Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Trigonometric Ratios:: Institute of Academic Services
Hochgeladen von
ataaisgreatOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Trigonometric Ratios:: Institute of Academic Services
Hochgeladen von
ataaisgreatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Institute of Academic Services
Mathematics Formulae
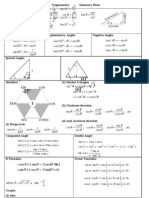
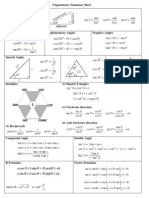
Trigonometric Ratios:
Perp
.Hyp
90
Sin=
Hyp
.Perp
90
Cos=
Hypt.
Per
Tan=
Sin=
1
Cosec
Base
Hyp
Cos=
Perp
Base
Tan=
1
Sec
Tan=
Sin
Cos
Cot=
Cos
Sin
1
Cot
Bas
Pythagorean Theorem & Basic Trig. Identities:
(Base)2+(Perp)2=(Hyp)2
sin2 +cos 2 =1
1+tan 2 =sec 2
1+cot 2 =cosec 2
Sign Identities: ()
sin()=sin cos()=cos tan ()=tan csc()=csc sec()=sec cot()=cot
Fundamental Identities:
sin( + )=sin . cos +cos . sin
sin( )=sin .cos cos . sin
cos( + )=cos . cos sin . sin
cos( )=cos . cos +sin . sin
tan ( + )=
tan +tan
1tan . tan
tan ( )=
tan tan
1+tan . tan
Double Angle Identities:
tan 2 =
cos 2 =cos2 sin 2
sin 2=2 sin cos
2 tan
2
1tan
Half Angle Identities:
1cos
sin =
2
2
1+cos
cos =
2
2
1cos
tan =
2
1+cos
Sum to Product:
( P+2Q ) cos( PQ
2 )
P+ Q
PQ
cosP+ cosQ=2cos (
cos (
)
2
2 )
sinP + sinQ=2 sin
PQ
sin (
( P+Q
)
2
2 )
P+Q
PQ
cosPcosQ=2sin (
sin (
)
2
2 )
sinPsinQ=2 cos
Product to Sum:
2 sin . cos =sin ( + ) +sin ( )
2 cos . sin =sin ( + ) sin ( )
2 cos . cos =cos ( + ) +cos ( )
- 2 sin . sin =cos ( + ) cos ( )
Law of Sine:
a
b
c
=
=
sin sin sin
Ata-Ul-Mustafa (0313-0001555)
Institute of Academic Services
Mathematics Formulae
2
b 2+ c2 a2
Cos=
2 bc
a =b +c 2 bc (Cos )
Law of Cosine:
b2=a2 +c 22 ac ( Cos )
Cos=
a2+ c 2b2
2ac
c 2=a 2+ b22 ab(Cos )
Cos=
a 2+ b2c 2
2 ab
Law of Tangent:
+
(
2 )
a+b
=
ab
tan (
2 )
tan
(i)
+
(
2 )
b+c
=
bc
tan (
2 )
+
(
2 )
c+ a
=
ca
tan (
2 )
tan
(ii)
tan
(iii)
Half Angle Formulas:
(sb)(sc)
sin =
2
bc
(sa)(sc)
sin =
2
ac
(sa)( sb)
sin =
2
ab
s( sa)
cos =
2
bc
s (sb)
cos =
2
ac
s (sc)
cos =
2
ab
Circumcircle:
The Circumcircle or Circumscribed circle of a Triangle is a circle which passes through all
the vertices of the Triangle. The center of this circle is called the Circumcenter (R) .
R=
abc
4
; where
sb ( sc)
s( sa)
=
and
s=
a+ b+c
2
In-Circle:
The In-Circle or Inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle contained in the triangle,
or a circle inscribed in a triangle is called In-Circle or Inscribed circle. It touches (inwardly) the
three sides of triangle. The center of the In-Circle is called the In-C enter (r).
r=
s
; where
sb (sc)
s( sa)
=
and
s=
a+ b+c
2
Escribed Circle:
An excircle or escribed circle is a circle that lying outside the triangle, touching externally to
one of its sides and touching internally to the extensions of the other two sides.
