Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 3 Study Guide Marketing
Hochgeladen von
юрий локтионов0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten2 SeitenChapter 3 Study Guide Marketing external marketing environment. World trade Flow of goods and services, money and labor o Established trade agreements ex: NAFTA Canada, US & Mexico Protectionism: Import quotas (how much?) sanctions, tariffs, non-tariff barriers Sanctions Cuba and North Korea GM and Ford are held to higher environmental standards in Europe.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
4de8aa7f5367f03259de25e113d90f3d_chapter-3-study-guide-marketing.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenChapter 3 Study Guide Marketing external marketing environment. World trade Flow of goods and services, money and labor o Established trade agreements ex: NAFTA Canada, US & Mexico Protectionism: Import quotas (how much?) sanctions, tariffs, non-tariff barriers Sanctions Cuba and North Korea GM and Ford are held to higher environmental standards in Europe.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
5 Ansichten2 SeitenChapter 3 Study Guide Marketing
Hochgeladen von
юрий локтионовChapter 3 Study Guide Marketing external marketing environment. World trade Flow of goods and services, money and labor o Established trade agreements ex: NAFTA Canada, US & Mexico Protectionism: Import quotas (how much?) sanctions, tariffs, non-tariff barriers Sanctions Cuba and North Korea GM and Ford are held to higher environmental standards in Europe.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
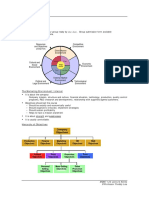
Chapter 3 Study Guide Marketing
Global Marketing
External Marketing Environment
International Market (Product, Price, Place, Promotion)
Ex: Coca-Cola [45% Revenue Overseas, 55% Profit
Overseas]
o Pepsi [70% Revenue Overseas, 75% Profit
Overseas]
American-Made looked down upon (Not reliable/ not even
American made most times) Saturn
World Trade Flow of goods & services, money & labor
o Established trade agreements ex: NAFTA Canada, US
& Mexico
Protectionism: Import quotas (how much?) sanctions,
tariffs, non-tariff barriers
Sanctions Cuba & North Korea
GM & Ford are held to higher environmental standards in
Europe
Trade: World Trade Organization (Amount of Tariffs)
Deregulation/Regulation
Economic Issues:
o G8 (US, UK, Canada, France, Italy, Germany, Japan,
Russia)
o Developing Countries (BRIC) (Brazil, India, China,
Russia)
o Least Developed Countries (Mostly African
Countries)
o
Business Cycle (Able to Identify: Prosperity, Recession,
Recovery)
o Industries that benefit from recession (Fast Food,
Public Transport, Education)
Competitive Environment
o Level I: Discretionary Income (Hulu & Amazon Prime
to Netflix)
o Level II: Attempt to satisfy similar needs (Going to
movies, video games, concerts)
o Level III: Offering similar products for price (Gasoline
industry)
Structure
o Monopoly: No competition (Energy companies)
o Oligopoly: Few Sellers (Wireless companies)
o Monopolistic: Many Sellers (Cars)
o Perfect Competition: Many small sellers
Brand Name (prices increase after patent ex: drugs)
Sociocultural Environment: McDonalds introducing salads
between 2005-2008
Cultural Environment (All different, cultural differences,
collectivism vs. individualism [I vs. Me])
o Values
o Norms
o Language
o Ethnocentricity
o Cultural Change
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Export Now: Five Keys to Entering New MarketsVon EverandExport Now: Five Keys to Entering New MarketsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chapter 5 Developing A Global VisionDokument23 SeitenChapter 5 Developing A Global Visionrizcst9759Noch keine Bewertungen
- Smooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1Von EverandSmooth Sailing: A Quick Guide to Effective Cargo Import and Export: Logistics, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: The Scope and Challenge of International MarketingDokument15 SeitenChapter 1: The Scope and Challenge of International MarketingAbhishek SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- International MarketingDokument37 SeitenInternational Marketingjames_theme007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument19 SeitenChapter 1Adeel PervezNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Marketing: - Czinkota & Ronkainen - Fall 2009 - Web Slides - Ch1-5, 8-10Dokument127 SeitenInternational Marketing: - Czinkota & Ronkainen - Fall 2009 - Web Slides - Ch1-5, 8-10Star RaghuNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBM - Intro The World Is NOT EnoughDokument40 SeitenIBM - Intro The World Is NOT EnoughsheelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 GlobalizationDokument55 SeitenChapter 1 Globalizationfrancis albaracinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mba Fa Iv Sem 404 Major Decision of International MarketingDokument15 SeitenMba Fa Iv Sem 404 Major Decision of International MarketingŠöbíķá RáņčíNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 5 - International MarketingDokument27 SeitenSession 5 - International MarketingGaming Theater33% (3)
- Course Note For Class 22Dokument41 SeitenCourse Note For Class 22박서희Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laduree PowerPoint Report - Final - UpdateDokument61 SeitenLaduree PowerPoint Report - Final - Updatewinki0312Noch keine Bewertungen
