Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Semester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirements-Physci
Hochgeladen von
api-261484540Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Semester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirements-Physci
Hochgeladen von
api-261484540Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Name: ______________________________________ Phy Sci - _____ Date of Exam___________________
Semester I Exam Study Questions and Notebook Check Prep
NOTEBOOKS WILL BE CHECKED ON TUESDAY, DECEMBER 16th
Unit 4 Notebook (26 points) & Planner Check (5 points)
Bellringers #57 - #72 16 points
Cornell Notes
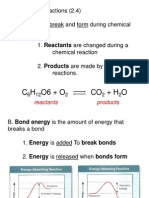
Class Notes: Forms of Energy (Stamped) 4 points
Mr. Andersen: Kinetic and Potential Energy (Stamped) 2 points
Chapter 5.1: The Nature of Energy(Stamped) 2 points
Chapter 5.2: Conservation of Energy(Stamped) 2 points
Planner-Since November 18 , 2014 5 points
Chapter 1: Scientific Inquiry
Standards:
Process Standard 1: Observe and Measure
1. Identify qualitative and quantitative changes in cells, organisms, populations, and ecosystems given conditions (e.g.,
temperature, mass, volume, time, position, length, quantity) before, during, and after an event.
2. Use appropriate tools with accuracy and precision (e.g., metric ruler, graduated cylinder, thermometer, balances,
spring scales, stopwatches) when measuring objects and/or events.
3. Use appropriate International System of Units (SI) (i.e., grams, meters, liters, degrees Celsius, and seconds) and SI
prefixes (i.e., micro-, milli-, centi-, and kilo-) when measuring objects and/or events.
Process Standard 3: Experimental Design
1. Identify the independent variables, dependent variables, controlled variables, and control set-up in an experiment.
2. Use mathematics to show relationships within a given set of observations.
3. Identify a hypothesis for a given problem in physical science investigations.
4. Recognize potential hazards and practice safety procedures in all physical science activities.
Process Standard 4: Interpret and Communicate
1. Select appropriate predictions based on previously observed patterns of evidence.
2. Interpret data tables, line, bar, trend, and/or circle graphs from existing science research or student experiments.
Process Standard 5: Model
1. Interpret a model which explains a given set of observations.
2. Select predictions based on models, and when appropriate, apply mathematical reasoning to make accurate
predictions.
3. Compare a given model to the physical world.
Key Terms and Topics:
scientific method (SEE pg. 8 and foldable), hypothesis, experiment, control, independent variable,
dependent variable, constant, theory, quantitative data, qualitative data, volume, mass, density, bar graph,
line graph, pie chart
QUESTIONS: Page 13: #1-3, Page 23: #1-2, Page 16: Applying Math Practice Problems: #1-2, Page 21: #15, Page 24: Applying Math Practice Problems: # 1-3, Page 26: #1-5, Page 32 -33: # 12-17, 27-29, Page 34-35:
#1-8
Chapter 3: Motion
Standards:
Standard 3: Motion and Forces The motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and
speed. A change in motion occurs as a result of a net force.
1. Objects change their motion only due to a net force. Laws of motion are used to determine the effects of forces on
the motion of objects. Gravitation is a universal force that each object exerts on any other object.
Key Terms and Topics:
displacement, vector, speed, average speed, velocity, acceleration, positive acceleration, negative
acceleration, distance-time graph, velocity-time graph
QUESTIONS: Page 72: Applying Math Practice Problems: #1-2, Page 75: #1-7, Page 80: #1-7, Page 92-93:
#9-15, 23-27, Page 94-95: #1-8
Chapter 3.3 and 4: Force
Standards:
Standard 3: Motion and Forces The motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and
speed. A change in motion occurs as a result of a net force.
1. Objects change their motion only due to a net force. Laws of motion are used to determine the effects of forces on
the motion of objects. Gravitation is a universal force that each object exerts on any other object.
Key Terms:
force, net force, balanced vs. unbalanced, friction, air resistance, first law of motion, inertia, second law of
motion, third law of motion, gravity, weight, centripetal acceleration and force, momentum, law of
conservation of momentum
Page 86; #1-5, Page 102: Applying Math Practice Problems: #1-3, Page 103: #6, Page 111: #1-8, Page 116:
Applying Practice Problems: #1-3, Page 117: #1-4, 6, Page 122-123: #7-14,
Chapter 5 and 6.1: Energy
Standards:
Standard 4: Interactions of Energy and Matter Energy can be transferred or transformed but never destroyed.
1. Energy can be classified as kinetic energy (energy of motion) or potential energy (e.g., positional, elastic, chemical,
nuclear).
