Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
English River Watershed Snapshot Report
Hochgeladen von
api-228244514Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
English River Watershed Snapshot Report
Hochgeladen von
api-228244514Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ENGLISH RIVER
WATERSHED:
WATER QUALITY
SNAPSHOTS
2014
11/1/2014
Summary of Findings
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
English River Watershed: Water
Quality Snapshots 2014
As part of the English River Watershed Management Authoritys ongoing effort to develop a comprehensive
watershed management plan for the 627 square mile English River watershed the Iowa Soybean Association
was hired as a subcontractor to support the planning effort. One of the tasks charged to the Iowa Soybean
Association was to conduct three water quality snapshots at approximately twenty locations in the English
River Watershed. The Iowa Soybean Association conducted these three water quality snapshots on April 28th,
July 17th and October 21st, 2014. This report summarizes the monitoring locations and reports the results from
these three snapshots. All samples were collected by Iowa Soybean Association staff and were analyzed in
the Iowa Soybean Associations accredited water lab in Ankeny, Iowa.
Site Selection
The Iowa Soybean Association used maps of the English River watershed to select the twenty monitoring
locations. The locations are all located at bridge crossings and were selected as close as possible to the
outlet of the twenty subwatersheds (HUC-12) which are
Table 1. Site Locations.
contained in the larger English River watershed. A listing of
the site locations and UTM coordinates is provided in Table
Site Name
UTM X
UTM Y
1. A map of the site locations is provided at the end of this
ERW1
621760.7
4593097.0
report. It should be noted that site ERW1 is the location of the
ERW2
609271.2
4590957.7
Iowa Department of Natural Resources single ambient
ERW3
609526.0
4591535.3
monitoring location in the watershed. Data from this location
ERW4
602897.3
4594610.7
can be downloaded from the SRORET Database
ERW5
601802.1
4592576.0
(https://programs.iowadnr.gov/iastoret/), the station ID is
ERW6
597741.6
4593411.9
10920001. This location has monthly monitoring results dating
ERW7
588167.9
4594131.4
back to 1998.
ERW8
587940.5
4596736.9
ERW9
579880.6
4600696.1
Results
ERW10
576383.5
4598444.8
Samples collected by the Iowa Soybean Association were
ERW11
576353.1
4598011.9
analyzed for chloride, nitrite, nitrate, phosphates, and sulfates.
ERW12
571656.7
4590985.0
The April 28th sample also was analyzed for turbidity. Since
ERW13
572749.9
4606617.2
the April 28th samples was the only runoff/event sample this
ERW14
570648.9
4606018.7
was the only set of samples analyzed for turbidity. Samples
ERW15
561127.1
4608197.1
were not collected from ERW17 and ERW18 on April 28th due
ERW16
560150.4
4604047.0
to a severe thunderstorm warning for the area of sample sites.
ERW17
553053.9
4593967.3
ERW18
552208.2
4593649.7
ERW19
555900.9
4609806.8
ERW20
545386.1
4610691.1
Page 1
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Chloride
From IOWATER Chemical Assessment guidance document:
Chloride is a chemical found in salts, which tend to dissolve easily in water. In natural waters, elevated levels of chloride may
indicate inputs of human or animal waste, or inputs from fertilizers, many of which contain salts. During winter months, elevated
chloride levels in streams may occur as a result of road salt runoff to nearby streams. Chloride can be used as a "conservative"
measure of water contamination since other natural processes, such as breakdown by bacteria, do not affect it. The amount of
chloride dissolved in water is expressed in milligrams per liter of water (mg/L). Average chloride concentrations for Iowa streams
range from 16 to 29 mg/L.