- International MarketingDokument18 SeitenInternational MarketingHimanshu BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 IMMDokument101 SeitenUnit 1 IMMSanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Business: Prof Benny ThomasDokument23 SeitenInternational Business: Prof Benny ThomasRAHUL GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- International MarketingDokument15 SeitenInternational Marketingsagi_debaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Marketing ChallengesDokument17 SeitenGlobal Marketing ChallengesalfreandreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adms 1000 Finals NotesDokument5 SeitenAdms 1000 Finals NotesSaf PopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview GRUPO BIMBO InterDokument4 SeitenInterview GRUPO BIMBO Interstudent_8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2globalDokument21 SeitenLecture 2globalzoyamalik27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wall Mart Stores Inc (WMT) : A Case Study Presentation byDokument55 SeitenWall Mart Stores Inc (WMT) : A Case Study Presentation byrknanduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Marketing Ch1 2021Dokument77 SeitenInternational Marketing Ch1 2021esraa karamNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Business UNIT IDokument47 SeitenInternational Business UNIT ISharanya KaparthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Objectives: MGMT 120 Lecture Notes ©professor Freddy LeeDokument6 SeitenCompany Objectives: MGMT 120 Lecture Notes ©professor Freddy LeenarayanasigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Product PolicyDokument36 SeitenInternational Product Policydeepakgiri2310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scope Challenges International Marketing PDFDokument0 SeitenScope Challenges International Marketing PDFmonirba48Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Marketing NewDokument34 SeitenInternational Marketing NewSheetal RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section A (40 Marks) 2Q Choose 1Dokument3 SeitenSection A (40 Marks) 2Q Choose 1Shakeeb AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- International MarketingDokument59 SeitenInternational Marketingrupeshdahake100% (1)
- 05 Intl Biz Globalisation Session 7 & 8Dokument21 Seiten05 Intl Biz Globalisation Session 7 & 8Kapil PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andreea Onofrei-Global MarketingDokument11 SeitenAndreea Onofrei-Global MarketingAndreea PopoviciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Marketing 8 OctoberDokument18 SeitenGlobal Marketing 8 OctoberjrecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P. 3 Introduction and Overview: Chapter 1. Introduction To Global MarketingDokument9 SeitenP. 3 Introduction and Overview: Chapter 1. Introduction To Global MarketingArt VandelayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cateora18ePPt Ch01 WH BKGRNDDokument29 SeitenCateora18ePPt Ch01 WH BKGRNDbittu.abhishek99Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Global Market PlaceDokument21 SeitenThe Global Market PlacePinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Advertising EffectivenessDokument21 SeitenGlobal Advertising EffectivenessMunish Nagar100% (1)
- Ceoguidetogloballeadership BK DdiDokument23 SeitenCeoguidetogloballeadership BK DdiNasir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Essentials: Understand The Global Context of BusinessDokument49 SeitenBusiness Essentials: Understand The Global Context of BusinessMuhammad HasnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4.7 PPT International MarketingDokument17 SeitenChapter 4.7 PPT International MarketingAmit ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Business Environment: Going Global To Stay Local?Dokument47 SeitenGlobal Business Environment: Going Global To Stay Local?gurgurgurgurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 - International TradeDokument28 Seiten1.1 - International Tradejessicamarieogbinar37Noch keine Bewertungen
- WalmartDokument36 SeitenWalmartMohan Lal AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadbury Marvelous Creations Marketing PlanDokument32 SeitenCadbury Marvelous Creations Marketing PlanLaila RashedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Export MarketingDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Export Marketing062 Mehta UrmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Marketing MKT 504: Sharon Loane University of Ulster ML010 Extn. 75096Dokument31 SeitenInternational Marketing MKT 504: Sharon Loane University of Ulster ML010 Extn. 75096TonyTawfikNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Product PolicyDokument35 SeitenInternational Product PolicyMegha KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swot Analysis of Strategic Management Case StudiesDokument21 SeitenSwot Analysis of Strategic Management Case StudiesKp FawwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MKT MGTDokument125 SeitenMKT MGTArfa AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlobalisationDokument14 SeitenGlobalisationPragya Rathor Shah100% (1)
- Dani Rodrik 2007Dokument25 SeitenDani Rodrik 2007sawingbahar100% (1)
- NBS8509: International Brand Management Topic 1Dokument28 SeitenNBS8509: International Brand Management Topic 1周振刚Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Global BusinessDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Global BusinessAkhil VighNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To International BusinessDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To International Businesssolo_sudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Economics of Globalisation Lecture 3: Trade Policy: Annina Kaltenbrunner G.19Dokument31 SeitenThe Economics of Globalisation Lecture 3: Trade Policy: Annina Kaltenbrunner G.19Ujjwal Kumar DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To International BusinessDokument49 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To International Businessbittugolumolu100% (1)
