Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Topic 11 Unit Plans
Hochgeladen von
api-275333643Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Topic 11 Unit Plans
Hochgeladen von
api-275333643Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
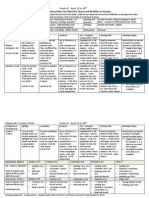
Topic 11 Unit Overview: This is a 2 weeklong lesson plan that uses blended learning.
All groups start together for the 'warm up thinking', the essential question, I can review, mini whole group lesson with a formative assessment to check student
progress through standards. Students then break out into personalized groups around the room and use a blended learning menu that allows them to differentiate by
process, product, or interest. I meet with each group do discuss their progress and, depending on the skill or strategy, formatively assess their understanding at where
they are in their standards/goals. Once time is up, students determine their next steps and independent practice - via homework sheets, problem solving - and include
the video for the next lesson when appropriate.
MAFS.4.OA.2.4 Investigate factors and
MAFS.4.NF.1.1 Explain why a fraction a/b is
MAFS.4.NF.1.2 Compare two fractions with
Standards
multiples. a. Find all factor pairs for a
equivalent to a fraction aXn/bXn by using
different numerators and different denominators, e.g.,
whole number in the range 1-100. b.
visual fraction models, with attention to how
by creating common denominators or numerators, or
Recognize that a whole number is a
the number and size of the parts differ even
by comparing to a benchmark fraction such as .
multiple of each of its factors. Determine
though the two fractions themselves are the
Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the
whether a given whole number in the range same size. Use this principle to recognize and
two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the
1-100 is a multiple of a given one-digit
generate equivalent fractions. Level 2
results of comparisons with symbols >, =, or <, and
number. c. Determine whether a given
justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction
whole number in the range 1-100 is prime
model. Level 2
or composite. Level 2
Must : Create a model to show if a number Should: Explain how two fractions are
Could: Use a variety of strategies to compare
I can
is prime or composite.
equivalent.
fractions.
How
does
my
understanding
of
factors
and
Gifted
Goals:
Learning Styles Addressed: Naturalistic, Visual,
Essential
multiples help me compare fractions?
Musical, Logical, Word, Art, Body
Question
Cognitive Levels: Level 1: Recall, Level 2:
Accommodations: Students do have extra time.
21st Century Technology, team work, independent
Differentiation: Students choose pacing and activity
Basic Application of Skills & Concepts, Level
choice
(menus). Activities have been built around MI and
3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning
learning styles. Desert Choice on Menu
Vocabulary
Lessons
Format
Prime, composite, whole numbers, factors,
numerator, divide, denominator, compare,
common denominator, visual fraction models, justify,
multiples.
fraction, equivalent, fraction bar, multiply
Factors, Prime and Composite Numbers,
Equivalent Fractions, Number Lines,
Multiples,
Comparing, Ordering, Writing to Explain
Start with Whole Group: 20 mins. BEST
Student Small Groups: 40 minutes
benchmark fractions,
Need to do: Resources: Hundred Squares (prime,
composite, multiples, factors, fraction bars, counters
(arrays), graph paper, vocabulary cards, quizlet, Math
Tools: Fractions (Pearson) Videos on Nooks/
IPADS/Sophia. All classes up on Sophia/Quizlet
Teacher Supported Small Groups:
Q1 & Q2. Teacher directed.
BEST Q2 and Q3. Blending Learning Menus.
Assessments Daily Whole Group: Teacher uses white
boards, questioning, and observation to
monitor student understanding. Struggling
students pulled for small group support.
Page 1 of 8
4th Grade Plans
Student choice and differentiated.
Student Work: Students will self assess
understanding through lesson activities.
Teacher will monitor groups and pull any
students who need additional support.
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
Work with Triangles Mon, Wed, Friday. Student requests.
Check on rest through questioning and observation.
Homework: Student Choice
Lessons: Student choice
End of Unit: FSA style assessment at the end of each
topic.
