Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Learning Objectives As91391
Hochgeladen von
api-252561013Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Learning Objectives As91391
Hochgeladen von
api-252561013Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Year 13 Chemistry 2015
Chemistry 3.5 (AS91391) Demonstrate understanding of the properties of
organic compounds (5 credits)
Learning Objectives:
At the end of this unit you should be able to:
Recognising, Naming and Drawing
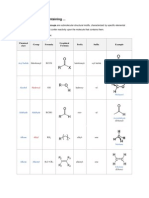
Recognise each of the following functional groups: alkane, alkene,
alkyne, haloalkane, carboxylic acid, amine, ester, aldehyde, ketone,
amide, acyl chloride
Name compounds from the above groups that contain 8 or less
carbon atoms in the main chain
Draw compounds from the above groups that contain 8 or less
carbon atoms in the main chain
Recognise one or more of these groups in more complex molecules
Identify organic reactions as: addition, substitution, condensation,
elimination or redox
Recognise the differences in empirical, molecular, structural and
condensed structural formula
Recognise the differences between constitutional (structural) and
stereoisomerism (geometrical and optical)
Identify the conditions needed for different types of isomerism to
occur
Explain the reasons for the different physical properties of isomers
of the same compound
Alkanes and Alkenes
Explain the different physical and chemical properties of alkanes
and alkenes
Write equations for the common reactions of alkanes and alkenes
Recognise the difference between substitution and addition
reactions and explain the reasons why each one occurs
Identify the major and minor products formed from the addition
reactions of asymmetric alkenes with asymmetric reagents
Alcohols
Classify alcohols as primary, secondary or tertiary
Explain the different physical and chemical properties of alcohols
Explain the differences in the physical properties of isomeric
alcohols
Identify the functional groups formed from the oxidation of primary,
secondary and tertiary alcohols
Identify the common oxidising agents used to perform the oxidation
reactions above
Identify the product formed, write equations for and state the
required reagent(s) for the common reactions of alcohols:
combustion, oxidation, elimination and halogenation
Identify the major and minor products formed from the elimination
reactions of asymmetric alcohols
Haloalkanes
Classify haloalkanes as primary, secondary or tertiary
Write equations for and state the common reagent(s) for the
formation of haloalkanes from alcohols, alkanes and alkenes
Explain the physical properties of haloalkanes
Write equations for and state the common reagent(s) for the
formation of alcohols, alkenes and amines from haloalkanes
Explain nucleophilic substitution with reference to the above
equations
Identify the major and minor products formed from the elimination
reactions of asymmetric haloalkanes
Amines
Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary
Explain the physical properties of amines using knowledge about
their intermolecular forces
Identify the product formed and write equations for the reactions of
amines with water and acids
Aldehydes and Ketones
Distinguish between aldehydes and ketones
Write equations for and state the required reagent(s) for the
formation of aldehydes and ketones from the appropriate alcohol
Explain the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones using
knowledge about their intermolecular forces
Describe how to distinguish between aldehydes and ketone
experimentally, stating the reagent(s) required to do so
Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Acyl Chlorides and Amides
Write equations for and state the required reagent(s) for the
formation of carboxylic acids from alcohols or esters
Explain the physical properties of carboxylic acids using knowledge
about their intermolecular forces
Identify the product formed and write equations for the reaction of
carboxylic acids with water, metals, carbonates, bases, PCl3, PCl5,
SOCl2 and ammonium carbonate
Write equations for and state the required reagent(s) for the
formation of esters from alcohols and carboxylic acids or acyl
chlorides
Explain the physical properties of esters using knowledge about
their intermolecular forces
Identify the product formed and write equations for the hydrolysis of
esters and the reaction of esters with ammonia
Describe the structure of fats
Write equations for and state the required reagent(s) for the
formation of acyl chlorides
Explain the physical properties of acyl chlorides using knowledge
about their intermolecular forces
Identify the product formed and write equations for the reaction of
acyl chlorides with water, ammonia solution, primary amines and
alcohols
Write equations for and state the required reagent(s) for the
formation of amides
Explain the physical properties of amides using knowledge about
their intermolecular forces
Identify the product formed and write equations for the hydrolysis of
amides using aqueous acids and alkalis
Polymers
Distinguish between addition and condensation polymers
Name some common polymers formed from addition polymerisation
reactions
Identify the monomers that make up a polymer
Describe the structure of proteins and carbohydrates
Describe the properties of amino acids
Explain the process of forming proteins from amino acids
Explain the hydrolysis of proteins and carbohydrates
Reaction Schemes
Name reagents and write equations for steps in an organic reaction
scheme.