Chloride Cl Results
45.0
40.0
35.0
mg/L
30.0
25.0
4/28/2014
20.0
7/17/2014
15.0
10/21/2014
10.0
5.0
0.0
Sample Site
4/28/2014
7/17/2014
10/21/2014
erw1
erw2
erw3
erw4
erw5
erw6
25.7
24.5
26.3
26.8
29.2
23.8
15.8
23.6
16.6
18.9
26.4
14.9
17.6
26.3
19.2
22.4
27.3
17.2
erw11
erw12
erw13
erw14
erw15
erw16
erw7
erw8
erw9
erw10
23.8
19.6
20.5
19.7
17.7
14.7
14.3
15.8
17.6
16.6
16.3
16.6
erw17
erw18
erw19
erw20
Page 2
4/28/2014
7/17/2014
10/21/2014
19.2
18.5
11.2
20.6
26.3
20.4
15.0
16.2
9.52
14.7
15.6
13.4
16.3
16.5
11.4
16.5
17.2
14.6
36.8
39.6
15.3
15.5
16.4
17.8
15.6
16.1
18.8
19.9
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Nitrite & Nitrate
From IOWATER Chemical Assessment guidance document:
Nitrate and nitrite are two forms of nitrogen. Nitrate is very easily dissolved in water and is more common in streams. Sources of
nitrate include soil organic matter, animal wastes, decomposing plants, sewage, and fertilizers. Because nitrate is very soluble in
water it can move readily into streams. Nitrite is another form of nitrogen that is rare because it is quickly converted to nitrate or
returned back to the atmosphere as nitrogen gas. Due to its instability, detectable levels of nitrite in streams and lakes are
uncommon. Detectable nitrite levels in streams and lakes may indicate a relatively fresh source of ammonia. The amount of nitrate
or nitrite dissolved in water is reported as nitrate-N (nitrate expressed as the element nitrogen) or nitrite-N in milligrams per liter
of water (mg/L). Iowa's drinking water standard for nitrate is 10 mg/L as nitrate-N. The concentration of nitrate-N in water may
vary greatly depending on season and rainfall, fertilizer application rates, tillage methods, land use practices, soil types, and
drainage systems. Consistently high nitrate readings (over 10 mg/L) may be cause for concern and warrant further investigation.
Nitrite NO2-N Results
0.60
0.50
mg/L
0.40
0.30
4/28/2014
7/17/2014
0.20
10/21/2014
Detection Limit
0.10
0.00
Sample Site
erw1
erw2
erw3
erw4
erw5
4/28/2014
0.38
0.47
0.41
0.39
0.45
7/17/2014
0.18
0.23
0.18
0.21
0.22
10/21/2014
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
erw11
erw12
erw13
erw14
erw15
erw6
erw7
erw8
erw9
erw10
0.34
0.21
0.30
0.35
0.20
0.16
0.20
<0.12
<0.12
0.17
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
erw16
erw17
erw18
erw19
erw20
4/28/2014
0.24
0.37
0.09
0.29
0.22
7/17/2014
0.19
0.18
0.17
<0.12
0.16
10/21/2014
<0.12
0.19
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
0.16
0.18
0.20
0.20
0.16
0.18
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
<0.12
0.47
0.50
Page 3
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Nitrate NO3-N Results
18.00
16.00
14.00
mg/L
12.00
10.00
4/28/2014
8.00
7/17/2014
6.00
10/21/2014
4.00
2.00
0.00
Sample Site
erw1
erw2
erw3
erw4
4/28/2014
5.39
16.4
10.7
9.43
7/17/2014
7.45
13.9
7.87
14.3
10/21/2014
7.42
15.7
8.57
12.4
erw11
erw12
erw13
erw14
erw5
erw6
erw7
erw8
erw9
erw10
6.96
5.76
7.26
6.57
6.22
8.04
9.91
7.45
9.19
7.29
7.33
7.65
11.7
7.34
7.98
7.05
7.12
6.15
erw15
erw16
erw17
erw18
erw19
erw20
Page 4
4/28/2014
10.7
10.4
3.66
6.91
7/17/2014
7.68
10.1
4.62
8.19
10/21/2014
7.14
8.68
3.94
7.49
8.95
9.60
9.24
8.11
11.4
10.2
9.81
11.1
8.31
7.20
9.77
8.58
9.12
10.3
9.66
10.9
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Phosphate
From IOWATER Chemical Assessment guidance document:
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for plants and animals and is usually present in natural waters attached to sediment,
in organic material, and dissolved in the water. Plant growth in surface waters is generally limited by the amount of
orthophosphate, the dissolved form of phosphorus, present. It is the simplest form of phosphorus found in natural
waters and is most available for plants to use. In most waters, orthophosphate is present in very low concentrations. The
amount of phosphate dissolved in water is expressed in milligrams per liter of water (mg/L).
