Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Algoritma Bradycardia
Hochgeladen von
Fiya SahrulCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Algoritma Bradycardia
Hochgeladen von
Fiya SahrulCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
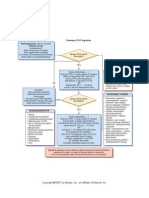
Bradycardia With
a Pulse Algorithm
Assess appropriateness for clinical condition.
Heart rate typically 50/min if bradyarrhythmia.
Identify and treat underlying cause
Maintain patent airway; assist breathing as necessary *
Oxygen (if hypoxemic)
Cardiac monitor to identify rhythm; monitor blood pressure and oximetry
IV access
12-Lead ECG if available; don't delay therapy
N
Monitor and observe
Persistent bradyarrhythmia causing:
Hypotension?
Acutely altered mental status?
Signs of shock?
Ischemic chest discomfort?
Acute heart failure?
Y
Atropine IV Dose:
First dose: 0.5 mg bolus
Repeat every 3-5 minutes
Maximum: 3 mg
If atropine ineffective:
Transcutaneous pacing**
OR
Dopamine IV infusion:
2-10 mcg/kg per minute
OR
Epinephrine IV infusion:
2-10 mcg per minute
Consider:
Expert consultation
Transvenous pacing
* Dorges V, Wenzel V, Knacke P, Gerlach K, Comparison of different airway management strategies to ventilate apneic, nonpreoxygenated
patients. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:800-804
** Link MS, Atkins DL, Passman RS, Halperin HR, Samson RA, White RD, Cudnik MT, Berg MD, Kudenchuk PJ, Kerber RE. Part 6: electrical
therapies: automated external defibrillators, defibrillation, cardioversion, and pacing: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2010; 122(suppl 3):S706S719. http://circ.ahajournals.org/
content/122/18_suppl_3/S706
(c) ACLS Training Center
877-560-2940
support@acls.net
Complete your ACLS recertification online with the highest quality courses at http://www.acls.net and use promo code PDF2014 during checkout for 15% off.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Algo Bradycardia DikonversiDokument5 SeitenAlgo Bradycardia DikonversiDaniel SitungkirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Arrest Circular AlgorithmDokument6 SeitenCardiac Arrest Circular Algorithmno_spam_mang80% (5)
- Aclspediatric BradycardiaDokument2 SeitenAclspediatric BradycardiasalamredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiogenic ShockDokument3 SeitenCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY 6 SHOCK StudentsDokument38 SeitenDAY 6 SHOCK StudentsTrisha UmaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Information From American Heart Association, Advanced Cardiac Life Support, 2006Dokument25 SeitenAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Information From American Heart Association, Advanced Cardiac Life Support, 2006karento1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and TachycardiaDokument55 SeitenManagement of Symptomatic Bradycardia and TachycardiaDewintha Airene NoviantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of AnesthesiologyDokument176 SeitenHandbook of AnesthesiologyarmelzahfauziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDokument21 SeitenCardiopulmonary ResuscitationVesnickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using The ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm For Managing BradycardiaDokument2 SeitenUsing The ACLS Bradycardia Algorithm For Managing BradycardiasetiamegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algoritma BradikardiaDokument2 SeitenAlgoritma BradikardiaDaniel SitungkirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Clinical Strategies: Handbook of AnesthesiologyDokument180 SeitenCurrent Clinical Strategies: Handbook of AnesthesiologydramaganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code Blue ManagemnetDokument36 SeitenCode Blue ManagemnetPreethi BNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENLS - V 4.0 Protocol - ICH - FinalDokument16 SeitenENLS - V 4.0 Protocol - ICH - FinalR.M.C vivNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Pulseless Arrest - Non-Shockable RhythmsDokument29 Seiten3 Pulseless Arrest - Non-Shockable RhythmsTejas Vivek WaghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHA ACLS Adult Bradycardia Algorithm: The Priority Should Be To Identify and Treat The Underlying CauseDokument1 SeiteAHA ACLS Adult Bradycardia Algorithm: The Priority Should Be To Identify and Treat The Underlying Causezkid0011546Noch keine Bewertungen
- Saudi CPR Guidlines in EnglishDokument16 SeitenSaudi CPR Guidlines in EnglishpiyushbamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Medical Guidelines: Congestive Heart FailureDokument2 SeitenSample Medical Guidelines: Congestive Heart FailureJohanna ShuulukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Case Study on Pacemaker Replacement in an Elderly WomanDokument6 SeitenCardiac Dysrhythmia Case Study on Pacemaker Replacement in an Elderly WomanCharlyn JenselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Dysrhythmia Case StudyDokument6 SeitenCardiac Dysrhythmia Case StudyCharlyn JenselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument34 SeitenCase StudyBSNNursing101Noch keine Bewertungen
