Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
English
Hochgeladen von
api-278092100Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
English
Hochgeladen von
api-278092100Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
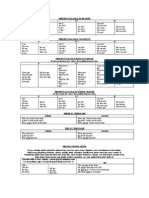
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
TENSE
FORMING THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
The present continuous of any verb is composed of two parts - the present tense of the verb to be +
the present participle of the main verb.
(The form of the present participle is: base+ing, e.g. talking, playing, moving, smiling)
Affirmative
Subject
+ to be
+ base + ing
She
is
talking.
Subject
+ to be + not
+ base + ing
She
is not (isn't)
talking
to be
+ subject
+ base + ing
Is
she
talking?
Negative
Interrogative
EXAMPLES: TO GO, PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Affirmative
Negative
Interrogative
I am going
I am not going
Am I going?
You are going
You aren't going.
Are you going?
He, she, it is going
He, she, it isn't going
Is he, she, it go
We are going
We aren't going
Are we going?
You are going
You aren't going
Are you going?
They are going
They aren't going
Are they going?
Note: alternative negative contractions: I'm not going, you're not going, he's not going etc.
FUNCTIONS OF THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
As with all tenses in English, the speaker's attitude is as important as the time of the action or event.
When someone uses the present continuous, they are thinking about something that is unfinished or
incomplete
THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS IS USED:
to describe an action that is going on at this moment: You are using the Internet. You are
studying English grammar.
to describe an action that is going on during this period of time or a trend: Are you still
working for the same company? More and more peopleare becoming vegetarian.
to describe an action or event in the future, which has already been planned or
prepared: We're going on holiday tomorrow. I'm meeting my boyfriend tonight. Are they
visiting you next winter?
to describe a temporary event or situation: He usually plays the drums, but he's playing bass
guitar tonight. The weather forecast was good, butit's raining at the moment.
with "always, forever, constantly", to describe and emphasise a continuing series of repeated
actions: Harry and Sally are always arguing!You're constantly complaining about your
mother-in-law!
BE CAREFUL! Some verbs are not usually used in the continuous form
VERBS THAT ARE NOT USUALLY USED IN THE
CONTINUOUS FORM
The verbs in the list below are normally used in the simple form because they refer to states, rather
than actions or processes.
SENSES / PERCEPTION
to feel*
to hear
to see*
to smell
to taste
OPINION
to assume
to believe
to consider
to doubt
to feel (= to think)
to find (= to consider)
to suppose
to think*
MENTAL STATES
to forget
to imagine
to know
to mean
to notice
to recognise
to remember
to understand
EMOTIONS / DESIRES
to envy
to fear
to dislike
to hate
to hope
to like
to love
to mind
to prefer
to regret
to want
to wish
MEASUREMENT
to contain
to cost
to hold
to measure
to weigh
OTHERS
to look (=resemble)
to seem
to be (in most cases)
to have(when it means "to possess")*
EXCEPTIONS
Perception verbs (see, hear, feel, taste, smell) are often used with can: : I can see... These verbs may
be used in the continuous form but with a different meaning
This coat feels nice and warm. (your perception of the coat's qualities)
John's feeling much better now (his health is improving)
She has three dogs and a cat. (possession)
She's having supper. (She's eating)
I can see Anthony in the garden (perception)
I'm seeing Anthony later (We are planning to meet)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Forming the Present ContinuousDokument4 SeitenForming the Present ContinuousGeorgiana DragoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectDokument10 SeitenPresent: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectIoana TrîmbițașNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Simple Present Tense in 40 WordsDokument6 SeitenLearn Simple Present Tense in 40 WordsMade AnomaharsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinousDokument4 SeitenPresent Continoususwatunkhs11Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16 TensesDokument18 Seiten16 TensesAnonymous eCws3ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument44 SeitenPresent ContinuoushootanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng 2 Activity 2 - HSGADokument7 SeitenEng 2 Activity 2 - HSGARosanelly Galindo ParraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectDokument7 SeitenPresent: Simple Present Present Continuous Present PerfectWaad AlteeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument4 SeitenPresent ContinuousAizack WiverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksDokument10 SeitenSimple Present: He Wants, She Needs, He Gives, She ThinksAisyah RasdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to English Verb TensesDokument81 SeitenGuide to English Verb TensesAisy AstarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continous TensesDokument12 SeitenPresent Continous TensesSenor PrivateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be Careful!: Present Continous/ Progressive TenseDokument4 SeitenBe Careful!: Present Continous/ Progressive TenseBrigitta Helena ModNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument6 SeitenPresent ContinuousAyy SykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple PresentDokument31 SeitenSimple PresentJuni DzibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous. თეკლა ყუფარაძეDokument6 SeitenPresent Continuous. თეკლა ყუფარაძეTekla KuparadzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous Form and UsesDokument12 SeitenPresent Continuous Form and UsesWalter Atao SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple - Continuous Lesson - 220109 - 213225Dokument6 SeitenPresent Simple - Continuous Lesson - 220109 - 213225wafaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Simple Present and Present Continuous TensesDokument7 SeitenLearn Simple Present and Present Continuous TensesAbdelhadi Ait AllalNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument67 SeitenEnglish Tensesdonisparta5Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses Learning AppDokument39 SeitenEnglish Tenses Learning AppDavid ArévalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Dokument9 SeitenNotas Sobre La Tercera Persona Del Singular Del "Simple Present"Anonymous thHFCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Hey There 2Dokument29 SeitenGrammar Hey There 2Kenny Valdez FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple and Present Continuous TensesDokument12 SeitenPresent Simple and Present Continuous TensessofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument4 SeitenPresent ContinuousDavid SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple and Present ContinuousDokument9 SeitenPresent Simple and Present ContinuouseeeeereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente Continuo - InglesDokument14 SeitenPresente Continuo - InglesMiyouba CarriganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Conjugation Chart for Present Simple TenseDokument13 SeitenVerb Conjugation Chart for Present Simple TenseClaudia BalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous Tense GuideDokument30 SeitenPresent Continuous Tense GuideSania KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple&Present Continous Grammar ExplanationDokument3 SeitenPresent Simple&Present Continous Grammar ExplanationHéctor León SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Notes - Simple, Continuous Past&Present TenseDokument7 SeitenGrammar Notes - Simple, Continuous Past&Present TenseNUR AMALINA BINTI MOHAMMAD MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraDokument17 SeitenUniversidad Tecnologica Del Suroeste de Guanajuato: Obed Armando Cabrera YbarraObed Armando Cabrera YbarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument6 SeitenPresent ContinuousyuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple PresentationDokument13 SeitenPresent Simple PresentationClaudia BalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides Uni I (MS) (RF)Dokument64 SeitenSlides Uni I (MS) (RF)Marilia PucciNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Form the Present Continuous in EnglishDokument2 SeitenHow to Form the Present Continuous in EnglishEufrasia CorsaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRESENT SIMPLE Vs PRESENT CONTINUOUSDokument85 SeitenPRESENT SIMPLE Vs PRESENT CONTINUOUSmia100% (1)
- The Simple Guide to Simple Present TenseDokument21 SeitenThe Simple Guide to Simple Present TenseHamza djioui - حمزة ادجيويNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Progressive - ClassDokument3 SeitenPresent Progressive - ClassJorge OriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engleski JezikDokument6 SeitenEngleski JezikAdnan PjanicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 4 Finite - Non FiniteDokument29 SeitenLec 4 Finite - Non Finitejahedul IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure: Paper Ratio: 10 To 30 % Unit 1: The Simple Present TenseDokument21 SeitenStructure: Paper Ratio: 10 To 30 % Unit 1: The Simple Present TenseMemoona MunzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Perfect ContinuousDokument2 SeitenPresent Perfect ContinuousNesreen WalledNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forming The Present ContinuousDokument2 SeitenForming The Present Continuousmounib khaddourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDokument42 