There are natural sources of phosphorus, such as certain soils and rocks, but most elevated levels of phosphorus are
caused by human activities. These include human, animal, and industrial wastes, as well as runoff from fertilized lawns
and cropland. Excess phosphorus in water speeds up plant growth, causes algal blooms, and can result in low dissolved
oxygen, or hypoxic, conditions that can lead to the death of certain fish, invertebrates, and other aquatic animals.
Phosphate PO4-P Results
0.35
0.30
mg/L
0.25
0.20
4/28/2014
0.15
7/17/2014
Detection Limit
0.10
10/21/2014
0.05
0.00
Sample Site
erw1
erw2
erw3
erw4
erw5
4/28/2014
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
7/17/2014
0.30
<0.10
0.28
0.29
0.17
10/21/2014
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
erw11
erw12
erw13
erw14
erw15
erw6
erw7
erw8
erw9
erw10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
0.25
0.28
0.19
0.26
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
erw16
erw17
erw18
erw19
erw20
4/28/2014
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
7/17/2014
<0.10
0.27
0.18
0.27
0.21
10/21/2014
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
0.22
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
<0.10
Page 5
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Sulfate
From Iowa DNR Fact Sheet on Understanding Iowa's Water Quality Standards:
Sulfate is a constituent of total dissolved solids and may form salts with sodium, potassium, magnesium and other
cations. Sulfate is widely distributed in nature and may be present in natural water at concentrations ranging
from a few to several hundred milligrams per liter.
Sulfate S04 Results
70.0
60.0
mg/L
50.0
40.0
4/28/2014
30.0
7/17/2014
10/21/2014
20.0
10.0
0.0
Sample Site
erw1
erw2
erw3
4/28/2014
28.4
28.3
31.2
7/17/2014
23.1
25.8
23.8
10/21/2014
24.6
30.9
25.6
erw11
erw12
erw13
erw4
erw5
erw6
erw7
erw8
erw9
25.5
50.4
27.7
26.3
25.1
28.7
20.0
62.5
22.8
19.5
23.9
24.7
23.1
44.4
24.4
23.0
23.6
24.4
erw10
21.6
19.0
20.2
Page 6
4/28/2014
23.7
22.1
22.2
7/17/2014
19.6
16.6
20.1
10/21/2014
21.8
22.2
19.7
erw14
erw15
erw16
erw17
erw18
erw19
27.7
26.0
27.1
27.0
24.8
21.8
21.9
16.3
12.8
22.0
23.9
22.9
23.2
17.1
14.0
23.1
erw20
24.2
19.9
21.2
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Turbidity
Turbidity is a measure of water clarity, the more suspended material in the water the less light is able to pass
through a sample of water. Turbidity is measured by how much light is scattered by suspended particles using
NTUs or Nephelometric Turbidity Units. Higher turbidity increases water temperatures because suspended
particles absorb more heat. This, in turn, reduces the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO) because warm
water holds less DO than cold. Higher turbidity also reduces the amount of light penetrating the water, which
reduces photosynthesis and the production of DO. Suspended materials can clog fish gills, reducing resistance
to disease in fish, lowering growth rates, and affecting egg and larval development. As the particles settle,
they can blanket the stream bottom, especially in slower waters, and smother fish eggs and benthic
macroinvertebrates. Sources of turbidity include soil erosion, waste discharge, urban runoff, eroding stream
banks, large numbers of bottom feeders (such as carp), which stir up bottom sediments and excessive algal
growth (EPA).
Turbidity Results
1000
900
800
700
NTU
600
500
400
4/28/2014
300
200
100
0
Sample Site
erw1
erw2
erw3
4/28/2014
461
185
203
erw11
erw12
erw13
erw4
erw5
erw6
erw7
erw8
erw9
103
87.6
493
689
432
246
erw14
erw15
erw16
erw17
erw18
erw19
erw10
398
erw20
4/28/2014
270
919
89.1
600
220
233
167
153
Page 7
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Photos
The following photos were taken while conducting water quality monitoring of the English River watershed.