January 6, 2015
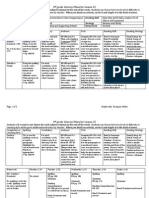
Whole Group Activities
Week 1
Focus
Monday
Whole Group: 20 min. daily BEST Q1 &W2
Students that need support, pull for small group.
Resources
No school Create Topic 13 videos
Tuesday
Review
Introduce
division
Sophia in AM
Introduce
1 Day of
Using white board, warm up with 3 simple division 0-300, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
White board
estimation. Break apart.
Student white
Watch for those that need support in division. Pull for small group.
boards
factors and
Introduce Vocabulary Cards.
LearnZillion
Topic may
multiples.
Show learnzillion video: LZ785.
Video LZ785
take 25 to 30.
Mention prime
Model how ARRAYS can help find FACTORS and MULTIPLES using arrays. Factors: create the different arrays for
st
and composite.
10, 12, 24 using Pearson Math Tools or Drawing on Board. If you can make more than one array, a number has more
Pearson Math
than 2 factors and it is called COMPOSITE. (root compose). Place arrays in a T-Chart and model how you can start
Tool
from factor 1 X n, 2 X, ect until you reach the number in the left column. Explain that these are FACT FAMILIES.
Wednesday Review
What about 2, 3, 7? You can only make one array the number has only 2 factors and is called PRIME. Show in the t-
Use 100 square
Chart that there are only 2 options 1 X n and n X 1.
to find patterns.
Use Pearson Math Tools
Go Over any Menu Options for Lesson 1 students dont understand
Using white board, warm up with 3 simple division 0-300, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
division
estimation.
Watch for those that need support in division. Pull for small group. Link in multiples, factors
Factor,
Show Learn Zillion: LZ799
Multiples,
Review Vocabulary cards
Prime &
Model how to use a Rainbow to find factors of a number. Link to the T-Chart. Start with 1 X n and go in.
Composite
Show Video: Introduce Study Jams on Scholastic.com. Look at the fractions section. (Google or click here)
Go Over any Menu Options for Lesson 2 students dont understand
Use Pearson Math Tools
Page 2 of 8
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
Same
Thursday
Review
division
Fractions/
Equivalent
Fractions
Using white board, warm up with 3 simple division 0-9000, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
White board
estimation.
Student white
Watch for those that need support in division. Pull for small group. Link in multiples, factors
Introduce what is a fraction and vocabulary. What does it mean to be the chosen or not chosen part of the whole?
boards
(numerator). What is the denominator? Represents how many parts make up the whole.
Website
Model fraction bars to find the numerator and denominators. Then, model how to find equivalent fractions . What is
Fraction Bars
the root for equivalent?
Friday
Review
Look at website: http://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/fraction-number-line.html.
Go Over any Menu Options for Lesson 3 students dont understand
Using white board, warm up with 3 simple division 0-9000, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
Same
estimation.
With Khan
Division
Creating an
equivalent
Review:. Numerator, denominator, equivalent fraction. What does it mean to be the chosen or not chosen part of
Video
the whole? (numerator). What is the denominator? Represents how many parts make up the whole.
Large cut out
fraction
using X:
Show: Khan Video: 4 Grade Equivalent Fractions Click Here
Model how 1 = n/n and discuss why. How can we create equivalent fractions? Multiple by 1 or n/n.
Discuss how fraction a/b is equivalent to fraction aXn/bXn because you X by 1 which is the identify
property. Using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts
differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize
and generate equivalent fractions. (Use pizzas as an example or circles folded).
Discuss the idea that equivalent fractions have the same value but are not superposable (use the
example of area of a two different area 2X5 and 1X10the area is equivalent and has same value
but the parts may look different. For equivalent fractions, model a pizza cut in and one cut in
.
factors, and
multiples
What is an
equivalent
fraction?
