Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Atomic Structure Questions Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Molecular Mass & Mass Spectros
Hochgeladen von
Andrei FloreaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Atomic Structure Questions Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Molecular Mass & Mass Spectros
Hochgeladen von
Andrei FloreaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Atomic Structure Questions
Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Molecular Mass & Mass Spectroscopy
Deduce the relative atomic masses of the following
elements.
1.Silicon (28Si 92.21%, 29Si 4.70%, 30Si 3.09%)
2.Silver (107Ag 51.88%, 109Ag 48.12%)
3.Boron (10B 19.7%, 11B 80.7%)
4.Gallium (69Ga 60.2%, 71Ga 39.8%)
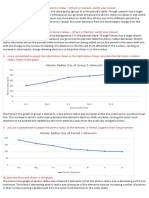
5.Zirconium (use the Fig.1 for guidance):
Figure 1
Assume in all cases the relative isotopic mass is equal to the mass number.
-------6. Bromine has two isotopes, with mass numbers 79 and 81. Its relative atomic mass is often given as
80. What does that tell you about the relative abundance of the two isotopes?
7. Most argon atoms have a mass number 40. How many neutrons does this isotope have? The
relative isotopic mass of this isotope is 39.961, but the relative atomic mass of argon is 39.948.
What can you deduce about the other isotopes of argon?
---------8. For each of the following stages in a mass spectrometer, state which part of the spectrometer is
responsible for it and how it works:
a) ionization
b) acceleration
c) deflection
d) detection
-------------------9. Deduce, giving reasons, the relative molecular mass of compound A, which has the following mass
spectrum:
100
80
relative
abundance
60
29
57
40
15
20
43
72
Ionisation energy questions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
How do you define the ionisation energy of a certain chemical species?
Why does the first ionisation energy of atoms generally increase across a period?
Why is the first ionisation energy of boron less than that of beryllium?
Why is the first ionisation energy of oxygen less than that of nitrogen?
Why do first ionisation energies decrease down a group?
Why does helium have the highest first ionisation energy of all the elements?
Why is the second ionisation energy of an atom always greater than the first?
Why does atomic size decrease across a period?
Why does atomic size increase down a group?
Why are cations always smaller than the corresponding atoms?
Why are anions always larger than the corresponding atoms?
Electronic configuration
Write the electronic configuration of the following using the arrow and box method:
1.
2.
Cu
3.
Mg+
Write the electronic configuration of the following using the orbital method:
4.
N3-
5.
Ar
6.
Sc3+
7.
Mn2+
8.
Fe3+
9.
V3+
Write the electronic configuration of the following using the shorthand arrow and box
method: 10.Cl-,
11.Fe, 12.Br.
Write the electronic configuration of the following using the shorthand orbital method:
13.
Cr
14.
Ga3+
15. Pb2+
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sefako Makgatho Health Sciences University: (Chemistry 1A)Dokument6 SeitenSefako Makgatho Health Sciences University: (Chemistry 1A)MotseilekgoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure Questions Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Molecular Mass & Mass SpectrosDokument2 SeitenAtomic Structure Questions Relative Atomic Mass, Relative Molecular Mass & Mass SpectrosAndrei FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Exercise 2 - Ram, RMM and Mass Spectra. MASS SPECTROMETRYDokument2 Seiten1.1 Exercise 2 - Ram, RMM and Mass Spectra. MASS SPECTROMETRYDr.AndrewMatovuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass SpecDokument6 SeitenMass Specapi-182809945Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen PDF 26Dokument1 SeiteDokumen PDF 26Farhan FarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure QuestionsDokument4 SeitenAtomic Structure QuestionsHovan Tall Nut TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Homework (Short)Dokument1 SeiteUnit 2 Homework (Short)api-3697114Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Tutorial 1Dokument3 SeitenYear 1 Tutorial 1Mel ManningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic STR & Periodictable Week Assignment 01Dokument2 SeitenAtomic STR & Periodictable Week Assignment 01Mary MannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and Molecules PG 1-30Dokument30 SeitenAtoms and Molecules PG 1-30muhammadbazlia0% (1)
- 2022-23 Class - 11TH Assignment of Chemistry Chapters - 1 To 4Dokument8 Seiten2022-23 Class - 11TH Assignment of Chemistry Chapters - 1 To 4carsk403Noch keine Bewertungen
- July 2023 Paper +1Dokument2 SeitenJuly 2023 Paper +1lotus25369Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 1701 - Week 4 - Note Taking Template: Chemistry I For Pre-Health SciencesDokument5 SeitenCHEM 1701 - Week 4 - Note Taking Template: Chemistry I For Pre-Health Sciencesapi-535501316Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic STR & Periodictable WSDokument4 SeitenAtomic STR & Periodictable WSMary MannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1bDokument5 SeitenTopic 1bapi-336093393Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1bDokument5 SeitenTopic 1bapi-336093393Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure and Periodic TrendsDokument5 SeitenAtomic Structure and Periodic TrendsJithesh ParambathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stiso H W Topic 2 QuestionsDokument7 SeitenStiso H W Topic 2 Questionsapi-235839943Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure Practice (#3)Dokument2 SeitenAtomic Structure Practice (#3)Brooks RalphNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem11 SM 1 RDokument8 