Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
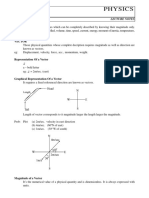
θ A d CB V V x: + AB � � − Abba � � � � − ≠ − A (B C) (A B) C � � � � � � − − ≠ − −
Hochgeladen von
WillSmithOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
θ A d CB V V x: + AB � � − Abba � � � � − ≠ − A (B C) (A B) C � � � � � � − − ≠ − −
Hochgeladen von
WillSmithCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
and the diagonal
NM represents A B
+
a) subtraction of vectors does not obey commutative law A B B A
b) subtraction of vectors does not obey Associative law A (B C) (A B) C
A
d
CB
VB
VR
x
d
BC
BV
RV
NL
AO
B
M
Elements of Vectors
29
c) subtraction of vectors obeys distributive law m(A B) mA mB
75. If two vectors each of magnitude F act at a point, the magnitude of their
difference depends on
the angle between then
Magnitude of difference of vectors = 2Fsin
76. Relative velocity : When the distance between two bodies is altering either in
magnitude or
direction or both, then each is said to have a relative velocity with respect to the
other.
Relative velocity is vector difference of velocities.
a. The relative velocity of body 'A' w.r.t. 'B' is given by VR VA VB
=
b. The relative velocity of body 'B' w.r.t. 'A' is given by VR VB VA
c. VA VB and VB VA
are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction
d. V = V V = V + V 2.VAVB. cos
2
B
2
RABA
e. For two bodies moving in the same direction, relative velocity is equal to the
difference of
velocities. ( = 0.cos 0 = 1)
RV
= V A VB
f. For two bodies moving in opposite direction, relative velocity is equal to the
sum of their
velocities. ( =180;cos180 = 1)
RV
=VA + VB
g. If they move at right angle to each other, then the relative velocity
= 22
2
v1 + v .
77. Rain is falling vertically downwards with a velocity
and a person is
travelling with a velocity VP.
Then the relative velocity of rain with respect
to the person is V VR VP
|B|
RV
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Master the Fundamentals of Electromagnetism and EM-InductionVon EverandMaster the Fundamentals of Electromagnetism and EM-InductionNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS-103 Engineering PhysicsDokument16 SeitenBS-103 Engineering PhysicsMuhammad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute Dependent Motion NotesDokument26 SeitenAbsolute Dependent Motion NotesYadana100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - VectorsDokument15 SeitenChapter 3 - VectorsShort BossNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorsDokument24 SeitenVectorsahmed massoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Quantities Vectors & ScalarsDokument41 SeitenPhysical Quantities Vectors & ScalarsLin Xian Xing100% (1)
- FORMULASDokument60 SeitenFORMULASmtorreslumiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors & ScalersDokument16 SeitenVectors & ScalersRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics of Machines Compiled HariraoDokument94 SeitenKinematics of Machines Compiled HariraoUpender DhullNoch keine Bewertungen
- MME 2323-Mechanics of Machines April 2019 Marking SchemeDokument18 SeitenMME 2323-Mechanics of Machines April 2019 Marking Schemecharles ondiekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Dsu PDFDokument32 SeitenModule 1 Dsu PDFVinu RamadhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.6 Four-Link Mechanism: Velocity AnalysisDokument4 Seiten2.6 Four-Link Mechanism: Velocity AnalysisMushini NagabhushanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aandb : Angle Between Forces Magnitude of ResultantDokument2 SeitenAandb : Angle Between Forces Magnitude of ResultantWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsDokument10 SeitenTeaching Notes - (Xiii) : VectorsSankar KumarasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Notes On VectorDokument7 SeitenRevision Notes On VectorPavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorsDokument46 SeitenVectorsmonika gompa100% (1)
- 1 - Fundamentals of VectorsDokument3 Seiten1 - Fundamentals of Vectorsa85609616Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics 12-10Dokument16 SeitenDynamics 12-10Abdullatif AlOmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion 2d AakashDokument10 SeitenMotion 2d AakashNavin RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion in Straight LineDokument12 SeitenMotion in Straight LineamitctoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 VectorsDokument14 Seiten3 VectorsArvindhkandhavel RNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorsDokument28 SeitenVectorsChill Kwong100% (1)
- 2.6 Four-Link Mechanism: Velocity AnalysisDokument4 Seiten2.6 Four-Link Mechanism: Velocity AnalysisNAGU2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Some Basic Rules of Tensor Calculus PDFDokument26 SeitenA Some Basic Rules of Tensor Calculus PDFrenatotorresa2905Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPH 110 - Full NotesDokument101 SeitenSPH 110 - Full NotesErick Wangila WanyonyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2&3 HRDokument60 SeitenUnit2&3 HRtarasasankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector & 3D - SheetDokument71 SeitenVector & 3D - SheetRAVI NAGARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Illustrative Examples Physics Vectors RDokument20 SeitenIllustrative Examples Physics Vectors RVishal KalraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Motion of Projectiles: Sunil Kumar SinghDokument12 SeitenRelative Motion of Projectiles: Sunil Kumar SinghVishal GaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- A DA N 36: Chapter - 11 - Vector AlgebraDokument26 SeitenA DA N 36: Chapter - 11 - Vector AlgebraPratham MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Content Outline: Review of Vector CalculusDokument81 SeitenContent Outline: Review of Vector CalculusEsubalew TeleleNoch keine Bewertungen
