Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dynamic Analysis Vs
Hochgeladen von
Ymon Tualla0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
6 Ansichten1 Seiteok
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenok
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
6 Ansichten1 SeiteDynamic Analysis Vs
Hochgeladen von
Ymon Tuallaok
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
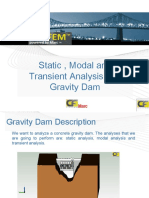
Dynamic Analysis vs.
Static Analysis
Dynamic analysis is the testing and evaluation of an application during runtime.
Static analysis is the testing and evaluation of an application by examining the code without
executing the application.
2.1 Definition of Static Analysis
A static analysis calculates the effects of steady loading conditions on a structure,
while ignoring inertia and damping effects, such as those caused by time-varying
loads. A static analysis can, however, include steady inertia loads (such as gravity and
rotational velocity), and time-varying loads that can be approximated as static
equivalent loads (such as the static equivalent wind and seismic loads commonly
defined in many building codes).
Two basic aspects of dynamic analysis differ from static analysis. First, dynamic loads are applied as
a function of time or frequency-. Second, this time or frequency-varying load application induces time
or frequency-varying response (displacements, velocities, accelerations, forces, and stresses).
These time or frequency-varying characteristics make dynamic analysis more complicated and more
realistic than static analysis.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sourav Kabiraj - Structural Dynamics Ca1Dokument11 SeitenSourav Kabiraj - Structural Dynamics Ca1Sourav KabirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing The Principles of Static and Dynamic Analysis in Finite Element MethodDokument8 SeitenComparing The Principles of Static and Dynamic Analysis in Finite Element Methodpaul ostepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Linear Pushover AnalysisDokument10 SeitenNon Linear Pushover AnalysisyibungoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 Introduction 2023Dokument19 SeitenLecture 1 Introduction 2023yakwetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-3 Methodology 3.1 GeneralDokument35 SeitenChapter-3 Methodology 3.1 GeneralNoor MohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Linear Static Analysis Procedure, LSPDokument3 Seiten2.1 Linear Static Analysis Procedure, LSPSrinivas NagarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- A4 Structural Vibration and Ways To Avoid It ArticleDokument4 SeitenA4 Structural Vibration and Ways To Avoid It Articlegiovanni1912Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering-Ch 1-5Dokument58 SeitenStructural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering-Ch 1-5Lucas PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irjet A Nonlinear Time History AnalysisDokument8 SeitenIrjet A Nonlinear Time History AnalysisRathod IndravadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On: Sal Institute of Technlogy & ENGG. ResearchDokument11 SeitenPresentation On: Sal Institute of Technlogy & ENGG. ResearchSunil KadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organizedby Centro Internazionaledi Aggiornamento SperimentaleDokument18 SeitenOrganizedby Centro Internazionaledi Aggiornamento SperimentaleFernando SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnalysisDokument14 SeitenAnalysisSangeeta DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dam ST043 LeclercDokument10 SeitenDam ST043 LeclercRicardo Jesus Mallma CubasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysi of Static & Dynamic LoadsDokument3 SeitenAnalysi of Static & Dynamic LoadssyednajaffiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' Policy and Guidance For Seismic Design of Dams-Anjana Chudgar and Enrique E. MatheuDokument9 SeitenCurrent U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' Policy and Guidance For Seismic Design of Dams-Anjana Chudgar and Enrique E. Matheurajesh005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Design For Anchors PDFDokument55 SeitenDynamic Design For Anchors PDFJeferson QuispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Application GuidelinesDokument391 SeitenDesign and Application GuidelinesonspsnonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One: 1-1introductionDokument77 SeitenChapter One: 1-1introductionahmedanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Analysis of Multistoried Regular BuildingDokument6 SeitenDynamic Analysis of Multistoried Regular BuildingapirakqNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Procedure To Perform Pushover AnalysisDokument16 SeitenGeneral Procedure To Perform Pushover AnalysisalbikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part IDokument18 SeitenPart IAditi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Linear and Non-Linear Analysis For Practicing Structural Engineers PDFDokument27 SeitenOverview of Linear and Non-Linear Analysis For Practicing Structural Engineers PDFMin Thiha NaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective of A Pushover AnalysisDokument3 SeitenObjective of A Pushover Analysishemantkle2uNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAESAR II Dynamic Text BookDokument120 SeitenCAESAR II Dynamic Text BookKagira Drawing Soltuion100% (1)