SeitenChem11 SM 1 RdudoocandrawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Radius and Electronegativity - QuestionsDokument4 SeitenAtomic Radius and Electronegativity - QuestionsAnonymous Mj0pfScNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH - 3Dokument3 SeitenCH - 3Phantom GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Reviewing Content Questions 4.1 Defining The AtomDokument7 SeitenChapter 4 Reviewing Content Questions 4.1 Defining The AtomTouheed RamzaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplementary ProblemsDokument30 SeitenSupplementary ProblemsMike PatenaudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2.3 - Atomic Structure and Symbolism Student ManualDokument2 SeitenChemistry 2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2.3 - Atomic Structure and Symbolism Student ManualsiewyonglimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and The Mole (Pre-AP)Dokument13 SeitenAtoms and The Mole (Pre-AP)ddhhdhdhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isotope Atomic-MassDokument7 SeitenIsotope Atomic-MassMetro ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isotopes Atomic-Mass Guided-Inquiry StudentHandoutDokument7 SeitenIsotopes Atomic-Mass Guided-Inquiry StudentHandoutMetro ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sã©rie 2 STIDokument3 SeitenSã©rie 2 STIjosbenachenhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 NewDokument59 SeitenChapter 6 NewhoiminhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure QuestionsDokument1 SeiteAtomic Structure QuestionsJames MungallNoch keine Bewertungen
- P4 Atomic Structure Combined ScienceDokument42 SeitenP4 Atomic Structure Combined Sciencesamibarcelona08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1Dokument12 SeitenActivity 1tlchewNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chem Isotopes and Mass Spectrometry ADokument19 SeitenAP Chem Isotopes and Mass Spectrometry AharhourzbedamnedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsDokument13 Seiten2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsCHAKRI BABLUNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Unit2 Lec5 Subatomic ParticlesDokument17 Seiten2014 Unit2 Lec5 Subatomic ParticlesSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT Chemistry Eng-11-12 G AdvancedDokument80 SeitenSAT Chemistry Eng-11-12 G AdvancedАрнур ОспановNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6A Practice MT2 F13Dokument4 Seiten6A Practice MT2 F13Aileen LiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part I: Multiple Choice 008questions (15 Points)Dokument6 SeitenPart I: Multiple Choice 008questions (15 Points)Duy Do MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument24 SeitenAtomic StructureKris DookharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDokument16 SeitenAtoms, Molecules and IonsIsabelle HasheelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Brown 13-14Dokument12 SeitenChapter 2 Brown 13-14bellatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemisrty Assignments Class 11Dokument4 SeitenChemisrty Assignments Class 11affanshaikh182008Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 1010 Tutorial Sheet 3Dokument5 SeitenCHE 1010 Tutorial Sheet 3Chimuka Onson MapikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 Module 1 Lesson 3Dokument7 SeitenQuarter 1 Module 1 Lesson 3Myka Ella VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igcse 71 Atoms&RadioactivityDokument29 SeitenIgcse 71 Atoms&RadioactivityHany ElGezawy100% (3)
- EE 340 Recitation Review Section For Exam1Dokument5 SeitenEE 340 Recitation Review Section For Exam1Yasir ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 AP Unit PacketDokument35 Seiten1 AP Unit Packetmohamed harbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imp. QuestionDokument5 SeitenImp. Questionvinayak PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 103-Problem Set 1 SolutionsDokument7 SeitenCHEM 103-Problem Set 1 SolutionsAracsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssessmentDokument5 SeitenAssessmentAdrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision QuestionsDokument7 SeitenRevision QuestionsShazia FarheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure WorksheetsDokument21 SeitenAtomic Structure Worksheetssantoshkumarsir7706100% (1)
- Structure 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 PracticeDokument6 SeitenStructure 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 PracticeEthan ElliotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure TutorialDokument3 SeitenAtomic Structure Tutorialchong56Noch keine Bewertungen
- One Mark QuestionsDokument4 SeitenOne Mark Questionshari95Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer)Dokument9 SeitenENT145/3 Materials Engineering Tutorial 1 (Answer)Hữu Danh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interpretation of MS-MS Mass Spectra of Drugs and PesticidesVon EverandInterpretation of MS-MS Mass Spectra of Drugs and PesticidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Y12 Unit 1 Test 4 1.4 Periodicity: SECTION A TOTAL ../18 Section B Total /7 TOTAL ./25Dokument5 SeitenY12 Unit 1 Test 4 1.4 Periodicity: SECTION A TOTAL ../18 Section B Total /7 TOTAL ./25Andrei FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding RevisionDokument7 SeitenBonding RevisionAndrei FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonding HomeworkDokument8 SeitenBonding HomeworkAndrei Florea100% (1)
- Program VaraDokument1 SeiteProgram VaraAndrei FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romanian Coat of Arms Arge General Ș School Inspectorate LogoDokument1 SeiteRomanian Coat of Arms Arge General Ș School Inspectorate LogoAndrei FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen