Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Apafricatimeline
Hochgeladen von
api-230184052Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Apafricatimeline
Hochgeladen von
api-230184052Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
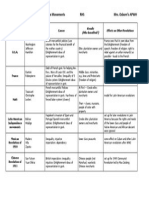
Regional Timeline/Outline for: Sub-Saharan Africa
PERIOD 1 & 2
8000BCE-600CE
PERIOD 3
600-1450
RHS
Mrs. Osborn
PERIOD 4
1450-1750
PERIOD 5
1750-1900
PERIOD 6
1900-Present
Re-colonization of Africa;
Sierra Leone, Liberia ;
coastal kingdoms ruled
by warlords/merchants;
intertribal war;
Revolutions;
White Mans Burden
End of Atlantic Slave
TradeIslamic states
of West Africa still trade
slaves; rely on slave
trade more; economic
slump
Rapid population growth
Decolonization of Africa;
attempt at representative
government; involved in
WWII; renewed
independence efforts
civil war, government
corruption; socialism
Industrialization; guns,
textiles, alcohol
(importance of foreign
imports); Enlightenment
Slow technological
development due to
colonization, mercantilism,
internal instability; miners;
no money for industrial
goods after WWI; oil
(Nigeria)
Pharaoh/queen (living
incarnation of sun god),
internal disorder, invasions
(900 BCE), irrigation
Kingship legitimized by Islam,
People of The Book, Bantu
(stateless societies)
leaders cooperated with
slave traders; monarchy
Trade with Kush and
Mesopotamia, agricultural
villages engaged in trade.
Trade, with Islam as unifying
factor, trans-Saharan trade
routes; Ghana (gold), Mali;
gold, salt, honey, slaves, ivory,
imports, trade with Byzantine
Empire, agriculture
Triangular Trade/ TransAtlantic Slave Trade;
guns traded for slaves;
slave trade with
Mediterranean world
Patriarchal, but women
manage household, own
property, regents of rulers,
priestesses, scribes, can
divorce, high priest class
Merchants valued; patriarchal
society, rich women more
restricted; Islamic law, People
of the Book, religious
tolerance, class centered
around age group
Hieroglyphics, bronze
tools, papyrus, 365 day
calendar, medicine, math,
astronomy, iron
Hellenistic thought,
science/math
Demographic shifts;
more males in the slave
trade than females
(females traded more in
the East coast);
depopulated
manioc, maize, sweet
potatoes (from America);
technology suffered due
to slave trade
Pyramids, temples,
hieroglyphics
Linguistic, architectural, artistic
version of Christianity;
calligraphy, Mosques, minarets
Islamic art/architecture,
paper making; arts
suffered due to slave
trade
Christian/ Islamic arts;
literary/artistic forms of
the west
Western artistic forms,
religious art, native art
(export)
Islamic urban center, Bantu
Migrations, trade centers,
Trans-Saharan trade route
Open to foreign takeover
due to economic slump;
colonized by Europe
Islam , Christianity in Ethiopia
and Egypt, animistic,
syncretism
Islam, Christianity,
animism, ancestor
worshipsyncretism
Islam, Christianity,
animism, atheists
Religion
Polytheism , afterlife
(mummification), Book of
the Dead
Part of Triangular Trade
(with Europe and
America); beginnings of
European exploration ;
Kongo, Benin, Mali,
Songhai
Islam, Christianity,
animism, ancestor
worshipsyncretism
Decolonizationnew
sovereign nations
Empire
Geographyprotected,
unique civilization, not as
urban as Mesopotamia,
Nile River
Politics
Economy
Social
Class/Gender
Science/Inventions
Art/Architecture
Globalized economies;
mercantilism in former
colonies; poverty
stricken countries;
international debt
Spanish Flu (global
epidemic); clear black
majority making
decolonization easier
(apartheid in South
Africa)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- King Minos Labyrinth: Amber, Ivory, Grain, Metals Like Gold, Copper, TinDokument3 SeitenKing Minos Labyrinth: Amber, Ivory, Grain, Metals Like Gold, Copper, TinJosh'z LlamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- King Minos Labyrinth: Amber, Ivory, Grain, Metals Like Gold, Copper, TinDokument3 SeitenKing Minos Labyrinth: Amber, Ivory, Grain, Metals Like Gold, Copper, TinJosh'z LlamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 AfricaDokument2 Seiten1 AfricaJennie YanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harzig and Hoerder 2009 CH 2.5-2.9Dokument16 SeitenHarzig and Hoerder 2009 CH 2.5-2.9Mia KisicNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Civilization (S1)Dokument12 SeitenAfrican Civilization (S1)Siham BoularouahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Persian Ay - 8Dokument2 SeitenPersian Ay - 8apwhhchsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrs. Osborn's APWH Cram Packet: Period 3 - Regional and Transregional Interactions, C. 600CE To 1450 CE, Chapters 10-16 (20% of APWH Exam)Dokument6 SeitenMrs. Osborn's APWH Cram Packet: Period 3 - Regional and Transregional Interactions, C. 600CE To 1450 CE, Chapters 10-16 (20% of APWH Exam)Elize ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Textbooks Obscure and Distort The History of Slavery: Race-Myths From The Extreme LeftDokument5 SeitenHow Textbooks Obscure and Distort The History of Slavery: Race-Myths From The Extreme LeftJ.J.