Page 3 of 8
Watch for those that need support in division. Pull for small group. Link in multiples, factors
th
Go Over any Menu Options for Lesson 4 students dont understand
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
circles (plate
size) to fold
into 1/2
, , 1/8, 1/16,
1/3 (cut)
Week 2
Focus
Monday
Number Lines,
Whole Group: 20 min. daily BEST Q1 &W2
Students that need support, pull for small group.
benchmark
Resources
Using white board, warm up with 3 simple division 0-9000, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
White board
estimation. Break apart. What for those that need support in division and pull for small group.
Student white
fractions to
Model using a number line to find fractions with different numerator and the same denominators.
boards
compare and
Introduce common denominators and link to how they are multiples of the fractions being grouped. Show on relative
Number lines
number lines..2, 4, 8, 16..why not 10 for that group? Is 10 a multiple of 2, 4, 8? Link to fraction bars.
Website
Compare different number lines and show how the denominator links to how the number line is broken up. Review
Fraction bars
order numbers.
Introduce
the difference between the hash marks and the equal parts between 0 and 1. 1 is n/n
common
denominator
http://www.mathsisfun.com/numbers/fraction-number-line.html.
using factors
Introduce a benchmark fractions and create a list of which ones students know readily. How can benchmark fractions
or multiples.
help use understand where a fraction will fit on a number line to help us place them in order from least to greatest.
Discuss starting the number line on the right and going left even though many will start left and go right. Link to
decimals. (right of 0 will be less that 0 in the future).
Tuesday
Review
Go Over any Menu Options for Lesson 5 students dont understand
Using white board, warm up with 2 simple division 0-9000, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
White board
estimation. Break apart. What for those that need support in division/factors/multiples and pull for small group.
Student white
division/factor
s/multiples
Have students find factors and multiples of numbers on a hundred square.
boards
Comparing:
Use a number line and compare two numbers 1, 2 then 1 and 3. How does a number line help you compare and
Number lines
Using what we
understand the value of numbers?
How review number lines with fractions..use to compare fractions , 3/4 , 4/5, 5/8, 6/10. Which fraction has the
Pearson Math
equivalent
greatest value? Which has the least? Using signs < > = Justify. Common error: the larger denominator has the
Tool
fractions,
highest value.
know about
create
common
denominators.
Page 4 of 8
What if you dont have a number line? You can use common denominators! Link to multiples and factors. A
common denominator is a multiple of all the fractions you are comparing. What is a multiple of 2, 4, 5, 8, 10?
Model the butterfly/cross multiplying method to find equivalent fractions with the same denominators.
o Over any Menu Options for Lesson 6 students dont understand
Discuss how multiplication helps use compare?.
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
Wednesday Review
division
Ordering:
Have students find factors and multiples of numbers on a hundred square.
Using
Review the butterfly/cross multiplying method to find equivalent fractions with the same denominators. What is a
denominators,
common denominator?
Now review fractions , 3/4 , 4/5, 5/8, 6/10. Which fraction has the greatest value? Which has the least? Can you use
number lines,
what you know about common denominators to place them in order from Greatest to Least? Common error: the larger
benchmark
denominator has the highest value and language greatest to least
fractions,
Try again with student generated fractions..find the common denominator and then order.
order
What strategies can you use to order fractions? Number lines, fraction bars, common denominators. Have students
fractions.
Writing to
Same
estimation. Break apart. What for those that need support in division/factors/multiples and pull for small group.
common
Thursday
Using white board, warm up with 2 simple division 0-9000, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
discuss when they could or might need to use each strategy.
Over any Menu Options for Lesson 7 students dont understand
Using white board, warm up with 2 simple division 0-9000, 1 digit divisors, with and without remainders and using
White board
estimation. Break apart. What for those that need support in division/factors/multiples and pull for small group.
Student white
Explain
model
Have students find equivalent fractionshave a multiplication square up and look for patterns.
boards
finding key
Show the Pearson Video 11 8
Website
words in
Open up Text book and review Writing to Explain. Go through some problems and identify key words. Link to the
Fraction Bars
operation and create 3 or 4 steps to help students remember how to write a strong explanation.
Multiplication
Square
math
problems
Over any Menu Options for Lesson 8 students dont understand
and using
Model how to take pictures.
Have students discuss what they learned and use PearsonRealize quick check as a
formative assessment whole group. Students will start to use this in the future to
check what they know before the assessment.
the TEA
paragraph.
Friday
Review and
have
students
self assess
Page 5 of 8
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
Internet
Notes for Topic 11 Standards, Targets, and KUDs
MAFS.4.OA.2.4 Investigate factors and multiples.a. Find
a/b
MAFS.4.NF.1.1 Explain why a fraction
is equivalent
all factor pairs for a whole number in the range 1-100.b.
nXa/nXb
Recognize that a whole number is a multiple of each of its
to a fraction
by using visual fraction models, with
factors. Determine whether a given whole number in the
attention to how the number and size of the parts differ
range 1-100 is a multiple of a given one-digit number. c.
even though the two fractions b nb themselves are the
Determine whether a given whole number in the range 1same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate
100 is prime or composite.
equivalent fractions.
My Targets: OA 2.4
I can explain the difference between prime and composite
numbers.
I can identify the factors or multiples of whole numbers.
I understand that whole numbers are factors of their
product.
I understand the difference between prime and composite
numbers
I understand that multiples are products of any two whole
numbers.
Assessment (Do)
I can create a model that shows factors of any given whole
number up to 100.
I can complete a fact family.
I can compose a list of prime and composite numbers.
MAFS.4.NF.1.2 Compare two fractions with different
numerators and different denominators, e.g., by creating
common denominators or numerators, or by comparing to
1/2
a benchmark fraction such as
. Recognize that
comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to
the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with
symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by
using a visual fraction model.
Targets: MAFS.4.NF.1.1
I know that a fraction is part of a whole and has a
numerator and denominator.
I know what makes fractions equivalent.
I know equivalent means the numbers have the same
value.
I can use my multiplication facts and multiples to find
equivalent fractions.
I understand that fractions can be equivalent even when
numerators and denominators are not the same.
I can create models of fractions to see the parts of a
fraction.
Targets: MAFS.4.NF.1.2
I know how numerators and denominators are used to
compare fractions.
I know when the common denominator is and can explain
how it is a multiple of the denominators being compared.
I understand that the denominator is how many equal parts
make the whole and the numerator is the number of parts
chosen or not chosen.
I understand that comparisons are valid only when the two
fractions refer to the same whole.
I understand that other fractions can be used as
benchmarks to help make comparisons.
Assessment (Do)
I can manipulate fraction tools to make equivalents.
I can explain how two fractions are equal.
I can draw pictures to represent equivalent fractions
I can create number sentences using equivalent fractions.
Vocabulary: numerator, divide, denominator, compare,
fraction, equivalent, fraction bar, multiply
Assessment (Do)
I can construct a visual model of 2 fractions being
compared.
I can use the correct symbol to compare fractions.
I can apply multiplication and division skills to change
denominators in order to compare fractions.
I can use a variety of strategies to compare fractions.