Site 1. 4/28/14
Page 8
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 2. 4/28/14
Page 9
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 3. 4/28/14
Page 10
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 4. 4/28/14
Page 11
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 5. 4/28/14
Page 12
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 6. 4/28/14
Page 13
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 7. 4/28/14
Page 14
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 8. 4/28/14
Page 15
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 9. 4/28/14
Page 16
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 10. 4/28/14
Page 17
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 11. 4/28/14
Page 18
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 12. 4/28/14
Page 19
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 13. 4/28/14
Page 20
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 14. 4/28/14
Page 21
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 15. 4/28/14
Page 22
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 16. 4/28/14
Page 23
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 19. 4/28/14
Page 24
English River Watershed: Water Quality Snapshots 2014
Site 20. 4/28/14
Page 25
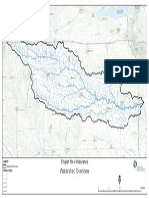
English River Watershed
Monitoring Locations
20
19
15
14 13
16
9
10
11
18 17
8
7
12
4
1
3
5
2
Legend
Monitoring Location
Watershed
HUC12_Subwatersheds
0
2.5
10 Miles
Sources: Esri, DeLorme, NAVTEQ, TomTom, Intermap, increment P Corp., GEBCO, USGS, FAO, NPS, NRCAN, GeoBase, IGN,
Kadaster NL, Ordnance Survey, Esri Japan, METI, Esri China (Hong Kong), swisstopo, and the GIS User Community
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Introduction To GIS - Final Research ReportDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To GIS - Final Research ReporttaylorplummerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Rathbun Technical SummaryDokument13 Seiten2010 Rathbun Technical SummarykateachesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- N P Ag StreamsDokument4 SeitenN P Ag StreamsAhmad HosamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studies On Some Physico-Chemical Parameters of River Argungu, North-Western NigeriaDokument3 SeitenStudies On Some Physico-Chemical Parameters of River Argungu, North-Western NigeriaIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Kandungan N-Nitrogen (Amonia, Nitrat, Nitrit) Dan Fosfat Di Perairan Teluk Pandan Provinsi LampungDokument10 SeitenAnalisis Kandungan N-Nitrogen (Amonia, Nitrat, Nitrit) Dan Fosfat Di Perairan Teluk Pandan Provinsi Lampungmuhammad raisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watersheds, Non-Point Pollution, and HydrologyDokument54 SeitenWatersheds, Non-Point Pollution, and HydrologyraghurmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Water Pollution in Freshwater Inle Lake Based On EutrophicationDokument99 SeitenAnalysis of Water Pollution in Freshwater Inle Lake Based On EutrophicationThant Zaw Soe100% (8)
- Waste Water Treatment Using Slag: Supervised by Prof. Dr. Asiful HoqueDokument6 SeitenWaste Water Treatment Using Slag: Supervised by Prof. Dr. Asiful HoqueAhsanurRahmanShuvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA WQ PosterDokument1 SeiteRA WQ PosterkateachesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijseer 2014 3 (4) 178 184Dokument7 SeitenIjseer 2014 3 (4) 178 184Aprill ApriiliantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Status of Phosphate (PO) Anion Concentration in Waste Water From Six Selected Undetermined Areas of Guyana Using A Spectrophotometric MethodDokument11 SeitenThe Status of Phosphate (PO) Anion Concentration in Waste Water From Six Selected Undetermined Areas of Guyana Using A Spectrophotometric MethodidaayudwitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Your Gardening Choices Can Have A Positive Impact in Your Watershed, Sowing The Seeds For Healthy WaterwaysDokument47 SeitenHow Your Gardening Choices Can Have A Positive Impact in Your Watershed, Sowing The Seeds For Healthy WaterwaysFree Rain Garden ManualsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leather Leaf EvapotranspirationDokument122 SeitenLeather Leaf EvapotranspirationRicardo CachupeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal EditedDokument32 SeitenProposal EditedFariha RasulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lake Hyd Sediment and WQDokument0 SeitenLake Hyd Sediment and WQAshokkumar SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal NitratDokument15 SeitenJurnal NitratnelsonsnlinggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Waste Dumping and Its Implications On Groundwater Resources in Anambra State, Nigeria.Dokument14 SeitenSolid Waste Dumping and Its Implications On Groundwater Resources in Anambra State, Nigeria.Angela Iloduba Akanwa100% (2)