- ) - The Arrow Specifies The Vector Graphically. The Displacement VectorDokument2 Seiten) - The Arrow Specifies The Vector Graphically. The Displacement VectorpmagrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velocity and AccelartionDokument56 SeitenVelocity and Accelartionadus lakshmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector AlgebraDokument10 SeitenVector AlgebraSamrat JanjanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Three Five Kilograms Twenty-Two Degrees Celsius: Scalar QuantitiesDokument6 SeitenA Three Five Kilograms Twenty-Two Degrees Celsius: Scalar QuantitiesDars- Limos SaludezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 2. ELMAG - 1 - Vector AlgebraDokument43 SeitenMicrosoft PowerPoint - 2. ELMAG - 1 - Vector AlgebraDeni Ristianto100% (1)
- Chapter 2.7 - Relative Motion - StudentversionDokument17 SeitenChapter 2.7 - Relative Motion - StudentversionAmirulHanif AlyahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Motion of ProjectilesDokument13 SeitenRelative Motion of Projectilesumapavani0% (1)
- Physics NotsDokument4 SeitenPhysics NotsMujahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorDokument34 SeitenVectorImam HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word - VectorsDokument23 SeitenMicrosoft Word - Vectorsjitender8Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 03Dokument10 SeitenCH 03Qassem MohaidatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Vector Analysis-Dot, Vector and Triple Scalar Product SY 2021-2022 EEDokument37 Seiten2-Vector Analysis-Dot, Vector and Triple Scalar Product SY 2021-2022 EEMarc RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1vectorsDokument27 SeitenChapter 1vectorsDagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC8451 Unit IDokument19 SeitenEC8451 Unit INagai KumaresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector AlgebraDokument15 SeitenVector AlgebraKarthik NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - Ch5 VectorsDokument25 SeitenPhysics - Ch5 VectorsNur IffatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Scalarsvectors 161127184703Dokument85 Seiten4 Scalarsvectors 161127184703Kamal KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics Questions and Answers - Addition of A System of Coplanar ForcesDokument3 SeitenEngineering Mechanics Questions and Answers - Addition of A System of Coplanar ForcesAnonymous FHYNiBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec8451 Emf Lecture NotesDokument61 SeitenEc8451 Emf Lecture NotesNarenthra BaalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics (1000 MCQS)Dokument199 SeitenEngineering Mechanics (1000 MCQS)IyfiyffiiyvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Revision Notes Vector AlgebraDokument8 SeitenClass 12 Revision Notes Vector Algebrashubham upadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Theory MCQDokument278 SeitenElectromagnetic Theory MCQSatwik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Algebra Class 12Dokument10 SeitenVector Algebra Class 12Abhayraj SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Vectors Questions With Answers @moeremedialprojectDokument3 SeitenUnit 1 Vectors Questions With Answers @moeremedialprojectsemiramisbah69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz TimeDokument122 SeitenQuiz TimejohnnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP VectorDokument10 SeitenDPP VectorKunalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2. Mathematical MethodsDokument17 SeitenChapter 2. Mathematical Methodsdeep34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sciensctist ChartDokument4 SeitenSciensctist ChartWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Albert Einstein. 1879-1955. A Biographical Memoir by John Archibald WheelerDokument23 SeitenAlbert Einstein. 1879-1955. A Biographical Memoir by John Archibald Wheelergbabeuf100% (1)
- I Hav ItDokument1 SeiteI Hav ItWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Words For MarchDokument1 SeiteWords For MarchWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vulnerability in The Temple Area Is Associated With TheDokument1 SeiteVulnerability in The Temple Area Is Associated With TheWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buy LandDokument3 SeitenBuy LandWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbdullaDokument1 SeiteAbdullaWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- God Is Great IsDokument1 SeiteGod Is Great IsWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ganand ChandrasekaranDokument1 SeiteGanand ChandrasekaranWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word of The Day Words For March, 2015: HospiceDokument14 SeitenWord of The Day Words For March, 2015: HospiceWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word of The DayDokument14 SeitenWord of The DayWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Words For MarchDokument1 SeiteWords For MarchWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sagar Is AbsentDokument1 SeiteSagar Is AbsentWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Go Went GoneDokument1 SeiteGo Went GoneWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am ArtDokument1 SeiteI Am ArtWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Candy CrushDokument1 SeiteCandy CrushWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam IdeaDokument1 SeiteExam IdeaWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- LaughDokument1 SeiteLaughWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- C V RamanDokument5 SeitenC V RamanWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am Going To Tell YouDokument1 SeiteI Am Going To Tell YouWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Phy ChemDokument1 SeiteMath Phy ChemWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am Going To Gujrat, It Is A Very Nice PlaceDokument1 SeiteI Am Going To Gujrat, It Is A Very Nice PlaceWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am WhoDokument1 SeiteI Am WhoWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel Service CentreDokument11 SeitenAlcatel Service CentreWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other Parts of PlantsDokument1 SeiteOther Parts of PlantsWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refine Byrefine byDokument68 SeitenRefine Byrefine byWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rate of Respiration Is Fast. 3.they Lack Respiratory Surface 3. Respiratory Surface Is Generally Present. AerobicDokument1 SeiteThe Rate of Respiration Is Fast. 3.they Lack Respiratory Surface 3. Respiratory Surface Is Generally Present. AerobicWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rate of Respiration Is Fast. 3.they Lack Respiratory Surface 3. Respiratory Surface Is Generally Present. AerobicDokument1 SeiteThe Rate of Respiration Is Fast. 3.they Lack Respiratory Surface 3. Respiratory Surface Is Generally Present. AerobicWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mumbai CST To Neral Train TimetableDokument3 SeitenMumbai CST To Neral Train TimetableWillSmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aadhaar Data Update FormDokument1 SeiteAadhaar Data Update FormAbhishek Kumar100% (2)
- School of Mathematics and Statistics: MATH1151 - AlgebraDokument4 SeitenSchool of Mathematics and Statistics: MATH1151 - AlgebrabosadpapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banach Algebras An Introduction Pure and Applied MathematicsDokument358 SeitenBanach Algebras An Introduction Pure and Applied MathematicsoctbudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01Dokument47 SeitenChapter 01Ye NoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooperative Object Transportation With Differential-Drive Mobile Robots Control and ExprimentationDokument10 SeitenCooperative Object Transportation With Differential-Drive Mobile Robots Control and ExprimentationAbdrahmane BenaouadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concepts in Calculus IIIDokument508 SeitenConcepts in Calculus IIIcantor2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of The Caputo-FabrizioDokument9 SeitenProperties of The Caputo-FabriziomeshachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Optimal TransportDokument56 SeitenComputational Optimal TransportRuigang WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 122 PGTRB Maths Unit 6 Study Material PDFDokument8 Seiten122 PGTRB Maths Unit 6 Study Material PDFkarunakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- M832 Approximation Theory Course NotesDokument94 SeitenM832 Approximation Theory Course NotesViator in TerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teuvo Kohonen - Self-Organizing MapsDokument438 SeitenTeuvo Kohonen - Self-Organizing MapsAdri Dos Anjos100% (2)
- 10.1007/978 3 642 30668 6Dokument427 Seiten10.1007/978 3 642 30668 6Atul ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fergusson College (Autonomous) Pune: With Effect From July 2019Dokument33 SeitenFergusson College (Autonomous) Pune: With Effect From July 2019Om S panchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calc2 6a Vectors and 3d Geometry PDFDokument7 SeitenCalc2 6a Vectors and 3d Geometry PDFAnkit RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Power in Alternating-Current CircuitsDokument35 SeitenVector Power in Alternating-Current CircuitselectrosciNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT523 Project PDFDokument4 SeitenMAT523 Project PDFMuhd IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- System of Linear Equations: Direct & Iterative MethodsDokument36 SeitenSystem of Linear Equations: Direct & Iterative MethodsLam WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC 400 Notes For Class 1 PDFDokument46 SeitenEC 400 Notes For Class 1 PDFAvijit PuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Matrices and VectorsDokument32 SeitenReview of Matrices and Vectorschanphat01001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Statics and Mechanics HW 1 PITTDokument4 SeitenStatics and Mechanics HW 1 PITTAbdulazeez AbiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.8 DataMiningDokument4 Seiten2.8 DataMiningChinmayi Kulkarni100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Motion Along A Line: StudentDokument17 SeitenChapter 2 Motion Along A Line: StudentQassem MohaidatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Analytic GeometryDokument24 Seiten03 Analytic Geometrysami ullah saleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 1 ProblemsDokument4 SeitenHW 1 ProblemsBorisRibicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus III - Notes of B. TsirelsonDokument129 SeitenCalculus III - Notes of B. Tsirelsontom-manor-1138Noch keine Bewertungen
- Páginas DesdeM 3Dokument84 SeitenPáginas DesdeM 3Armando LiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- LW 1115 Math245notes (Waterloo)Dokument50 SeitenLW 1115 Math245notes (Waterloo)user2357Noch keine Bewertungen
- Long - History of Monge Problem 11pDokument11 SeitenLong - History of Monge Problem 11pDino SolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-Adic Hilbert SpacesDokument16 SeitenP-Adic Hilbert SpacesdmtriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ORF523 Lec2Dokument13 SeitenORF523 Lec2navid babaeiNoch keine Bewertungen