Vocabulary: common denominator, visual fraction models,
justify, benchmark fractions,
Page 6 of 8
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
Tomassis Original Groups: Changed 10/15, 11/15, 12/15
Tory (60), Tieler (50), Jaylen, Ben, Alexa (60), Faith (based on understanding of place value)
Cohen (95) & Jackson (100) (based on inventory)
Vinni, Madi, Aiden, Brielle, Ben, Haley, Joshua, Ethan, Pierce (50), Sami (50)
Jaden (40), Nevaeh (45), Christopher (40)
By aptitude and demonstrated pacing: 12/15
Stars: Jaylen, Cohen, Vinnie
Hexagons: Brielle, Ben,
Pentagons: Aiden, Jackson
Trapezoids: Tieler, Alexa, Faith, Aiden, Haley, Madi
Squares: Ethan, Pierce, Triangles: Sami, Nevaeh, Tori Joshua, Christopher, Jaden, Carlos, Abby
Jenns Groups
Whites Groups
Page 7 of 8
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
MAXS Math Caf Topic 11 Menu
Standards & Objectives: OA 2.4, NF 1.1, NF 1.2
Must: Create a model to show if a number is prime or
composite.
Should: Explain how two fractions are equivalent.
Could: Use a variety of strategies to compare fractions.
Appetizer: Must complete for each lesson or unit
o
Vocabulary Choice/once a unit
o
Watch video on Nook or on Sophia (Mrs.Ts Version)
Main Course: Must complete ALL for each lesson. Review and discuss
results with a partner. Self-Assess Understanding (0 to 5)
o Guided Practice (review and discuss with partner)
o Select from Main Course options.
o Problem Solving: All
Carry Out: (Homework): Choose one for each lesson then review
and discuss with partner. Self-Assess understanding (o to 5).
o Independent Practice: evens or odds
o Homework practice sheet
o Create a model for 5 Independent Practice Problems. Illustrate in IAN.
o Write to Explain: How you solve 4 Practice Problems
Dessert: Go to the Dessert Table and choose one AFTER you have completed 3 or 4
meals. Then reflect in your IAN with your thoughts and question.
Main
Course Selections
Lesson 1/Factors :
Hands on: Use blocks or counters to create different arrays to find the factors for
numbers 36, 55, 79, 88 in the 100 block. Draw your arrays.
Artistic: Create factor rainbows for 36, 55, 79, 88 and explain the steps.
Logical: Learnzillion Video LZ782. Create a flow map.
Lesson 2/Prime and Composite: Answer questions in your IAN.
Hands on: Use blocks to make arrays for numbers higher in the 100 block. Can
you make more than one array for the number? How do you know if its prime?
Artistic: Draw an illustration that explains the difference between a prime and
composite number. Create a Venn diagram to compare prime and composite.
Logical: Learnzillion VideoLZ786. Take 2 column notes in your IAN.
Musical: Im Prime Rap on Sophia or Nooks. Explain the difference between
prime and composite numbers in your IAN. Give examples.
Hands on: Using counters, create arrays that show multiples of 3, 13, 9, and 12.
Find the lowest common multiple for 3 and 13, then 9 and 12. Share.
Artistic: Using graph paper draw arrays to find the multiples of 3, 13, 9, 12 and
find the lowest common multiple for 3 and 13, then 9 and 12. Share.
Logical: Learnzillion Video LZ781. Explain how you know a number is a
multiple or a factor?
Lesson 4/Equivalent Fractions: After doing the activity, in your IAN, justify how you
know when 2 fractions are equivalent.
Hands on: Take circles and fold them into different fraction amounts , , 1/8
and find equivalent fractions.
Artistic: Using the fraction pieces, create an illustration that shows equivalent
fractions. (Teacher will model.)
Logical: Choose from Study Jams on Scholastic/Fractions. 2 Column Notes.
Musical: Rock the Core/Equivalent fractions (Sophia/Nook).
Lesson 5/Number Lines & Equivalent Fractions:
Hands on: Use the fraction bars to create 2 number lines and find equivalent
fractions. Draw your examples in your IAN.
Logical: Learnzillion Video LZ619 and LZ617. Create a Double Bubble to
compare the two videos.
Musical: What the Video above and create a verse that explains how to use
number lines to find equivalent fractions.
Lesson 6/Comparing: When you are finished with your activity, in your IAN, explain
how you know which fraction is the larger or smaller?
Hands on: Using fraction bars to compare fractions.