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Early Modern Era Notes For AP World History (1450-1750)Dokument3 SeitenEarly Modern Era Notes For AP World History (1450-1750)Girl powerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient Civilizations outside AfricaDokument55 SeitenAncient Civilizations outside AfricaChristabel OkoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronology of Human HistoryDokument9 SeitenChronology of Human HistoryepthompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civilzation of Ancient Axum and EthiopiaDokument10 SeitenCivilzation of Ancient Axum and EthiopiaZak StoophNoch keine Bewertungen
- WADE Student Colonial GovtDokument48 SeitenWADE Student Colonial GovtNatalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Chapter 3 AP World HistoryDokument8 SeitenNotes - Chapter 3 AP World HistoryJohn LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Native Merchants: The building of the black business class in South AfricaVon EverandNative Merchants: The building of the black business class in South AfricaBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Mali Empire ReadingDokument5 SeitenMali Empire Readingapi-469038025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civilizations in Africa Assn2Dokument3 SeitenCivilizations in Africa Assn2King Alvin KENoch keine Bewertungen
- Slavery and slave trade in Eastern AfricaDokument20 SeitenSlavery and slave trade in Eastern AfricaAdebayo WorshipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awesome 8000 B.C.E-600 C.E: By: Stephanie Lisette Moya, Dorathy Jane Scrudder, Stefanie Alyssa Lyon, Jigar Sanjay ShahDokument34 SeitenAwesome 8000 B.C.E-600 C.E: By: Stephanie Lisette Moya, Dorathy Jane Scrudder, Stefanie Alyssa Lyon, Jigar Sanjay ShahGonzalo Gabaliel RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of African CivilizationsDokument22 SeitenDevelopment of African CivilizationsJessalyn CilotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major World Regions, Feudalism, and the Spread of IslamDokument12 SeitenMajor World Regions, Feudalism, and the Spread of IslamKevin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ancient GreeceDokument8 SeitenAncient GreeceRamita UdayashankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emergence of Human Communities in the Ancient Mediterranean and Middle EastDokument7 SeitenThe Emergence of Human Communities in the Ancient Mediterranean and Middle EastUmay PelitNoch keine Bewertungen
- The African American Story Part 1Dokument27 SeitenThe African American Story Part 1Timothy100% (1)
- Africa InvestigationDokument4 SeitenAfrica InvestigationBrian Roberts100% (1)
- Tapper-Nomads in IranDokument38 SeitenTapper-Nomads in Iranexergy 33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slavery in Context: A Global PerspectiveDokument12 SeitenSlavery in Context: A Global PerspectiveLinda SaraviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PerbiDokument13 SeitenPerbiTim LaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kehinde2013 ReferenceWorkEntry Trans-SaharanSlaveTradeDokument4 SeitenKehinde2013 ReferenceWorkEntry Trans-SaharanSlaveTradeLuc CardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Southwest Asia Indo-European MigrationDokument24 SeitenSouthwest Asia Indo-European Migrationapi-259253396Noch keine Bewertungen
- APWH ReviewDokument637 SeitenAPWH Reviewdssguy99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report on Ancient Civilizations of the Middle East and AfricaDokument9 SeitenReport on Ancient Civilizations of the Middle East and Africa12 ABM A- ABAD, GLIZZLENoch keine Bewertungen
- History Research Paper Topics Before 1500Dokument7 SeitenHistory Research Paper Topics Before 1500ezkugohkf100% (1)
- Developments in Africa SupplementalDokument10 SeitenDevelopments in Africa Supplementalapi-690086282Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Origins and Nature of New World SlaveryDokument16 SeitenThe Origins and Nature of New World SlaveryAshanti NelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transoceanic Interchanges 1450-1750Dokument1 SeiteTransoceanic Interchanges 1450-1750Eunpyo ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arabia Before IDokument3 SeitenArabia Before IZain Malik ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Burn - Lyric Age of Greece (1978, Hodder & Stoughton Educational)Dokument448 SeitenBurn - Lyric Age of Greece (1978, Hodder & Stoughton Educational)Lucas Díaz LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khazars 2Dokument12 SeitenKhazars 2duschis2Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Enslavement PeriodDokument1 SeiteThe Enslavement PeriodElpidio ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- African Slave TradeDokument15 SeitenAfrican Slave TradeKern Grant100% (1)