- Swot Analysis of Strategic Management Case StudiesDokument21 SeitenSwot Analysis of Strategic Management Case StudiesMyo Kyaw SwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide 1 - Marketing ManagementDokument5 SeitenSlide 1 - Marketing ManagementAmit MirjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 Scope & Challeges of Intl MKTGDokument21 SeitenL1 Scope & Challeges of Intl MKTGBhavini ModiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIP BagsDokument32 SeitenVIP BagsAkshay KhimasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmailDokument1 SeiteEmailюрий локтионовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Russell-AthleticDokument28 SeitenRussell-Athleticюрий локтионовNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interconnected-WorldDokument1 SeiteInterconnected-Worldюрий локтионовNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSBC in ChinaDokument3 SeitenHSBC in Chinaюрий локтионов100% (1)
- Bolender-MemoDokument2 SeitenBolender-Memoюрий локтионовNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 9 NotesDokument1 Seite4 9 Notesюрий локтионовNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018耗材展 会刊 RemaxWorldDokument240 Seiten2018耗材展 会刊 RemaxWorldankit.patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- TranscendentalismDokument3 SeitenTranscendentalismapi-306116382Noch keine Bewertungen
- TVL-EMTECH-W-1-TUNAY-NA-TUNAY 70 CopiesDokument7 SeitenTVL-EMTECH-W-1-TUNAY-NA-TUNAY 70 CopiesMiyu VianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Design of Onshore Civil WorksDokument8 SeitenThe Design of Onshore Civil Workskkkelvin50% (2)
- The Chosen by Chaim PotokDokument12 SeitenThe Chosen by Chaim PotokDavid A. Malin Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cabuyao Zoning Ordinance No. 2019-562 S. 2019Dokument55 SeitenCabuyao Zoning Ordinance No. 2019-562 S. 2019melvin.francisco1078Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resting in The RiverDokument4 SeitenResting in The RiverNguyễn Văn TưởngNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThedinnerpartyDokument2 SeitenThedinnerpartyapi-287829605Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voting Methods and Apportionment AssessmentDokument3 SeitenVoting Methods and Apportionment AssessmentJune DungoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of The 2010 11 Flood Warnings and Reponse INTERIM REPORTDokument32 SeitenReview of The 2010 11 Flood Warnings and Reponse INTERIM REPORTABC VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Scholarship EssayDokument4 SeitenExample of Scholarship EssayertzyzbafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proforma Invoice - ConakryDokument1 SeiteProforma Invoice - ConakryAndy WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual For State ExciseDokument29 SeitenUser Manual For State ExciserotastrainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registration of Patient Transport VehicleDokument2 SeitenRegistration of Patient Transport VehicleMenGuitar100% (1)
- Wellington Investment v. TrajanoDokument1 SeiteWellington Investment v. TrajanoNicole Kalingking100% (1)
- Wireless Sensor NetworkDokument13 SeitenWireless Sensor NetworkRanjit PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secureworks E1 LearningfromIncidentResponseJan-Mar22Dokument12 SeitenSecureworks E1 LearningfromIncidentResponseJan-Mar22TTSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dubai Mall Landside Metro Bus - Dubai Design District Zõ - DC Ó% Ó? - V - C FO Ó% Eï (Ð ( @ (Dokument1 SeiteDubai Mall Landside Metro Bus - Dubai Design District Zõ - DC Ó% Ó? - V - C FO Ó% Eï (Ð ( @ (Dubai Q&ANoch keine Bewertungen
- PC63 - Leviat - 17 SkriptDokument28 SeitenPC63 - Leviat - 17 SkriptGordan CelarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Islam PPT Outline (Script)Dokument2 SeitenIslam PPT Outline (Script)Paulene MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEEBURGER WebEDI Wilo ENDokument1 SeiteSEEBURGER WebEDI Wilo ENmarketingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Urban Design and Cultural Diversity, by Nada Lazarevic Bajec, Marija MarunaDokument141 SeitenStrategic Urban Design and Cultural Diversity, by Nada Lazarevic Bajec, Marija MarunaArhitektonski fakultet100% (1)
- DDI - Company Profile 2024Dokument9 SeitenDDI - Company Profile 2024NAUFAL RUZAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutritional Status of Under-Five Children in Rural BangladeshDokument6 SeitenNutritional Status of Under-Five Children in Rural BangladeshIJPHSNoch keine Bewertungen
- LorealDokument2 SeitenLorealviaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters Particulars Page NoDokument48 SeitenChapters Particulars Page NoKuldeep ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arts Q2 Module 3 FINAL1Dokument14 SeitenArts Q2 Module 3 FINAL1halemahpacoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance and Safety Mechanism PDFDokument11 SeitenBalance and Safety Mechanism PDFKhesmin KapilNoch keine Bewertungen
- CounterfeitingDokument21 SeitenCounterfeitingnujahm1639Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Date:: The Punic WarsDokument3 SeitenName: Date:: The Punic Warsfruity pebblesNoch keine Bewertungen