Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Waves4 - 4.5
Hochgeladen von
AliiAmiirOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Waves4 - 4.5
Hochgeladen von
AliiAmiirCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
4.
5 Wave Properties
Reflection, refraction and transmission of waves
4.5.1
Describe the reflection and transmission of waves at a boundary between two
media.
Fixed end
Free end
incident
reflected
4.5.2
State and apply Snells law.
If the indices of refraction of the media are n 1 and n2, and the angle of
incidence 1 and refraction 2 are measured relative to the normal, then
n1sin 1 = n2sin 2
assuming both rays and the normal are in the same plane.
4.5.3
Explain and discuss qualitatively the diffraction of waves at apertures and
obstacles.
Wavelength < aperture
Wavelength > aperture
Negligible diffraction
Wavelength < obstacle
Wave is
spreading
Wavelength > obstacle
No wave
here
4.5.4
Describe examples of diffraction.
4.5.5
Water waves, sound waves around corners, etc.
State the principle of superposition and explain what is meant by constructive
interference and by destructive interference.
Principle of Superposition: When two or more waves pass the same point,
the resulting wave is the sum of the individual waves, and after passing, the
waves continue along their paths as if no encounter has occurred
4.5.6
State and apply the conditions for constructive and for destructive interference
in terms of path difference and phase difference.
4.5.7
Apply the principle of superposition to determine the resultant of two waves.
Sum of displacements:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IAL Physics WavesDokument17 SeitenIAL Physics Wavesvekariaraj99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Waves5 - 4.5 Part 2Dokument3 SeitenWaves5 - 4.5 Part 2AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavesDokument11 SeitenWavesdilsharakaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter SevenDokument10 SeitenChapter Sevensaed cabdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Wave OpticsDokument7 Seiten10 Wave OpticsNivil MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves, Particles, Light and Matter in U4Dokument28 SeitenWaves, Particles, Light and Matter in U4Kevin LEENoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Mod8 ActivitiesDokument3 SeitenScience Mod8 ActivitiesJose Ernesto OngocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves (Physics)Dokument55 SeitenWaves (Physics)Chloe HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klmpok 5 (Xi Mipa 3)Dokument15 SeitenKlmpok 5 (Xi Mipa 3)어록어록Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01-Unit-01-Waves and Optics Lectures L1-L3Dokument15 Seiten01-Unit-01-Waves and Optics Lectures L1-L3Evariste MigaboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interference of Light by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaDokument11 SeitenInterference of Light by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaCharis Israel Ancha100% (1)
- Articulo IeeeDokument5 SeitenArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- GenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 4Dokument18 SeitenGenPhysics2 - Q2 Module 4Jasmin SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave OpticsDokument12 SeitenWave Opticsrishi kaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 HuygenPrincipleDokument15 Seiten8 HuygenPrincipleShaina Joice PortugalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - 4 - Wave CharacteristicsDokument39 SeitenTopic 4 - 4 - Wave CharacteristicsRonak TopraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave and OpticsDokument21 SeitenWave and Opticsgerlie badilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves: Important PointsDokument23 SeitenWaves: Important PointsBunny TarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 09 Properties of Mechanical WavesDokument39 SeitenC 09 Properties of Mechanical Waveszaliha a-voyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffraction: Diffraction Refers To Various PhenomenaDokument70 SeitenDiffraction: Diffraction Refers To Various PhenomenaRizwanbhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defraction of LightDokument21 SeitenDefraction of Lightlyricafiesta1205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Waves Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 15 - Learn CBSEDokument9 SeitenWaves Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 15 - Learn CBSERishabh Singh RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Aries Triwidajati S. SPDDokument19 SeitenBy Aries Triwidajati S. SPDaries triwidajatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingDokument40 SeitenWaves: Ivan L. Saligumba Institute of Education and Teacher TrainingGellirose S. Bantayan100% (1)
- OpticsDokument35 SeitenOpticsMd. Sayeed HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 10 Wave Optics: Newton's Corpuscular TheoryDokument9 SeitenPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 10 Wave Optics: Newton's Corpuscular TheoryAnkush AnchliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction of LightDokument11 SeitenRefraction of Lightshamitmajor100% (1)
- Lecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1Dokument9 SeitenLecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1samarthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defraction-Of-Light (1) - Investigatory ProjectDokument17 SeitenDefraction-Of-Light (1) - Investigatory ProjectSankar AnanthyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Physics Submitted To: Dr. Muhammad Irfan Sahib Submitted By: Hammad Ghaffar Roll No. F20BPHYS3E01009Dokument8 SeitenInstitute of Physics Submitted To: Dr. Muhammad Irfan Sahib Submitted By: Hammad Ghaffar Roll No. F20BPHYS3E01009Hoomi ShbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4.2 - Traveling WavesDokument48 SeitenTopic 4.2 - Traveling Wavesusha pittyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Slit Project 6Dokument26 SeitenDouble Slit Project 6mnaqash272000Noch keine Bewertungen
- 07 WavesDokument23 Seiten07 Wavesfisica2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 Types and Properties of WavesDokument30 SeitenWeek 3 Types and Properties of WavesNyityo IsraelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4.4 - Wave BehaviorDokument49 SeitenTopic 4.4 - Wave BehaviorpepperoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011-01-22 U13 General Properties of WavesDokument3 Seiten2011-01-22 U13 General Properties of WavesGanesh MuthupalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light As An Electromagnetic WaveDokument30 SeitenLight As An Electromagnetic WaveKit Augustine TantoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defraction of Light (Physics Investigatory Project)Dokument20 SeitenDefraction of Light (Physics Investigatory Project)Darshan Patil100% (2)