The reagents you are expected to know in this course are:
Substitution reactions (including esterification, condensation,
hydrolysis and polymerisation): Br2 (with light or heat), conc. HCl,
HBr, SOCl2, NaOH, KOH, conc. NH3, primary amines, primary
alcohols/H+, H2O/H+ and H2O/OHOxidation reactions: MnO4-/H+, Cr2O72-/H+, Tollens reagent, Fehlings
reagent and Benedicts reagent
Reduction reactions: NaBH4
Elimination reactions: KOH (in alcohol) and conc. H2SO4
Addition reactions: Br2, conc. HCl, HBr, H2, Cl2
Physical properties that you will need to explain for each functional group
are
Solubility in polar and non-polar solvents
Melting and boiling point
Rotation of plane polarised light
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Learning Objectives As91165Dokument2 SeitenLearning Objectives As91165api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- c7 Revision Checklist - OrganicDokument5 Seitenc7 Revision Checklist - Organicapi-422428700Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alkane AlkeneDokument9 SeitenAlkane AlkeneM.zuhair asifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohols Mastery: Alcohols - Contain The - OH Functional GroupDokument2 SeitenAlcohols Mastery: Alcohols - Contain The - OH Functional GroupJoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Check List To Score ADokument11 SeitenChemistry - Check List To Score AMC KsyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Obj TrackerDokument1 SeiteHaloalkanes and Haloarenes - Obj TrackerraineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Revision ChecklistDokument14 SeitenOrganic Revision ChecklistLouise AmoahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 c3.5 Organic ChemistryDokument197 Seiten2019 c3.5 Organic Chemistryhydesh100% (1)
- Organic Chem Review With ANSWERSDokument16 SeitenOrganic Chem Review With ANSWERSRyan Christian PatriarcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Groups ContainingDokument8 SeitenFunctional Groups ContainingViku GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching Plan (RPT) Chemistry, Form 5 2017: Sekolah Menengah Perempuan Methodist, Pulau PinangDokument8 SeitenYearly Teaching Plan (RPT) Chemistry, Form 5 2017: Sekolah Menengah Perempuan Methodist, Pulau PinangThivya V NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Notes No6Dokument31 SeitenChem Notes No6AnyhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives That Need To Be Met For Topic 10Dokument8 SeitenObjectives That Need To Be Met For Topic 10sara bdeirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 10Dokument9 SeitenExp 10ChantalDanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives As91392Dokument1 SeiteLearning Objectives As91392api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Caps Organic ChemistryDokument56 SeitenCaps Organic ChemistryIamThatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Organic Chemistry 2020Dokument39 SeitenChapter 7 Organic Chemistry 2020lavanya.aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDokument17 SeitenCarboxylic Acids and Their DerivativessbroadweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class12 Chemistry2 Unit12 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionDokument32 SeitenClass12 Chemistry2 Unit12 NCERT TextBook EnglishEditionSidharth ThukralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan of Chemistry Form Five 2010Dokument9 SeitenYearly Plan of Chemistry Form Five 2010Adibah IsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Lec Homework 020714Dokument18 SeitenChem Lec Homework 020714Almarie PasaoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydeDokument62 SeitenModule 4 - Alcohol, Ether and AldehydePrincess NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuctional GroupsDokument12 SeitenFuctional GroupsNina HamadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDokument34 Seiten9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesgoverotaropafadzwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH4 Hots QuestionsDokument1 SeiteCH4 Hots Questionsprabhat7969tiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 11: Organic Chemistry 11.1 Homologous SeriesDokument8 SeitenTopic 11: Organic Chemistry 11.1 Homologous SeriesbnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional GroupsDokument37 SeitenFunctional GroupsKayla Denize GerardinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4Dokument11 SeitenExperiment 4kittyluna023Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - Notes On Alkanes To Esters-StudentDokument12 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Notes On Alkanes To Esters-Studentjasmineramkissoon786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Functional GroupDokument10 SeitenFunctional Groupbalweg mackyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Organic CompoundDokument103 SeitenLesson 1 - Organic CompoundFreshieeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydro Carbon and Functional GroupDokument36 SeitenHydro Carbon and Functional Groupfelisilda.136571140273Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final FinalDokument36 SeitenFinal FinalaprilrosesanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument2 SeitenUnit 3Thu ReinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes SlideDokument14 SeitenAlkanes Slidevictoryayapaye147Noch keine Bewertungen
