Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 14
Hochgeladen von
Sujay SantraOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 14
Hochgeladen von
Sujay SantraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
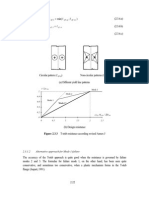
The simplified prediction of deformations of a rigid plate supported by an elastic half space is
considered first including the shape of the rectangular plate. In a second step, an indication is
given how to replace a flexible plate by an equivalent rigid plate. In the last step, assumptions
are made about the effect of the size of the block to the deformations under the plate for
practical base plates.
The deformation of a rectangular rigid plate in equivalent half space solved by different
authors is given in simplified form by Lambe & Whitman, 1967 as
r =
ar
E c Ar
(2.1.6)
where
r
F
ar
Ec
Ar
L
is the deformation under a rigid plate,
the applied compressed force,
the width of the rigid plate,
the Young's modulus of concrete,
the area of the plate, Ar = a r L ,
the length of the plate,
a factor dependent on ratio between L and ar .
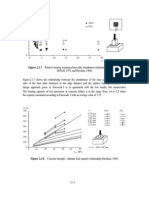
The value of factor depends on the Poison's ratio of the compressed material, see in
Table 2.1.1, for concrete ( 0,15). The approximation of this values as 0 ,85
L / ar
can be read from the following Table 2.1.1.
Table 2.1.1 Factor and its approximation
L / ar
according to
(Lambe and Whitman, 1967)
1
1,5
2
3
5
10
0,90
1,10
1,25
1,47
1,76
2,17
Approximation as
0 ,85
L / ar
0,85
1,04
1,20
1,47
1,90
2,69
With the approximation for , the formula for the displacement under the plate can be
rewritten
2.6
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 43Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 43Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 32Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 32Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 42Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 42Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 30Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 30Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 31Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 31Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 28Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 28Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 29Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 29Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 17Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 17Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 19Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 19Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 23Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 23Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 15Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 15Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 16Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 16Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength and Workability Characteristics of Concrete by Using Different Super PlasticizersDokument5 SeitenStrength and Workability Characteristics of Concrete by Using Different Super PlasticizersSujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: Component Characteristics: 2.1 Concrete in Compression and Base Plate in BendingDokument1 SeiteChapter 2: Component Characteristics: 2.1 Concrete in Compression and Base Plate in BendingSujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 13Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 13Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 10Dokument1 SeiteBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 10Sujay SantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)