Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
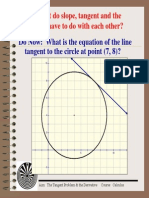
Graphing y F (X) : ! C Is Positive, The Function Is Shifted Up
Hochgeladen von
sdfnsofnsdiofnso1AaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Graphing y F (X) : ! C Is Positive, The Function Is Shifted Up
Hochgeladen von
sdfnsofnsdiofnso1AaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
Graphing y = f(x)
y = f (x)
y
10
(x-2) -3
((x-2)^2)-3
5
x
-10
-5
10
x
+
C
10
-5
-10
y = f ( x) + C
y
! C is positive, the function is shifted up
! C is negative, the function is shifted
down
10
-10
-5
-5
-10
y = f (x C)
y
10
! C > 0, shift function right C units
! C < 0, shift function left C units
The function becomes: y = f ( x + C )
5
x
-10
-5
5
-5
C
10
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 1
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y = C. f (x)
y
! C > 1, the function is steeper
! 0 < C < 1, the function is shallower
10
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = f (Cx )
! Multiply the x co-ordinate by
1
C
y
10
! C > 1, thinner, steeper
! C < 1, fatter, shallower
! (x, 1) remains the same
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 2
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y = f (x)
y
! Flip about the x-axis
! All positive become negative
! All negative become positive
10
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = f ( x)
y
10
! Flip about the y-axis
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 3
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y = f (x)
y
10
! All negative y values become positive
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = f (x)
y
10
! Positive x values are mirrored about the
y-axis
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = f (x)
y
10
! Positive y values are mirrored about the
x-axis
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 4
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y=
f (x)
! If y value is > 1, y value is smaller but
still > 1
! If y value is = 1, y value is the same
! If y value is 0 < y < 1, y value is larger
but still < 1
! If y value is < 0, y value doesnt exist
10
5
x
-10
-5
10
y
-5
2
1.5
1
-10
0.5
y 2 = f ( x)
-0.5
-0.5
x
0.5
1
y
10
sketch
y=
f (x) and y = f (x)
Both Brown and Green are y 2 = f ( x)
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = [ f (x)]
y = [ f ( x )]
20
If y value:
! = 0, y remains 0
! > 1, y becomes steeper (above)
! 0 < y < 1, y becomes steeper (below)
! if C is even, y = [ f ( x)] 0
15
10
5
x
! if C is odd, y = [ f ( x)] has the same sign
as f (x)
C
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 5
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y=
1
f ( x)
y
5
or
y = [ f ( x )]
! Asymptotes where y = 0
! For f(x), y values > 1 becomes small
_________ y values 0 < y < 1 becomes big
! Same case for y < 0, but negative
! Points along y = 1 and y = 1 stay the
same
-5
-5
y = f 1 ( x )
y
or
10
x = f ( y)
! INVERSE FUNCTION
Flip about the line y = x
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 6
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
Graphing y = f(x), y = g(x)
y = g (x)
y = sin x
y
10
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = f ( x) + g ( x)
y
! y co-ordinates are added
10
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y = f ( x) g ( x)
y
10
! g (x) co-ordinate is subtracted from the
f (x) y co-ordinate
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 7
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y = f ( x).g ( x)
y
! y co-ordinates are multiplied
10
5
5
x
x
-5
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
-5
y=
f ( x)
g ( x)
y
! Reciprocal, Multiplication rule
1
f ( x).