Artistic: Create cross-multiplying butterflies to compare fractions.
Logical: Study Jams/Scholastic Fractions. Write a 1 sentence summary.
Lesson 7/Ordering:
Hands on: Using fraction bars, show fractions and order them from least to
greatest. Draw them in your IAN.
Artistic: Draw an illustration that shows fractions with different denominators in
order. Note the steps you took to figure out how to order the fractions.
Logical : Study Jams/Scholastic/Fractions. Take 2 Column Notes.
Lesson 8/Writing to Explain: You will use the following activities to create a tool to
share your idea for key steps to write a good explanation.
Hands on: Create a Standing Cube Foldable to highlight 4 key reminders.
Artistic: Create a comic that explains some key points.
Logical: Create a flow chart that shows the steps to writing a good explanation.
When all meals (lessons) complete,
see teacher for final UNIT assessment.
Main Course Selections Continue
Lesson 3/Multiples: Still struggling? Learnzillion LZ789 and See teacher.
Page 8 of 8
4th Grade Plans
Mazlowski, Tomassi, White
January 6, 2015
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Ela April 13 To 24 Spelling ListDokument1 SeiteEla April 13 To 24 Spelling Listapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Tracking My Progress 2014Dokument2 SeitenTracking My Progress 2014api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Beginningof Year Parent SurveyDokument1 Seite0 Beginningof Year Parent Surveyapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Force For GoodDokument1 SeiteForce For Goodapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- 0pdf Version Blooms Taxonmy Posters Final 192012Dokument12 Seiten0pdf Version Blooms Taxonmy Posters Final 192012api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- 0pdf Version Blooms Taxonmy Posters Final 192012Dokument12 Seiten0pdf Version Blooms Taxonmy Posters Final 192012api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Topic 17 Whole Group Lesson PlanDokument7 SeitenTopic 17 Whole Group Lesson Planapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Lesson Plan Topic 15Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Topic 15api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Ela April 13 To 24 Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenEla April 13 To 24 Lesson Planapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Vocab Topic 15Dokument3 SeitenVocab Topic 15api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Kud Topic 15Dokument1 SeiteKud Topic 15api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Topic 13 KudDokument1 SeiteTopic 13 Kudapi-275333643100% (1)
- Ela April 13 To 24 MenuDokument2 SeitenEla April 13 To 24 Menuapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Topic 14 Vocab WordsDokument5 SeitenTopic 14 Vocab Wordsapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Menu Jan 26 To Feb 6 ElaDokument3 SeitenMenu Jan 26 To Feb 6 Elaapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Topic 14 KudsDokument1 SeiteTopic 14 Kudsapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Topic 14 MenuDokument1 SeiteTopic 14 Menuapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 16 Spelling ListDokument1 SeiteLesson 16 Spelling Listapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ela Feb 9 Belaa and Lesson 17 Menu OnlyDokument2 SeitenEla Feb 9 Belaa and Lesson 17 Menu Onlyapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spelling List 17Dokument1 SeiteSpelling List 17api-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 13 VocabDokument2 SeitenTopic 13 Vocabapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Topic 13 OverviewDokument6 SeitenTopic 13 Overviewapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 13 MenuDokument1 SeiteTopic 13 Menuapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ela Feb 9 Belaa and Lesson 17 Lesson OnlyDokument2 SeitenEla Feb 9 Belaa and Lesson 17 Lesson Onlyapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Ela Jan 26 To Feb 6 Lesson PlansDokument2 SeitenEla Jan 26 To Feb 6 Lesson Plansapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 15 Spelling WordsDokument1 SeiteLesson 15 Spelling Wordsapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ela Jan 20 Lesson 15 Literacy MenuDokument3 SeitenEla Jan 20 Lesson 15 Literacy Menuapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 12 Menu ADokument1 SeiteTopic 12 Menu Aapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Topic 12 Vocabulary Mrs TsDokument2 SeitenTopic 12 Vocabulary Mrs Tsapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 12 Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenTopic 12 Lesson Planapi-275333643Noch keine Bewertungen