- Fatigue Life Evaluation of Mechanical Components Using Vibration Fatigue Analysis TechniqueDokument7 SeitenFatigue Life Evaluation of Mechanical Components Using Vibration Fatigue Analysis TechniquemariomatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Span Bridge Health Monitoring System in Japan PDFDokument8 SeitenLong Span Bridge Health Monitoring System in Japan PDFblukututNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Dynamics, Therefore, Is A Type ofDokument5 SeitenStructural Dynamics, Therefore, Is A Type ofntah84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shape Optimization of Structures Under Earthquake Loadings: Amirhossein SadoughiDokument12 SeitenShape Optimization of Structures Under Earthquake Loadings: Amirhossein SadoughiBianca CalugaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Linear Static Push Over AnalysisDokument12 SeitenNon-Linear Static Push Over Analysismrnicus100% (1)
- Overview of Key Stability Concepts Applied For Real-Time OperationsDokument6 SeitenOverview of Key Stability Concepts Applied For Real-Time OperationsqbjohnnydpNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Practical Approximate Inelastic Seismic Design Procedures For New and Existing BuildingsDokument21 SeitenA Review of Practical Approximate Inelastic Seismic Design Procedures For New and Existing Buildingsm_ganea268973Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pushover Anlysis: 1.1 Definition of Pushover AnalysisDokument4 SeitenPushover Anlysis: 1.1 Definition of Pushover AnalysisRamkishore ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument29 SeitenLiterature ReviewKarl BognotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Stability Analysis of Gravity DamsDokument10 SeitenComputer Aided Stability Analysis of Gravity DamsgorkapagoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Structural Analysis and DesignDokument5 SeitenIntroduction To Structural Analysis and DesignOluwatobi OgunfoworaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Analysis: SeismicDokument3 SeitenNonlinear Analysis: SeismicBandula PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Major Design PhilosophiesDokument4 SeitenThree Major Design PhilosophiesFatima Ahmed100% (1)
- Dynamic Design For AnchorsDokument44 SeitenDynamic Design For AnchorshoustonhimselfNoch keine Bewertungen
- CivilFEM - Marc Gravity Dam3DDokument13 SeitenCivilFEM - Marc Gravity Dam3DHeb RuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13001319046Dokument9 Seiten130013190469046Mayank RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Application GuidelinesDokument617 SeitenDesign and Application GuidelinesVictor RomeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadam - Overview of Main Features and Analysis OptionsDokument1 SeiteCadam - Overview of Main Features and Analysis OptionsEnriqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Analysis of Bridge Under Vehicle Load Using MATLAB and Evaluation of AASHTO Impact FormulaDokument6 SeitenDynamic Analysis of Bridge Under Vehicle Load Using MATLAB and Evaluation of AASHTO Impact FormulaeddieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature ReviewDokument8 SeitenLiterature ReviewGio AsombradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Series Question SolveDokument31 Seiten16 Series Question SolveMd imam hossen mehediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name-Mayank Ranjan Roll-13001319046 Dept-Civil Topic-Dynamics of StructuresDokument9 SeitenName-Mayank Ranjan Roll-13001319046 Dept-Civil Topic-Dynamics of Structures9046Mayank RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Linear Static Push-Over Analysis: Modern-Spanish DesignDokument14 SeitenNon-Linear Static Push-Over Analysis: Modern-Spanish DesignmustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUSHOVERDokument5 SeitenPUSHOVERMehedi Bin SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time History Analysis: Submitted By: Sarita Acharya 2018016460 M.tech Structure Submitted To: Mrs. Chavvi GuptaDokument15 SeitenTime History Analysis: Submitted By: Sarita Acharya 2018016460 M.tech Structure Submitted To: Mrs. Chavvi Guptaer.praveenraj30Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isgtla17 TrendsDokument6 SeitenIsgtla17 TrendsAlejandro TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods For Reliability Analysis of Engineering Structures Based On Statistical TheoryDokument7 SeitenResearch Methods For Reliability Analysis of Engineering Structures Based On Statistical Theorynabin nitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' Policy and Guidance For Seismic Design of Dams PDFDokument9 SeitenCurrent U.S. Army Corps of Engineers' Policy and Guidance For Seismic Design of Dams PDFpicottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Fatigue Analysis Handbook: Practical Problem-solving Techniques for Computer-aided EngineeringVon EverandMetal Fatigue Analysis Handbook: Practical Problem-solving Techniques for Computer-aided EngineeringBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (5)