SeitenMakalah Bahasa InggrisMarsela Eka MarselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Guide 3-2017 PDFDokument48 SeitenGrammar Guide 3-2017 PDFRoberto Figueroa ZúñigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forming the Present Continuous TenseDokument7 SeitenForming the Present Continuous TenseJannis AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evision: Present Simple - Present ContinuousDokument28 SeitenEvision: Present Simple - Present ContinuousMaha Al AmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng GrammarDokument9 SeitenEng GrammarSeba Tube HDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tenses: Structure of Present SimpleDokument7 SeitenVerb Tenses: Structure of Present SimplexaglobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument4 SeitenPresent ContinuousYulia ChukarevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auxiliary VerbsDokument7 SeitenAuxiliary VerbsErma Chandra Saptarani100% (1)
- General English Module 2Dokument39 SeitenGeneral English Module 2shambhavi sinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Χρόνοι στα ΑγγλικαDokument22 SeitenΧρόνοι στα Αγγλικαangnikos100% (1)
- Grammar Performance 1Dokument32 SeitenGrammar Performance 1KarglezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Tenses RevisionDokument12 SeitenPresent Tenses RevisionMaja BulatovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ProgressiveDokument22 SeitenPresent ProgressiveMuAD TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEY 1 BachDokument13 SeitenKEY 1 BachParty CularNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Tense WorksheetDokument2 SeitenPresent Tense WorksheetOana Galbenu100% (1)
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Dokument3 SeitenPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Alessio MirarchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Dokument3 SeitenPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 1Alessio MirarchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 2Dokument3 SeitenPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 2IannaL77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spelling of Verb + INGDokument3 SeitenSpelling of Verb + INGEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous and Present SimpleDokument1 SeitePresent Continuous and Present SimpleEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous and Present Simple 2 PartDokument1 SeitePresent Continuous and Present Simple 2 PartEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous Form Positive and Negative 1Dokument3 SeitenPresent Continuous Form Positive and Negative 1Devita MezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ClausesDokument2 SeitenTypes of ClausesIndranil HatuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge advice after coronary proceduresDokument12 SeitenDischarge advice after coronary proceduresEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous Tense QuizDokument1 SeitePresent Continuous Tense QuizEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract NounsDokument3 SeitenAbstract NounsEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of NounsDokument2 SeitenDifferent Types of NounsEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous All Forms Exercise 2Dokument3 SeitenPresent Continuous All Forms Exercise 2IannaL77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinuousDokument3 SeitenPresent ContinuousILy SofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type of Nouns in The English LanguageDokument2 SeitenType of Nouns in The English LanguageEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepositions of Place GuideDokument3 SeitenPrepositions of Place GuideEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auxiliary Verbs - Be, Do, HaveDokument2 SeitenAuxiliary Verbs - Be, Do, HaveEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collective NounsDokument3 SeitenCollective NounsEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination For Beginners: NameDokument2 SeitenExamination For Beginners: NameWeam AlajamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Articles A, An, and TheDokument3 SeitenUsing Articles A, An, and TheEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- For/since: For Is Used When Specifying The Amount of Time (How Long)Dokument1 SeiteFor/since: For Is Used When Specifying The Amount of Time (How Long)Emma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Verb ObjectDokument1 SeiteSubject Verb ObjectEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovering From Coronary Angioplasty and Stent InsertionDokument42 SeitenRecovering From Coronary Angioplasty and Stent InsertionmichelbgggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise For Beginners 3Dokument4 SeitenExercise For Beginners 3Emma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepositions of TimeDokument1 SeitePrepositions of TimeEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word Order: Nick Nick He He He HeDokument1 SeiteWord Order: Nick Nick He He He HeEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Comparison of AdjectivesDokument2 SeitenThe Comparison of AdjectivesEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepositions of Place GuideDokument3 SeitenPrepositions of Place GuideEmma EmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Approach in Language AcuisitionDokument39 SeitenPsychological Approach in Language AcuisitionRach PangestoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chin and BenneDokument1 SeiteChin and Bennejeneil100% (1)