g ( x)
x
-5
-5
y
10
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 8
Maths Extension 2 - Graphs
y = f [g (x)]
! Composite functions
y = f (u ) , u = g (x)
y
10
Take:
f ( x) = e x
g ( x) = sin x
5
x
-10
-5
10
-5
-10
y
10
10
uy
ux
-10
-5
10
x
-10
-5
-5
-5
-10
-10
10
http://www.geocities.com/fatmuscle/HSC/ 9
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Elevator ControlDokument3 SeitenElevator ControlNATHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLEP CalculusDokument42 SeitenCLEP Calculusagenius1st100% (2)
- AP Calc Exam2Dokument25 SeitenAP Calc Exam2Jordan Miles100% (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYVon EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNoch keine Bewertungen
- FutbolistaDokument18 SeitenFutbolistaKaren Osses50% (2)
- Engineering Mathematics II Formulas Studyhaunters PDFDokument13 SeitenEngineering Mathematics II Formulas Studyhaunters PDFSriram J100% (1)
- Sawla - Laska (Lot - I) Road Project Hydrology - Hydraulics MDokument64 SeitenSawla - Laska (Lot - I) Road Project Hydrology - Hydraulics Mashe zinab100% (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- My Ideal Home: Name No. Class Date Mark TeacherDokument5 SeitenMy Ideal Home: Name No. Class Date Mark TeacherQuadrado MágicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bendable ConcreteDokument21 SeitenBendable ConcreteJulia Sebastian0% (1)
- NotesDokument20 SeitenNotesUPAHAR SWAPNASHISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cracking The 'Functions' Code For XAT 2012's Quantitative AptitudeDokument8 SeitenCracking The 'Functions' Code For XAT 2012's Quantitative AptitudeQuirking QuarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community College of Philadelphia Maths 161 Spring 2011 Practice For Exam I 1Dokument9 SeitenCommunity College of Philadelphia Maths 161 Spring 2011 Practice For Exam I 1Rateeb AsmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exact Equations (Section 1.4) : Solutions For Selected ProblemsDokument6 SeitenExact Equations (Section 1.4) : Solutions For Selected ProblemsTumi MothusiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 (A Math CD)Dokument17 Seiten22 (A Math CD)Qhayyum1998Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 MavDokument23 Seiten2011 MavlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arihant PhysicsDokument22 SeitenArihant PhysicsManishKumar0% (1)
- Control 3 Calculo2Dokument9 SeitenControl 3 Calculo2camilo_akuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Tangent, Slope and DerivativeDokument22 Seiten21 Tangent, Slope and DerivativeMegha BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDokument25 SeitenBab Xiii Integral: 13. 1 DefinisiDeazzy AndriyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM ch01Dokument43 SeitenSM ch01Bibah GeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LGRCB Im Ch17Dokument102 SeitenLGRCB Im Ch17Nguyễn Phượng NhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and DifferentiabilityDokument39 SeitenNCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and DifferentiabilityVidyakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Law ExerciseDokument5 SeitenLinear Law ExercisemangimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTH 2003 Sample Final DDokument9 SeitenMTH 2003 Sample Final DCTLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tre Ci Kolokvij Iz Matematike II 2009./2010.: R Diferencijabilna Funkcija Dviju Varijabli., yDokument8 SeitenTre Ci Kolokvij Iz Matematike II 2009./2010.: R Diferencijabilna Funkcija Dviju Varijabli., yTARELIC1802Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math102 Equation SheetDokument0 SeitenMath102 Equation SheetMaureen LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A SolDokument16 SeitenRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A Solvishal110085Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Continuity & Differentiability Ex.2 (A)Dokument13 SeitenAdvanced Continuity & Differentiability Ex.2 (A)swagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide For The Advanced Placement Calculus AB ExaminationDokument20 SeitenStudy Guide For The Advanced Placement Calculus AB ExaminationrgurvareddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number of Movies RentedDokument11 SeitenNumber of Movies RentedDaniela BereniceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberDokument8 SeitenContinuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberAakash ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: MTHE01P03Dokument12 SeitenMathematics: MTHE01P03Tarek AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get Full PointsDokument6 SeitenGet Full PointsChing-Ting WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Group C) : Matcts@nus - Edu.sgDokument23 Seiten(Group C) : Matcts@nus - Edu.sglzyabc597Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADokument7 SeitenAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2Dokument5 SeitenP2NmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesDokument16 SeitenSolution+V1 VG MVG MaD6NVC08+Trigonometry+and+DerivativesEpic WinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Dokument53 SeitenNarayana Institute Iit Jee 2008 Paper 1 2Pranjal AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 41Dokument4 SeitenDPP 41mmoriarity309Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differential