- CMT 565 Experiment 6 Ltm-Phosphorus (P) : Name Student Id Group Name of PartnersDokument14 SeitenCMT 565 Experiment 6 Ltm-Phosphorus (P) : Name Student Id Group Name of PartnersAiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doc063 53 30625Dokument2 SeitenDoc063 53 30625Sakthi VelayuthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurunegala Summary Water Quality-FinalDokument4 SeitenKurunegala Summary Water Quality-FinalmimrusfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 219 PDFVDDFDFSDDokument5 Seiten219 PDFVDDFDFSDSanatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 115423-Article Text-321360-1-10-20150409Dokument4 Seiten115423-Article Text-321360-1-10-20150409the great artNoch keine Bewertungen
- FR GREEN Notebook 041511 PhosphorousDokument6 SeitenFR GREEN Notebook 041511 PhosphorousLoh Ri JianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17 Full PDFDokument9 Seiten17 Full PDFPriscilia YuniarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rathbun Lake and Watershed 2013 Monitoring SummaryDokument5 SeitenRathbun Lake and Watershed 2013 Monitoring SummarycleanwaterforallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19 2174 1322015 IjcsDokument16 Seiten19 2174 1322015 Ijcsselviramadoss4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medford Regional Water Reclamation Facility Outfall Assessment StudyDokument43 SeitenMedford Regional Water Reclamation Facility Outfall Assessment StudyMail TribuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shang Liu EMSC 470W Spring 2012Dokument16 SeitenShang Liu EMSC 470W Spring 2012sql5199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Impacts of Aquaculture On The Water Quality of Santubong River, Sarawak by Michelle Christine MiodDokument6 SeitenImpacts of Aquaculture On The Water Quality of Santubong River, Sarawak by Michelle Christine MiodMichelle Christine100% (1)
- Investigation of Pollution State of Aba River Along Its Course Using Pollution IndexDokument5 SeitenInvestigation of Pollution State of Aba River Along Its Course Using Pollution IndexIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EutrophicationDokument26 SeitenEutrophicationSurendra BamNoch keine Bewertungen
- EZ Series: Continuous Monitoring of Total Phosphorus: Key Applications: Surface Water Monitoring, Wastewater TreatmentDokument2 SeitenEZ Series: Continuous Monitoring of Total Phosphorus: Key Applications: Surface Water Monitoring, Wastewater TreatmentMrMsmaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSF Highlands Companies Aggregate Proposal - Letter To OMNR - FinalDokument11 SeitenDSF Highlands Companies Aggregate Proposal - Letter To OMNR - FinalSTOP THE QUARRYNoch keine Bewertungen
- On-Site Sanitation and Its Effects On The Groundwater Resources of Nyali-Bamburi-Shanzu and Diani-Chale, KenyaDokument11 SeitenOn-Site Sanitation and Its Effects On The Groundwater Resources of Nyali-Bamburi-Shanzu and Diani-Chale, KenyaTemesgen M. MandersoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shigut2017 Article AssessmentOfPhysico-chemicalQuDokument10 SeitenShigut2017 Article AssessmentOfPhysico-chemicalQuofarmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physico-Chemical Characterization of Layawan River: Daryl Ann V. Cuivillas, Ma - Rio Naguit, Arnelm. CuivillasDokument7 SeitenPhysico-Chemical Characterization of Layawan River: Daryl Ann V. Cuivillas, Ma - Rio Naguit, Arnelm. CuivillasIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of Phosphate Concentration in Agricultural Soil Samples and Water Samples Using Molybdenum Blue MethodDokument6 SeitenSpectrophotometric Analysis of Phosphate Concentration in Agricultural Soil Samples and Water Samples Using Molybdenum Blue Methodshai dunayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report Ntcc.Dokument36 SeitenFinal Report Ntcc.Shruti MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report NTCCDokument36 SeitenFinal Report NTCCShruti MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Water