprise TCO Calculator Rev 1 4Wilson MosqueraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Backup SOPDokument6 SeitenBackup SOPaossereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 PDFDokument14 SeitenLecture 6 PDFtestscribd9898Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- PameDokument2 SeitenPamePaul Arvin Manalaysay EndrinalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multitrack HistoryDokument5 SeitenMultitrack HistoryMatt GoochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disk Drive TechonologyDokument11 SeitenDisk Drive TechonologyakdenizerdemNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan: Direction: You Are To Choose The Word or Phrase The Best Completes The SentenceDokument4 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kejuruan: Direction: You Are To Choose The Word or Phrase The Best Completes The SentenceMuhammad MuhsoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PendriveDokument6 SeitenPendriveSubodh SonawaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BDP 2900Dokument18 SeitenBDP 2900Andreskoira100% (1)
- Magnetic Surface Storage DevicesDokument8 SeitenMagnetic Surface Storage DevicesvidyawarrierNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHILIPS-Service Information Dvp3454kDokument5 SeitenPHILIPS-Service Information Dvp3454kJose Domingo Maltez VallecilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory Notes DEMG (U1Ch1)Dokument5 SeitenTheory Notes DEMG (U1Ch1)Pravin KarleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Report On HVD by Gaurav AnandDokument33 SeitenSeminar Report On HVD by Gaurav AnandGaurav Nigam50% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Raid Controller Via Vt6421Dokument42 SeitenRaid Controller Via Vt6421Anonymous dhJ30QINoch keine Bewertungen
- RAID Spindle CalculatorDokument2 SeitenRAID Spindle CalculatorrahulhclNoch keine Bewertungen
- BD J4500R XU Web ENG 1027Dokument21 SeitenBD J4500R XU Web ENG 1027fuilkjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Disk FilesDokument17 SeitenHard Disk Filesivopaz85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Construction and Operation of The Hard DiskDokument7 SeitenConstruction and Operation of The Hard DiskSupreet NarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- BDP 3110Dokument2 SeitenBDP 3110drastir_777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lite-On Ssds Move at The Speed of YouDokument2 SeitenLite-On Ssds Move at The Speed of Yourv_diplomatNoch keine Bewertungen
- A USB Flash Drive Consists of Flash Memory Data Storage Device Integrated With A USBDokument3 SeitenA USB Flash Drive Consists of Flash Memory Data Storage Device Integrated With A USBMalakhatusAt-TohirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11: Storage and File Structure Classification of Physical Storage MediaDokument7 SeitenChapter 11: Storage and File Structure Classification of Physical Storage MediaHarrison MmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mix Magazine - History of DolbyDokument2 SeitenMix Magazine - History of DolbyMartinAggroweNoch keine Bewertungen
- TR-4070 NetApp Flash Pool Design and Implementation GuideDokument23 SeitenTR-4070 NetApp Flash Pool Design and Implementation GuideShyamalendu BiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Legs Akimbo Records PDFDokument3 SeitenLegs Akimbo Records PDFRoentgineNoch keine Bewertungen