- Binomial ProbabilityDokument14 SeitenBinomial ProbabilityNajib HamdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generating Functions: 1 From Recurrences To Closed FormDokument9 SeitenGenerating Functions: 1 From Recurrences To Closed FormvarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand-In 4B 2023Dokument3 SeitenHand-In 4B 2023zubinbhatt003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Exercises 2011 PartIDokument27 SeitenSolution Exercises 2011 PartIcecch001100% (1)
- Additional Math 0606 Nov 15 - QP - 21Dokument16 SeitenAdditional Math 0606 Nov 15 - QP - 21CorinSaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Control Theory Applications With MatlabDokument152 SeitenAn Introduction To Control Theory Applications With MatlabDimitris TzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imaginary PhysicsDokument70 SeitenImaginary PhysicsesotecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mat 1512 (Calculus A)Dokument169 SeitenMat 1512 (Calculus A)Anonymous 7TSpgrU100% (1)
- 4D Seismic ProcessingDokument20 Seiten4D Seismic Processinggatt100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Dynamics Chapter 7Dokument118 SeitenDynamics Chapter 7Hisyammudin RoslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science 3A - CSC3A10/CSC03A3: Lecture 2: Arrays, Linked Lists and RecursionDokument66 SeitenComputer Science 3A - CSC3A10/CSC03A3: Lecture 2: Arrays, Linked Lists and Recursionthapelo mokoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- AM 5030 - Linear Dynamical Systems: Assignment-1Dokument1 SeiteAM 5030 - Linear Dynamical Systems: Assignment-1spartha_beNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOL - Slides Part 1Dokument157 SeitenFOL - Slides Part 1karthika geethanandNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgrammingDokument35 SeitenC ProgrammingKartik ShroffNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMW ReviewerDokument2 SeitenMMW ReviewerPatricia May CayagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number System Conversions: Name: DateDokument2 SeitenNumber System Conversions: Name: DateAileenD.EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Levin Chapter 1Dokument4 SeitenLevin Chapter 1Vibhav MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mixed Revision 2Dokument4 SeitenMixed Revision 2Ly ShanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Math FormulasDokument3 SeitenBasic Math FormulasRachel BranchNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLMC (Africa) 2022: Curriculum Guide: July 14 2021Dokument4 SeitenCLMC (Africa) 2022: Curriculum Guide: July 14 2021Onyinyechi SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mumbai University Sem III-IV Electronics and Telecommunication EnggDokument49 SeitenMumbai University Sem III-IV Electronics and Telecommunication EnggAbhijit SomnatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Operations On IntegersDokument2 SeitenFundamental Operations On IntegersShou WakahisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASIC CALCULUS 5thDokument11 SeitenBASIC CALCULUS 5thLaika LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 07L Integral Calculus Differential EquationsDokument1 SeiteMathematics 07L Integral Calculus Differential Equationsjake luis matthewNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR 410101 Computer Aided AnalysisDokument8 SeitenNR 410101 Computer Aided AnalysisSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- A, B, C, D, E, F, G Adb, Age, Afc, Bec, BGF, CGD, FdeDokument2 SeitenA, B, C, D, E, F, G Adb, Age, Afc, Bec, BGF, CGD, FdeJohn Esteves GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uncertainties and Data Graphing - Assignment Excel InstructionsDokument16 SeitenUncertainties and Data Graphing - Assignment Excel InstructionsuwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Number GB Sir Module PDFDokument24 SeitenComplex Number GB Sir Module PDFXyzAbccNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-RMO Major # SolutionDokument15 SeitenPre-RMO Major # SolutionSapna AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Performance Improvement PlanDokument4 SeitenAcademic Performance Improvement PlancindyNoch keine Bewertungen