Quality Index Result of Robertson Lake Jabalpur in Remote Sensing ApplicationDokument4 SeitenUse of Water Quality Index Result of Robertson Lake Jabalpur in Remote Sensing ApplicationGRD JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variation in Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Water Quality of Bhindawas Wetland, Jhajjar, Haryana, IndiaDokument6 SeitenVariation in Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Water Quality of Bhindawas Wetland, Jhajjar, Haryana, Indiatawseef ahmad mirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Kandungan N-Nitrogen (Amonia, Nitrat, Nitrit) Dan Fosfat Di Perairan Teluk Pandan Provinsi LampungDokument10 SeitenAnalisis Kandungan N-Nitrogen (Amonia, Nitrat, Nitrit) Dan Fosfat Di Perairan Teluk Pandan Provinsi LampungBeriman Syaputra BagariangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using EF PLI and Igeo For The Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Sediment Quality of Asejire Reservoir Southwest NigeriaDokument14 SeitenUsing EF PLI and Igeo For The Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Sediment Quality of Asejire Reservoir Southwest NigeriaEmilia DuncaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence 1 EportfolioDokument7 SeitenEvidence 1 Eportfolioapi-263210614Noch keine Bewertungen
- WatershedDokument22 SeitenWatershedpancadewisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Microorganisms in Phosphorus CyclingDokument3 SeitenRole of Microorganisms in Phosphorus CyclingGOWTHAM GUPTHA100% (3)
- Bournbrook AssesmentDokument9 SeitenBournbrook AssesmentYsmael Alongan B. MangorsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arimoro 2007 Water QuanlityDokument12 SeitenArimoro 2007 Water QuanlityTan DaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antiescalants - Theoretical and Practical Experience of Calcium Phosphate Inhibition in Waste Water RO PlantDokument14 SeitenAntiescalants - Theoretical and Practical Experience of Calcium Phosphate Inhibition in Waste Water RO PlantBenjamin MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- E3sconf Isffs2023 02015Dokument14 SeitenE3sconf Isffs2023 02015rudyismaelkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nitrate Nitrite EngDokument8 SeitenNitrate Nitrite EngOproiu VladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elimination of Fluoride Ions From Water of Wells and Tyikomiyne Sources by The Hydroxyapatite Phosphocalcic, Talssint (Eastern Morocco)Dokument5 SeitenElimination of Fluoride Ions From Water of Wells and Tyikomiyne Sources by The Hydroxyapatite Phosphocalcic, Talssint (Eastern Morocco)AJER JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality of Water For Irrigating Urban Vegetable Farms: An Assessment of Toxic and Essential Metals in Water From An Urban LakeDokument6 SeitenQuality of Water For Irrigating Urban Vegetable Farms: An Assessment of Toxic and Essential Metals in Water From An Urban LakeEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrobiological Assessment of Zoshk River, Mashhad City: H. Nazari and R. Mosavi-NadoshanDokument4 SeitenHydrobiological Assessment of Zoshk River, Mashhad City: H. Nazari and R. Mosavi-NadoshanShakeel RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 185080600111030 Muhammad Farhan AnshoryDokument7 Seiten26 185080600111030 Muhammad Farhan AnshoryEka WidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eutrophication of LakesDokument7 SeitenEutrophication of Lakesmanoj_rkl_07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Aqua Ponic WaterDokument20 SeitenTesting Aqua Ponic Waterpelopas3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 11 1640003253 Ijcseierdjun20221Dokument10 Seiten2 11 1640003253 Ijcseierdjun20221TJPRC PublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report 5 Kita!!!Dokument10 SeitenLab Report 5 Kita!!!Zaidi Zakaria100% (1)
- WMP CSRDokument1 SeiteWMP CSRapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- WMP HelDokument1 SeiteWMP Helapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
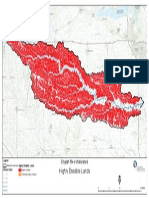
- Erw 2013 Land CoverDokument1 SeiteErw 2013 Land Coverapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- WMP WetlandsDokument1 SeiteWMP Wetlandsapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- WMP OverviewDokument1 SeiteWMP Overviewapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- Erw Depth To BedrockDokument1 SeiteErw Depth To Bedrockapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- MonitoringlocationsfinalDokument1 SeiteMonitoringlocationsfinalapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Straightening of The English River3 - Dave JacksonDokument26 SeitenThe Straightening of The English River3 - Dave Jacksonapi-228244514Noch keine Bewertungen