EqutionDokument4 SeitenDifferential EqutionthinkiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Functions HWT - 1Dokument7 SeitenSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Functions HWT - 1varunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System TutorialDokument3 SeitenOperating System TutorialJunaid AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Edexcel Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (6663) January 2010Dokument13 SeitenMathematics Edexcel Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (6663) January 2010Don WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1 Sol 2009Dokument32 SeitenAlgebra 1 Sol 2009imsungbaekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examview - CH 7 Problem SetDokument10 SeitenExamview - CH 7 Problem Setapi-236184654Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Solutions) : Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XI Subject - MathematicsDokument9 Seiten(Solutions) : Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XI Subject - Mathematicsrimo15Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Term General Exam: Maths 4 ESODokument4 Seiten2 Term General Exam: Maths 4 ESORaquel Gil PuertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 9 Line Drawing Algorithims 1 2Dokument9 SeitenL 9 Line Drawing Algorithims 1 2306 NamrtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXAMPLE Admission Test MathematicsDokument5 SeitenEXAMPLE Admission Test MathematicsTheodor PetreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Paper 1Dokument53 Seiten2008 Paper 1Aashray KothaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1Dokument12 SeitenSolutions To Home Practice Test-5/Mathematics: Differential Calculus - 2 HWT - 1varunkohliinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus 1000A, Section 007Dokument30 SeitenCalculus 1000A, Section 007arrowroot1Noch keine Bewertungen
- LNX (LN X) (LN X) (LN X)Dokument5 SeitenLNX (LN X) (LN X) (LN X)Ching-Ting WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Von EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unusual and Marvelous MapsDokument33 SeitenUnusual and Marvelous MapsRajarajan100% (1)
- Pharma Iii To Viii PDFDokument57 SeitenPharma Iii To Viii PDFRaja PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental and Technical Analysis of Iron and Steel SIP PROJECTDokument34 SeitenFundamental and Technical Analysis of Iron and Steel SIP PROJECThaveuever910Noch keine Bewertungen
- BOQ For Softscape and Hardscape Bendungan Karian-3Dokument23 SeitenBOQ For Softscape and Hardscape Bendungan Karian-3greenorchidresidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CT GenerationsDokument3 SeitenCT GenerationssanyengereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023Dokument6 SeitenMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023Priyanshu KasanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CDokument2 SeitenAssignment Class X Similar Triangles: A D E B CCRPF School100% (1)
- Pakistan PresentationDokument17 SeitenPakistan PresentationYaseen Khan100% (1)
- 12V-100Ah FTA DatasheetDokument1 Seite12V-100Ah FTA Datasheetchandrashekar_ganesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Semi FowlerDokument6 SeitenJurnal Semi FowlerHartina RolobessyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory-Set & Relations PDFDokument4 SeitenTheory-Set & Relations PDFmp SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deutz Fahr Rear Axle T 7100 Workshop ManualDokument22 SeitenDeutz Fahr Rear Axle T 7100 Workshop Manualcindybennettmd040595jbw100% (133)
- XL4016 Step Down Buck DC DC ConverterDokument7 SeitenXL4016 Step Down Buck DC DC ConverterCésar Fernando Rueda PortillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm A479Dokument7 SeitenAstm A479Martin RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM E 1066 - 95 Standard Practice For Ammonia Colorimetric Leak Testing PDFDokument5 SeitenASTM E 1066 - 95 Standard Practice For Ammonia Colorimetric Leak Testing PDFАртем ТитовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kasuti of KarnatakaDokument2 SeitenKasuti of KarnatakarhlkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afm Udc A320-500Dokument600 SeitenAfm Udc A320-500melitiyaprorok100% (1)
- Material Control Procedure - TemplateDokument5 SeitenMaterial Control Procedure - TemplateHernandito Rahmat KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HK USP CompactDokument56 SeitenHK USP CompactJonathan CrenshawNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Lightweight True Random Number Generator For Root of Trust ApplicationsDokument11 SeitenA Lightweight True Random Number Generator For Root of Trust ApplicationsMADDULURI JAYASRINoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Soil Classification Numerical PDFDokument5 Seiten03 Soil Classification Numerical PDFabishrantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Alkaline Food ChartDokument3 SeitenAcid Alkaline Food Chartgime2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D3078-02Dokument3 SeitenAstm D3078-02Geoff EricksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starlift MetricDokument2 SeitenStarlift MetricCralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationDokument13 SeitenX-Ray Radiation and Gamma RadiationVence MeraNoch keine Bewertungen