r 1=
sa
r 2=
sb
r3 =
sc
Area of Triangle (
):
Ata-Ul-Mustafa (0313-0001555)
Institute of Academic Services
Mathematics Formulae
sb ( sc)
s( sa)
=
s=
a+ b+c
2
(Also called Heron's or Heros Area Formula)
1
1
1
= ab sin = bc sin = ca sin
2
2
2
=
a2 sin sin b 2 sin sin c 2 sin sin
=
=
2 sin
2 sin
2 sin
Inverse Formulas:
sin 1 A +sin 1 B=sin1 ( A 1B 2+ B 1 A2 )
sin 1 Asin1 B=sin1 ( A 1B2B 1A 2 )
cos1 A +cos1 B=cos1 ( AB (1 A 2)(1B 2) )
cos Acos B=cos
( AB+ (1 A 2)(1B 2))
tan 1 A + tan1 B=tan 1
A +B
1 AB
2 tan 1 A=tan1
tan 1 Atan 1 B=tan 1
AB
1+ AB
2A
1 A2
Table of Trigonometric Values:
/2
degr
ee
in
radia
n
30
45
60
90
180
270
360
3
2
sin :
1
2
1
2
cos :
1
2
1
2
1 Quad.
Sin +ve
All +ve
Tan +ve
Cos +ve
nd
st
2 Quad.
rd
3 Quad.
th
4 Quad.
Ata-Ul-Mustafa (0313-0001555)
Institute of Academic Services
Mathematics Formulae
tan :
1
3
3/2
Derivatives Formulas
The Chain Rule
dy dy du
= .
dx du dx
Also Chain Rule is
d
'
fog ( x ) ] = [ f ( g ( x ) ) ] . g' (x)
[
dx
The Power Formula
d n
( x )=n x n1
dx
Product Rule
d
( u . v )=v . u' + u . v '
dx
Quotient Rule
d u v .u' u. v '
=
dx v
v2
()
Others:
d
1
( log a x )= x . ln a
dx
d
1
( ln x )=
dx
x
d x
( a )=a x .lna
dx
d x
x
(e )=e
dx
d
( sinx )=cosx
dx
d
( cosx )=sinx
dx
d
( tanx )=sec 2 x
dx
d
( secx ) =secx . tanx
dx
Ata-Ul-Mustafa (0313-0001555)
Institute of Academic Services
d
( cosecx )=cosecx . cotx
dx
Mathematics Formulae
d
( sechx ) =sechx .tanhx
dx
d
( cotx )=cosec 2 x
dx
d
(cschx)=cosechxcothx
dx
d
( sin1 x ) = 1 2
dx
1x
d
( cothx )=cosech 2 x
dx
d
( cos1 x )= 1 2
dx
1x
d
( sinh1 x ) = 12
dx
x +1
d
( tan1 x )= 1 2
dx
1+ x
d
( cosh1 x )= 12
dx
x 1
d
( sec 1 x )= 12
dx
x x 1
d
( tanh1 x )= 1 2 ; if |x|<1
dx
1x
d
( cosec1 x ) = 12
dx
x x 1
d
( coth1 x ) = 1 2 ;if |x|>1
dx
1x
d
( cot1 x ) = 1 2
dx
1+ x
d
( sech1 x ) = 1 2
dx
x 1x
d
( sinhx )=coshx
dx
d
( cosech1 x )= 1 2
dx
x 1+ x
d
( coshx )=sinhx
dx
d
( tanhx )=sech2 x
dx
Ata-Ul-Mustafa (0313-0001555)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Trig Cheat Sheet 1.4Dokument2 SeitenTrig Cheat Sheet 1.4agentc0re0% (1)
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsDokument27 Seiten© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsPrasanth VarrierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDokument10 SeitenTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- EquationsDokument17 SeitenEquationshasanmt23100% (1)
- Math Resources Trigonometric FormulasDokument10 SeitenMath Resources Trigonometric FormulasAnonymous j3w8EmJb8Noch keine Bewertungen
- X X X X TGX CTGX X X F X FX F X FX X X X X TG X TGX CTG X CTGXDokument1 SeiteX X X X TGX CTGX X X F X FX F X FX X X X X TG X TGX CTG X CTGXVesna Suvala100% (1)
- Sheet - 01 - Compound AngleDokument17 SeitenSheet - 01 - Compound AngleNoob Game PlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Extension 1 NotesDokument8 SeitenMathematics Extension 1 Notesfishybobo123Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of FormulaDokument2 SeitenList of FormulaAin NajlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometria FormulasDokument2 SeitenGeometria Formulasdaniel esteban salazar camachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometria FormulasDokument2 SeitenGeometria Formulasdaniel esteban salazar camachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)Dokument4 SeitenFormula Sheet - New Zealand Level 3 Calculus (2009)naedkcinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes MathDokument4 SeitenNotes MathNaveed Atta UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument6 SeitenTrigonometrylee_yi_5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry For LeafletDokument2 SeitenTrigonometry For LeafletSantoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trignometry Basic QuestionsDokument18 SeitenTrignometry Basic Questionsdev1996100% (1)
- Iit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsDokument6 SeitenIit - Jee Model Grand Test - Ii Paper - 1 SolutionsSayan Kumar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrigDokument1 SeiteTrigrajsalgyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in MathematicsDokument12 SeitenSome Important Formulae, Definitions and Results in Mathematicsparchure123100% (1)
- Opp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan TanDokument3 SeitenOpp Adj Opp Hyp Hyp Adj: Sin Sin Cos Cos Tan Tanchoosg100% (1)