- QtreeDokument12 SeitenQtreesaimadhukargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of ProbabilityDokument58 SeitenFundamentals of Probabilityhien05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems 2012Dokument5 SeitenPractice Problems 2012Anonymous Fj3YPHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rman Command DocumentDokument22 SeitenRman Command DocumentanandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nalsar 2006Dokument84 SeitenNalsar 2006anuragchoubey1Noch keine Bewertungen
- HO4 EstimationDokument9 SeitenHO4 EstimationMirza Naveed BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artefact 2 Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenArtefact 2 Lesson Planapi-223100574Noch keine Bewertungen
- Virginia Henderson TheoryDokument20 SeitenVirginia Henderson Theoryezvip100% (2)
- MLDokument8 SeitenMLankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CofisaDokument2 SeitenCofisaTony Starks0% (1)
- Ctenocephalides Felis Felis vs. Ctenocephalides Canis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) : Some Issues in Correctly Identify These SpeciesDokument11 SeitenCtenocephalides Felis Felis vs. Ctenocephalides Canis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) : Some Issues in Correctly Identify These SpeciesstfnhmwnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam IDokument7 SeitenExam IJoshMatthewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- UK Environment Agency RM-QG6 - Calibrating Particulate-Monitoring Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMs), Especially For Low Concentrations of Particulate MatterDokument7 SeitenUK Environment Agency RM-QG6 - Calibrating Particulate-Monitoring Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems (CEMs), Especially For Low Concentrations of Particulate MatterTomy SetiyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TcbrasterDokument1 SeiteTcbrasterjimusosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Lab Act 2Dokument3 SeitenMicro Lab Act 2RHINROMENoch keine Bewertungen
- Vivek TiwariDokument4 SeitenVivek TiwariMehul ThakorNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSC Issue 30Dokument32 SeitenPSC Issue 30nkosidlaminiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Plan Template: Yale University Human Resources Internal Communications 10/3/2014Dokument6 SeitenCommunication Plan Template: Yale University Human Resources Internal Communications 10/3/2014pielzapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Term 3 Project 2021Dokument2 SeitenGrade 8 Term 3 Project 2021Londiwe PrincessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Air Bearing? 3. Why Air Bearing? 5. Working PrincipleDokument18 SeitenWhy Air Bearing? 3. Why Air Bearing? 5. Working PrinciplesachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Dokument119 SeitenQuantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Qonita NazhifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Training - DisysDokument12 SeitenJava Training - DisysArun KiliyaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Template IR For ManagementDokument13 SeitenPresentation Template IR For ManagementYosia SuhermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIS Project ProposalDokument2 SeitenGIS Project ProposalKevin OdonnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter #06 GravitationDokument13 SeitenChapter #06 GravitationSIR USMAN KHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science of Getting RichDokument150 SeitenScience of Getting RichTony Okpere Jr.100% (4)
- Accident and Incident Analysis Based On The AccideDokument12 SeitenAccident and Incident Analysis Based On The AccideAnees Balqis YunezzafrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documenting Childrens Learning Examples PDFDokument19 SeitenDocumenting Childrens Learning Examples PDFArief lukman100% (1)
- Froebelian Eglantyne Jebb, Save The ChildrenDokument3 SeitenFroebelian Eglantyne Jebb, Save The ChildrenLifeinthemix_FroebelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco TCL IvrDokument256 SeitenCisco TCL IvrKarol HermickiNoch keine Bewertungen