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresVon EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (22)
- Velocity Moments: Capturing the Dynamics: Insights into Computer VisionVon EverandVelocity Moments: Capturing the Dynamics: Insights into Computer VisionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis Procedure for Earthquake Resistant StructuresVon EverandAnalysis Procedure for Earthquake Resistant StructuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- PinterestDokument3 SeitenPinterestYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cle Notes 2ND PeriodicalDokument3 SeitenCle Notes 2ND PeriodicalYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practise Book Oet Listening Set1 Audio LinksDokument1 SeitePractise Book Oet Listening Set1 Audio LinksYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Nursing Lecture 59 Pages Pg. 274 332Dokument59 SeitenPediatric Nursing Lecture 59 Pages Pg. 274 332Ymon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Plan 3.pdf - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Dokument1 Seite1.2 Plan 3.pdf - (FreeCourseWeb - Com)Ymon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Probability Sampling MethodsDokument6 SeitenA. Probability Sampling MethodsYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Research: I. DefinitionsDokument7 SeitenNursing Research: I. DefinitionsYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership and ManagementDokument5 SeitenLeadership and ManagementYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Scheduling Schedule: Be Determined With A Simple Worker-Patient Ratio or FormulaDokument7 SeitenB. Scheduling Schedule: Be Determined With A Simple Worker-Patient Ratio or FormulaYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELearning Manual Handling Tutorial V 9 - June 2015 - ACN Approved Feb 2016Dokument29 SeitenELearning Manual Handling Tutorial V 9 - June 2015 - ACN Approved Feb 2016Ymon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8Dokument8 Seiten8Ymon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3Dokument5 Seiten3Ymon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout in MAPEH Grade 1 ABCDEDokument2 SeitenHandout in MAPEH Grade 1 ABCDEYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Health, Wellness and Illness: Self-Esteem Love and Belongingness Self-ActualizationDokument3 SeitenI. Health, Wellness and Illness: Self-Esteem Love and Belongingness Self-ActualizationYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agusan Del Sur Food and veggies-SADokument2 SeitenAgusan Del Sur Food and veggies-SAYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManageDokument6 SeitenManageYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Acuity: Eye AssessmentDokument3 SeitenVisual Acuity: Eye AssessmentYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants:: Blood PressureDokument3 SeitenDeterminants:: Blood PressureYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 5.5 Glasgow Coma ScaleDokument6 SeitenTable 5.5 Glasgow Coma ScaleYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PULSEDokument3 SeitenPULSEYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital Signs: PurposeDokument3 SeitenVital Signs: PurposeYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment TechniquesDokument3 SeitenAssessment TechniquesYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenComputer Answer KeyYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice TypingDokument1 SeitePractice TypingYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapeh3 PDFDokument2 SeitenMapeh3 PDFYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word: Handout in COMPUTER 4 Quarterly Examination Grade 1 ABCDEDokument3 SeitenMicrosoft Word: Handout in COMPUTER 4 Quarterly Examination Grade 1 ABCDEYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourth Mastery Test: Handout in COMPUTER Grade 1 ABCDEDokument2 SeitenFourth Mastery Test: Handout in COMPUTER Grade 1 ABCDEYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- APP FORM2 Renewal For AdultDokument2 SeitenAPP FORM2 Renewal For AdultYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form - Membership Registration For Regular MemberDokument1 SeiteForm - Membership Registration For Regular MemberYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form - Membership Registration For Associate MemberDokument1 SeiteForm - Membership Registration For Associate MemberYmon TuallaNoch keine Bewertungen