- DemostracionesDokument2 SeitenDemostracionesdaniel esteban salazar camachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 03 2011 EAMCET MathsDokument15 Seiten30 03 2011 EAMCET MathsAmbili MuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsDokument6 SeitenSolutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsPreethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Trigon" Triangle +"metry" Measurement Trigonometry: Review of Trigonometry For CalculusDokument10 Seiten"Trigon" Triangle +"metry" Measurement Trigonometry: Review of Trigonometry For CalculusAbdulaziz MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nützliche Formeln Zur Vorlesung Elektrische Antriebe": Eulersche FormelDokument4 SeitenNützliche Formeln Zur Vorlesung Elektrische Antriebe": Eulersche FormelbastechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesDokument2 SeitenTrig Cheat Sheet: Formulas and IdentitiesMuzamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulae of TrigonometryDokument3 SeitenFormulae of TrigonometryManoj Khandelwal100% (1)
- Iit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0Dokument16 SeitenIit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0ARYAN SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA1301 Help SheetDokument3 SeitenMA1301 Help SheetChng Pei SzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential FormulaeDokument16 SeitenEssential FormulaeMaruthappan Sundaram100% (1)
- Essential Formulae: Number and AlgebraDokument7 SeitenEssential Formulae: Number and AlgebraShinigami01001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths FormulasDokument13 SeitenMaths FormulasMadhu Pali100% (2)
- MATHS Trigonometric FormulaeDokument9 SeitenMATHS Trigonometric FormulaeMahesh AbnaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Tap Luong Giac THPTDokument11 SeitenOn Tap Luong Giac THPTngocha91Noch keine Bewertungen
- g11 6 TrigonometryDokument73 Seiteng11 6 Trigonometryapi-235269401Noch keine Bewertungen
- Integer Type Questions Trigonometrical IdentitiesDokument5 SeitenInteger Type Questions Trigonometrical IdentitiesabcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB - M2E05 Trigonometry 2Dokument48 SeitenQB - M2E05 Trigonometry 2AllyLauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function Part 2Dokument40 SeitenFunction Part 2Muhd HafidzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formulario Matematicas 2009Dokument0 SeitenFormulario Matematicas 2009JJOCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexagesimal System: 60'' 1' 60' Right Angle Centesimal System: 100'' 1' 100' Right AngleDokument6 SeitenSexagesimal System: 60'' 1' 60' Right Angle Centesimal System: 100'' 1' 100' Right Anglesudheesh1995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formula SheetDokument2 SeitenFormula SheetchoosgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics???Dokument6 SeitenMathematics???DEFRON GAMINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Trig Identity ProblemsDokument4 Seiten24 Trig Identity ProblemsAldrean TinayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Stats Booklet 1Dokument20 SeitenMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Rations & Fns QnsDokument6 SeitenTrigonometric Rations & Fns QnsLokesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Mathematics - TrigonometryDokument12 SeitenH2 Mathematics - TrigonometryMin YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Sum Property: 0 - TheDokument4 SeitenAngle Sum Property: 0 - ThensddnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summaryof Trigonometric F NDokument3 SeitenSummaryof Trigonometric F NAbd El Rahman OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- m30-1 Formula SheetDokument1 Seitem30-1 Formula Sheetapi-289565679Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics TrigonometryDokument129 SeitenMathematics TrigonometryUdayveerSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 17: Algebra and Trigonometry Trigonometric IdentitiesDokument1 SeiteMathematics 17: Algebra and Trigonometry Trigonometric IdentitiesSanny Domingo AfableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Class FormulaeDokument8 SeitenSenior Class FormulaeOP GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesVon EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesBewertung: 1.5 von 5 Sternen1.5/5 (2)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYVon EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNoch keine Bewertungen