Key Terms:
energy, kinetic energy, joule, potential energy, gravitational potential energy, all forms of energy,
mechanical energy, law of conservation of energy, work, power
QUESTIONS: Page 130: Applying Math Practice Problems #1-3, Page 133: #1-7, Page 143: #1-6, Page 148149: #7-12, 22-25, Page 156: Applying Math Practice Problems: #1-3, Page 159: #3-7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 4th Hour - Biology IDokument1 Seite4th Hour - Biology Iapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules Quick Review - BellringerDokument37 SeitenBiomolecules Quick Review - Bellringerapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Periodictablecerealboxproject KnightDokument7 SeitenPeriodictablecerealboxproject Knightapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- MitosispictureDokument1 SeiteMitosispictureapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 TestreviewkeyDokument5 SeitenUnit 7 Testreviewkeyapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 ReviewkeyDokument6 SeitenUnit 6 Reviewkeyapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecosystems Unit ReviewDokument5 SeitenEcosystems Unit Reviewapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Disorder Research Mini PosterDokument4 SeitenGenetic Disorder Research Mini Posterapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 ReviewkeyDokument3 SeitenUnit 6 Reviewkeyapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Semester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirements 3 KeyDokument8 SeitenSemester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirements 3 Keyapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit4review2014include On Final Due To Time WeeblyDokument6 SeitenUnit4review2014include On Final Due To Time Weeblyapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Semester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirements-PhysciDokument2 SeitenSemester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirements-Physciapi-2614845400% (1)
- Unit4review2014include On Final Due To Time WeeblyDokument6 SeitenUnit4review2014include On Final Due To Time Weeblyapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Semester Exam Study QuestionsnotebookrequirementsDokument4 SeitenSemester Exam Study Questionsnotebookrequirementsapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- CelltheoryslidesDokument7 SeitenCelltheoryslidesapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newtons Laws of MotionwebsiteDokument32 SeitenNewtons Laws of Motionwebsiteapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Molecular Models 1Dokument1 SeiteActivity Molecular Models 1api-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1 BiochemistryDokument11 SeitenUnit1 Biochemistryapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensional Analysis 1-ClasspracticeDokument2 SeitenDimensional Analysis 1-Classpracticeapi-261484540Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Daily Lesson Log School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Dates and Time November 25, 2022 QuarterDokument6 SeitenDaily Lesson Log School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area MATHEMATICS Dates and Time November 25, 2022 QuarterRydan MinorNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAGNETDokument50 SeitenMAGNETJason CookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 106 Static and Kinetic FrictionDokument5 SeitenLab 106 Static and Kinetic FrictionAbdulahad Malik0% (1)
- Class Xi PhysicsDokument160 SeitenClass Xi PhysicsAdarsh DhawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Mountain - Vol. 1 - Fall, Flow and Heat - The Adventure of PhysicsDokument603 SeitenMotion Mountain - Vol. 1 - Fall, Flow and Heat - The Adventure of Physicsmotionmountain100% (116)
- Kgmol, Kmol, GmolDokument3 SeitenKgmol, Kmol, GmolUmair FareedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Detailed Lesson PlanDokument11 SeitenSample Detailed Lesson PlanppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Namo Kaul Sir LecturesDokument57 SeitenNamo Kaul Sir LecturesAkshit Garg100% (1)
- General Relativity For Pedestrians - First 5 LecturesDokument11 SeitenGeneral Relativity For Pedestrians - First 5 LecturesBir HanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of TimeDokument101 SeitenA Brief History of Timeaadil86% (21)
- Traffic Accident ReconstructionDokument58 SeitenTraffic Accident Reconstructionsandeepsamarth100% (2)
- Physics Grade 10-12Dokument700 SeitenPhysics Grade 10-12SamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Passing Package Notes 2021Dokument31 SeitenPhysics Passing Package Notes 2021swathi80% (5)
- Konversi Energi AnginDokument20 SeitenKonversi Energi AnginReynaldo SembiringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Robotics EvolutionDokument46 SeitenIntroduction to Robotics EvolutionchetanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laws of Motion and FrictionDokument136 SeitenLaws of Motion and FrictionPriyankaMishra100% (1)
- Physics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMDokument13 SeitenPhysics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMShi JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Area Under The Torque vs. RPM Curve: Average PowerDokument22 SeitenArea Under The Torque vs. RPM Curve: Average PowerAdah BumboneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional Status Report of Secondary StudentsDokument3 SeitenNutritional Status Report of Secondary StudentsOliva Cabrales Cabornay100% (1)
- 2022 2024 Syllabus PDFDokument64 Seiten2022 2024 Syllabus PDFNguyen Van DuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and Power PDFDokument2 SeitenWork, Energy and Power PDFTanmay GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isaac NewtonDokument3 SeitenIsaac NewtonJasvinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- "To Find The Charge Induced On Styro Foam Balls Using Coulomb's Law" Physics Investigatory ProjectDokument22 Seiten"To Find The Charge Induced On Styro Foam Balls Using Coulomb's Law" Physics Investigatory ProjectShivendra Tripathi85% (20)
- Hex Web Honeycomb Energy Absorption BrochureDokument20 SeitenHex Web Honeycomb Energy Absorption Brochuresrinivas162Noch keine Bewertungen
- THE PHYSICS UNIVRSE - Units and MeasurementDokument32 SeitenTHE PHYSICS UNIVRSE - Units and MeasurementBrajendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitation QuestionsDokument2 SeitenGravitation QuestionsTrilok AkhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam4 Phy113 F07 Final - KeyDokument10 SeitenExam4 Phy113 F07 Final - Keyntarshish1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of Inertia PMMDokument5 SeitenMoment of Inertia PMMOliviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Elementary Hydraulics 1st Edition by CruiseDokument8 SeitenSolution Manual For Elementary Hydraulics 1st Edition by Cruisea88756243343% (7)
- Pages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter KinematicDokument3 SeitenPages From 5054 - s15 - QP - 21-7 - Chapter Kinematiclelon81Noch keine Bewertungen