- BLS and ACLS Case ScenariosDokument35 SeitenBLS and ACLS Case ScenariosrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac ArrestDokument21 SeitenCardiac Arrestashrf seadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (Acls)Dokument45 SeitenAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support (Acls)Erinne DefrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulseless VT/VF Algorithm First Impression: Sick or Not Sick? Primary SurveyDokument9 SeitenPulseless VT/VF Algorithm First Impression: Sick or Not Sick? Primary SurveyBa LitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Cardiac SuppDokument32 SeitenAdvance Cardiac SuppVijith.V.kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS TeoriDokument27 SeitenACLS TeoriTita Luthfia100% (1)
- 099 B SaroshDokument14 Seiten099 B SaroshUmair AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Status Epilepticus Pathway-FINALDokument5 SeitenPediatric Status Epilepticus Pathway-FINALvural kesikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS PEA Asystole AlgorithmDokument3 SeitenACLS PEA Asystole AlgorithmSafira RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shock ManagementDokument26 SeitenShock ManagementMuhammad Irfanuddin Bin IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- IU Health ACLS Study GuideDokument8 SeitenIU Health ACLS Study Guideeng78ineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementDokument40 SeitenLife Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementRuki HartawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiology Exam 2 - Lecture Notes: Treating Adult BradycardiaDokument5 SeitenCardiology Exam 2 - Lecture Notes: Treating Adult BradycardiaAddieNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCCN Clinical Guideline for Status EpilepticusDokument3 SeitenPCCN Clinical Guideline for Status EpilepticusAlex GasnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDokument28 SeitenAdvanced Cardiac Life SupportAbdulrahman AlsayyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPCRDokument51 SeitenCPCRAnushaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Shock Types and TreatmentsDokument75 SeitenUnderstanding Shock Types and TreatmentsaulianmediansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter3Shock CirculationDokument13 SeitenChapter3Shock CirculationSri AgustinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia Emergencies AccidentsDokument9 SeitenAnesthesia Emergencies Accidentsshubhangi godboleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) : By: Diana Blum MSN Metropolitan Community College Nursing 2150Dokument16 SeitenAdvanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) : By: Diana Blum MSN Metropolitan Community College Nursing 2150Vikneswara SoorianarayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pulmonary EmbolismDokument82 SeitenAcute Pulmonary Embolismincredible PragesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiopulmonary Resustication: By:-Dr - Gopal Krushna Nayak (P.T)Dokument24 SeitenCardiopulmonary Resustication: By:-Dr - Gopal Krushna Nayak (P.T)jaleswar bagNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Dokument6 SeitenACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Assessment in The EDDokument2 SeitenGeneral Assessment in The EDLaili CinthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Cardiovascular EmergenciesDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 Cardiovascular Emergenciesعلاء البناءNoch keine Bewertungen
- WI EMS Medical Guidelines BradycardiaDokument2 SeitenWI EMS Medical Guidelines BradycardiaCheewin KhawprapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support: Valentina, MD, FIHADokument34 SeitenAdvanced Cardiac Life Support: Valentina, MD, FIHAfaradibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify and Treat Underlying Cause: Persistent Tachyarrhythmia CausingDokument1 SeiteIdentify and Treat Underlying Cause: Persistent Tachyarrhythmia CausingLeigh DaltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medip, IJAM-724 CDokument3 SeitenMedip, IJAM-724 CKhalilSemlaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Life SupportDokument6 SeitenBasic Life SupportbhongskirnNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBLS - Pediatric Basic Life Support and Pediatric Advance Cardiac Life SupportDokument135 SeitenPBLS - Pediatric Basic Life Support and Pediatric Advance Cardiac Life SupportSteffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesVon EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesVon EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Guide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyVon EverandGuide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyRuth WillisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia Complications in the Dental OfficeVon EverandAnesthesia Complications in the Dental OfficeRobert C. BosackNoch keine Bewertungen