- DAT Organic MasterContentDokument77 SeitenDAT Organic MasterContentclaire LawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oc Hydrocarbon Classification Old FinalDokument10 SeitenOc Hydrocarbon Classification Old Finalapi-235935798Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHM241Dokument2 SeitenCHM241Necherem MissionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 Carboxylic Ester Amides PDFDokument22 SeitenChapter 14 Carboxylic Ester Amides PDFMADANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme 10 - Aldehydes and KetonesDokument50 SeitenTheme 10 - Aldehydes and KetonesSiphelele SimelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- S5 Chemistry Schemes of Work Term IiiDokument5 SeitenS5 Chemistry Schemes of Work Term IiiAgagwa AgagwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes Revision WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAlkanes Revision Worksheetvenetia_guoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Functional Groups and Homologous SeriesDokument38 SeitenIntro To Functional Groups and Homologous SeriesDrew BuchananNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVCL 9A Properties of Carboxylic Acids and EstersDokument8 SeitenAVCL 9A Properties of Carboxylic Acids and EstersGiane MadrigalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER - 4-Carbon and Its CompoundDokument2 SeitenCHAPTER - 4-Carbon and Its CompoundHimanshu JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarDokument53 SeitenCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives.: Lecture Notes in Chem. 206 (Organic Chemistry II) Dr. Joel R. SalazarPaul Jhon EugenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDokument7 SeitenCarbon and Its CompoundsVijeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem HSC 7,8Dokument114 SeitenChem HSC 7,8bodduvidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 Functional GroupsDokument81 SeitenChapter 23 Functional GroupsYudi PermanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan - Kimia F5 - 2015Dokument12 SeitenYearly Plan - Kimia F5 - 2015Damit Jaffar Mohd ThaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Groups: Organic Chemistry EssentialsDokument8 SeitenFunctional Groups: Organic Chemistry EssentialsJeremiah Paul Gotia HumiwatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry s5 Full NoteDokument383 SeitenChemistry s5 Full NotebravebahiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionVon EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Alcohol 101219212329 Phpapp02Dokument25 SeitenAlcohol 101219212329 Phpapp02BtgPeiiYiingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalytic Asymmetric SynthesisVon EverandCatalytic Asymmetric SynthesisIwao OjimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry: Structure, Mechanism, SynthesisVon EverandOrganic Chemistry: Structure, Mechanism, SynthesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Learning Objectives As91392Dokument1 SeiteLearning Objectives As91392api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- As 91435Dokument3 SeitenAs 91435api-271057641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2014Dokument12 SeitenExm 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2014Dokument16 SeitenExm 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2014Dokument5 SeitenAss 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2014Dokument4 SeitenAss 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2012Dokument4 SeitenAss 2012api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- As 91165Dokument3 SeitenAs 91165api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2013Dokument6 SeitenAss 2013api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2012Dokument12 SeitenExm 2012api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2014Dokument12 SeitenExm 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- As 91389Dokument2 SeitenAs 91389api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2013Dokument12 SeitenExm 2013api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives As91167Dokument1 SeiteLearning Objectives As91167api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2012Dokument6 SeitenAss 2012api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2014Dokument12 SeitenExm 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2014Dokument6 SeitenAss 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2013Dokument12 SeitenExm 2013api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2013Dokument5 SeitenAss 2013api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- As 91167Dokument2 SeitenAs 91167api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2014Dokument5 SeitenAss 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2014Dokument4 SeitenAss 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2012Dokument12 SeitenExm 2012api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2012Dokument12 SeitenExm 2012api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- As 91390Dokument3 SeitenAs 91390api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives As91390Dokument2 SeitenLearning Objectives As91390api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives As91393Dokument1 SeiteLearning Objectives As91393api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ass 2014Dokument6 SeitenAss 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exm 2014Dokument12 SeitenExm 2014api-252561013Noch keine Bewertungen
- PMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Dokument46 SeitenPMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Mughees AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- IsomerizationDokument10 SeitenIsomerizationRizwan Shehzad100% (2)
- Fixed-Bed Platforming General Operating Manual Rev 6 PDFDokument512 SeitenFixed-Bed Platforming General Operating Manual Rev 6 PDFaditya surya tama100% (4)
- Chemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsDokument7 SeitenChemical Properties of Carbon CompoundsAnonymous HLkNDToNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcanos, Alquenos y AlquinosDokument52 SeitenAlcanos, Alquenos y AlquinosagmirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level Organic Chemistry Test: 1) Which of The Following Statements About Alkenes Is Not Correct?Dokument5 SeitenA-Level Organic Chemistry Test: 1) Which of The Following Statements About Alkenes Is Not Correct?TubocurareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code Chemistry Course DetailsDokument41 SeitenCode Chemistry Course DetailsNauman MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 'A' Level Chemistry (Organic & Options)Dokument220 Seiten'A' Level Chemistry (Organic & Options)Wilbur Muzondo100% (1)
- Science: The Carbon Compounds and Chemical BondsDokument16 SeitenScience: The Carbon Compounds and Chemical BondsCelline Isabelle ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- (WGS) - Detailed Kinetics of Fischer Tropsch Synthesis On An Industrial Fe MN CatalystDokument25 Seiten(WGS) - Detailed Kinetics of Fischer Tropsch Synthesis On An Industrial Fe MN CatalystBamrung SungnoenNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEM Gen Chem 1 Q1 M2Dokument20 SeitenSTEM Gen Chem 1 Q1 M2Roland AgraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: (Syllabus 6092)Dokument33 SeitenChemistry: (Syllabus 6092)Francis Ho HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refining Crude OilDokument24 SeitenRefining Crude OilalagurmNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14-EFSA Supporting Publications - 2020 - Risk Assessment of Beeswax Adulterated With Paraffin and or Stearin Stearic AcidDokument65 Seiten14-EFSA Supporting Publications - 2020 - Risk Assessment of Beeswax Adulterated With Paraffin and or Stearin Stearic AcidOanh PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Chemistry TextbookDokument152 SeitenGrade 8 Chemistry TextbookМаксим РябовNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Science Model ExamDokument4 SeitenGeneral Science Model Examdinasamsonk100% (1)
- 010 - UOP Manual de Plataforma Manual PRT1 PDFDokument263 Seiten010 - UOP Manual de Plataforma Manual PRT1 PDFROMAN ALEXANDER FERNANDEZ ROCHA100% (2)
- chm207 Lab4Dokument12 Seitenchm207 Lab4ArniezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes: H2 Chemistry 9647 Alkanes NYJC 2014Dokument17 SeitenAlkanes: H2 Chemistry 9647 Alkanes NYJC 2014Chen ZhihaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit Jee Advanced Paper 15 PDFDokument44 SeitenIit Jee Advanced Paper 15 PDFJatin Kumar RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C15 HydrocarbonsDokument31 SeitenC15 HydrocarbonsKris DookharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Terms (Petrochemicals)Dokument5 SeitenGlossary of Terms (Petrochemicals)micahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISCC PLUS Material List 230411 Final-1Dokument24 SeitenISCC PLUS Material List 230411 Final-1thiru vaasagamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry Grade 10Dokument88 SeitenOrganic Chemistry Grade 10Sai Pranav100% (2)
- Ajit Sapre - ExxonMobilDokument48 SeitenAjit Sapre - ExxonMobilCarlos Augusto Arentz PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry of Coke Formation: M. Guisnet, P. MagnouxDokument14 SeitenOrganic Chemistry of Coke Formation: M. Guisnet, P. MagnouxaminsuhadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Florinsky 2010dDokument403 SeitenFlorinsky 2010dVostjeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEDokument1 SeiteHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEUnknownNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlkenesDokument31 SeitenAlkenesjesslynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 10 Alkanes - AnswersDokument7 SeitenTutorial 10 Alkanes - AnswersEugene ChanNoch keine Bewertungen