- Wave Optics: IntroductionDokument15 SeitenWave Optics: IntroductionChandra sekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- TG Science 9Dokument41 SeitenTG Science 9Norweena QuinonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Study Materials - Wave OpticsDokument7 SeitenPhysics Study Materials - Wave OpticschashmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaveDokument14 SeitenWaveLitiaMikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 5, Chapter 14Dokument36 SeitenCPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 5, Chapter 14Kyle TacisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ok 4Dokument25 SeitenOk 4mnaqash272000Noch keine Bewertungen
- WavefrontDokument9 SeitenWavefrontlavanyaamirtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavesDokument34 SeitenWavessridevi73Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysing Diffraction of WavesDokument20 SeitenAnalysing Diffraction of WavesAshley AngNoch keine Bewertungen
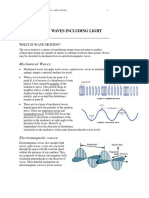
- Topic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?Dokument11 SeitenTopic 3 Properties of Waves Including Light and Sound: What Is Wave Motion?PichakornNoch keine Bewertungen
- InterferometryDokument30 SeitenInterferometryEjaz AshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH 11 Waves NotesDokument11 SeitenPH 11 Waves NotesTikeshwar Sharma100% (1)
- WavesDokument21 SeitenWavesTintinententen Christine TintinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4.2 - Traveling Waves - TeacherDokument46 SeitenTopic 4.2 - Traveling Waves - TeacherGhanshyam PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Kafeel Khan Cu-372-2017Dokument7 SeitenM Kafeel Khan Cu-372-2017khan janNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaveDokument54 SeitenWaveriyacomputerNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 4.4: WavesDokument7 SeitenOCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 4.4: WavesjmsonlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy PPT FinalDokument29 SeitenPhy PPT FinalReck OnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 - WavesDokument12 SeitenUnit 3 - WavesT. Christabel VijithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave 25 November 2021Dokument41 SeitenWave 25 November 2021Ulfa Mahfudli FadliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maxwell's Equations and the Principles of Electromagnetic PhenomenaVon EverandMaxwell's Equations and the Principles of Electromagnetic PhenomenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksVon EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Addition & Subtraction - Sept 24Dokument1 SeiteVector Addition & Subtraction - Sept 24AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Review IB Questions MSDokument7 SeitenTopic 1 Review IB Questions MSAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - Graphical TechniquesDokument1 SeiteLesson 3 - Graphical TechniquesAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1: "What Order of Magnitude?" Game - Getting A Feel For MagnitudesDokument4 SeitenPart 1: "What Order of Magnitude?" Game - Getting A Feel For MagnitudesAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson - 5 Vectors and ScalarsDokument3 SeitenLesson - 5 Vectors and ScalarsAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base UnitsDokument1 SeiteBase UnitsAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.5 Polarization: n = sin φ / cos φ or n = tan φDokument2 Seiten11.5 Polarization: n = sin φ / cos φ or n = tan φAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - Uncertainty and ErrorDokument3 SeitenLesson 2 - Uncertainty and ErrorAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphing: How Do I Make A Graph?Dokument8 SeitenGraphing: How Do I Make A Graph?AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macbeth CastingDokument5 SeitenMacbeth CastingAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lab - 03 Measurement Instrument CircusDokument1 SeiteIB Lab - 03 Measurement Instrument CircusAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - Oscillations and WavesDokument1 SeiteTopic 4 - Oscillations and WavesAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Instrument CircusDokument1 SeiteMeasurement Instrument CircusAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - Oscillations and WavesDokument1 SeiteTopic 4 - Oscillations and WavesAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves: 4.1. Waves in One Dimension (Sections 4.1 - 4.6)Dokument20 SeitenWaves: 4.1. Waves in One Dimension (Sections 4.1 - 4.6)Claudia Rosaleen LsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves3 - 4.4Dokument3 SeitenWaves3 - 4.4AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - Oscillations and Waves: 4.1 Kinematics of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)Dokument2 SeitenTopic 4 - Oscillations and Waves: 4.1 Kinematics of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.5.1 Describe The Reflection and Transmission of Waves at A Boundary Between Two MediaDokument3 Seiten4.5.1 Describe The Reflection and Transmission of Waves at A Boundary Between Two MediaAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
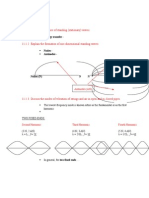
- 11.1.1 Describe The Nature of Standing (Stationary) WavesDokument3 Seiten11.1.1 Describe The Nature of Standing (Stationary) WavesAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves8 - 11.2Dokument2 SeitenWaves8 - 11.2AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves3 - 4.4Dokument3 SeitenWaves3 - 4.4AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitDokument4 Seiten11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitDokument4 Seiten11.3.1 Sketch The Variation With Angle of Diffraction of The Relative Intensity of Light Diffracted at A Single SlitAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.1.1 Describe The Nature of Standing (Stationary) WavesDokument3 Seiten11.1.1 Describe The Nature of Standing (Stationary) WavesAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves8 - 11.2Dokument2 SeitenWaves8 - 11.2AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - Oscillations and Waves: 4.1 Kinematics of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)Dokument2 SeitenTopic 4 - Oscillations and Waves: 4.1 Kinematics of Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)AliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.5 Polarization: n = sin φ / cos φ or n = tan φDokument2 Seiten11.5 Polarization: n = sin φ / cos φ or n = tan φAliiAmiirNoch keine Bewertungen