- Understanding by Design Lesson Plan in General Biology 1Dokument2 SeitenUnderstanding by Design Lesson Plan in General Biology 1NikkoOdejarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trends and Critical Thinking in the 21st CenturyDokument13 SeitenTrends and Critical Thinking in the 21st CenturyMatet LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foucault Versus Freud On Sexuality andDokument13 SeitenFoucault Versus Freud On Sexuality andBadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dogma PDFDokument2 SeitenDogma PDFAankh BenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Close Reading StrategiesDokument3 SeitenIntro Close Reading StrategiesaBloomingTreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culture, Society and Politics As Conceptual ToolsDokument32 SeitenCulture, Society and Politics As Conceptual ToolsDimphna Jel Lozada PacificoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Philosophy of Tim BurtonDokument307 SeitenThe Philosophy of Tim BurtonClaudia De Laurentis80% (5)
- Examples of EssayDokument6 SeitenExamples of Essaycatherine escomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DGT TT S2 Training EthodologyDokument13 SeitenDGT TT S2 Training EthodologyDharmendra SahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeremy Campbell - The Liars Tale A History of Falsehood PDFDokument362 SeitenJeremy Campbell - The Liars Tale A History of Falsehood PDFstephen_davis_31100% (5)
- Medical/Mental Health Professional Form: InitialDokument4 SeitenMedical/Mental Health Professional Form: InitialKarina Jacqueline Medina VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transational Model - Burnlund's Model: MeaningDokument6 SeitenTransational Model - Burnlund's Model: MeaningManika AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral CommDokument250 SeitenOral Commنجشو گحوش0% (1)
- Bba 101Dokument134 SeitenBba 101gollohtradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teachers Individual Plan For Professional Development IPPD Form 4Dokument6 SeitenTeachers Individual Plan For Professional Development IPPD Form 4kevin john quilinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background of The StudyintroductionDokument10 SeitenBackground of The StudyintroductionErnesto S. Caseres JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Predatory LeadershipDokument14 SeitenIntroduction To Predatory LeadershipMatt Kramer100% (1)
- Marital RapeDokument11 SeitenMarital RapeRishabh kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10game NotesDokument4 Seiten10game NotesMitansh ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Learning Theory-1Dokument14 SeitenSocial Learning Theory-1geetainderhanda4430Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eco-Generation Essay - Meidina Sekar NadistiDokument2 SeitenEco-Generation Essay - Meidina Sekar NadistiMeidinaSekarNadistiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divisions and Classifications of ArtDokument69 SeitenDivisions and Classifications of ArtLemuel Maliwat DupitasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Face ReadingDokument26 SeitenFace ReadingRajneesh Singh100% (2)
- The Modern Day Enneagram 9 Personality Type Theory: The Wakefield Doctrine (The Theory of Clarks, Scotts and Rogers)Dokument4 SeitenThe Modern Day Enneagram 9 Personality Type Theory: The Wakefield Doctrine (The Theory of Clarks, Scotts and Rogers)Jennifer WilsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bangladesh in A Golden Age - Priya Jose K.Dokument146 SeitenBangladesh in A Golden Age - Priya Jose K.Jonathan NeitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Vs Low Synergy v1Dokument10 SeitenHigh Vs Low Synergy v1Yasser Hasan MadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- U2 - Keith Haring Comprehension QuestionsDokument3 SeitenU2 - Keith Haring Comprehension QuestionsSteve GOopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think and Grow Rich Book Review & How To Apply The Concept of Think Grow Rich Book in International Business?Dokument9 SeitenThink and Grow Rich Book Review & How To Apply The Concept of Think Grow Rich Book in International Business?Hassan RazaNoch keine Bewertungen