- World History Final Exam Survival Guid1e RevisedDokument6 SeitenWorld History Final Exam Survival Guid1e RevisedBrianna HufferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Africa Before European ArrivalDokument2 SeitenAfrica Before European ArrivalBrigitterosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rise of The Atlantic Worl1Dokument1 SeiteThe Rise of The Atlantic Worl1dheerajroykumarroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black History Should Be Taught 365 Days A YearVon EverandBlack History Should Be Taught 365 Days A YearBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- APWorld EssayDokument3 SeitenAPWorld EssayJosh RoshalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Guide 3Dokument34 SeitenReview Guide 3Noah EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Empire Across The Three ContinentDokument6 SeitenAn Empire Across The Three ContinentKunsh WadheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP World History Key TermsDokument61 SeitenAP World History Key TermsDAJman726100% (4)
- Apush Chapter 1 Chapter TermsDokument11 SeitenApush Chapter 1 Chapter Termsaca2811Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atestat EnglezaDokument19 SeitenAtestat EnglezaPatrisia BorșanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoprecolonialsocieties AfricatheencounterDokument4 SeitenShoprecolonialsocieties Africatheencounterapi-367531995Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Erik Sass's The Mental Floss History of the WorldVon EverandSummary of Erik Sass's The Mental Floss History of the WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andrew Yang Period 7 Persian Chart AP World History Chapter 21: Africa and The Slave TradeDokument3 SeitenAndrew Yang Period 7 Persian Chart AP World History Chapter 21: Africa and The Slave Tradeapwhhchs100% (1)
- 2017-2018 District Calendar - Boe Approved 10-18-2016 4Dokument1 Seite2017-2018 District Calendar - Boe Approved 10-18-2016 4api-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Coming of Christianity To AxumDokument2 SeitenThe Coming of Christianity To Axumapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Whap 2016-17 Syllabus - Student VersionDokument6 SeitenWhap 2016-17 Syllabus - Student Versionapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- ApeastasiatimelineDokument1 SeiteApeastasiatimelineapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap PoldevDokument2 SeitenAp Poldevapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apwh How To NotecardsDokument1 SeiteApwh How To Notecardsapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Week 1 How To DoDokument3 SeitenAp Week 1 How To Doapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Major ReviewDokument16 SeitenMajor Reviewapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Whap Reading Calendar 2016-17 Revised 8-8Dokument2 SeitenWhap Reading Calendar 2016-17 Revised 8-8api-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2016-17 Bell Schedule PshsDokument1 Seite2016-17 Bell Schedule Pshsapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap RevsindDokument1 SeiteAp Revsindapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap TradeDokument2 SeitenAp Tradeapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Strayer Review Questions CH 20-23Dokument1 SeiteStrayer Review Questions CH 20-23api-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap GlobaltradeDokument2 SeitenAp Globaltradeapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap IndrevchartDokument1 SeiteAp Indrevchartapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccot 2 in Class Essay CH 22Dokument1 SeiteCcot 2 in Class Essay CH 22api-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap GenderissuesDokument2 SeitenAp Genderissuesapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap DemographicDokument3 SeitenAp Demographicapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Globalization Visual Sources CH 23Dokument6 SeitenGlobalization Visual Sources CH 23api-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Faiths Around WorldDokument2 SeitenFaiths Around Worldapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- China 1900-1949Dokument15 SeitenChina 1900-1949api-230184052100% (1)
- Classical Civs Chart PDFDokument3 SeitenClassical Civs Chart PDFgovandlaw4671Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chinese DynastiesDokument34 SeitenChinese Dynastiesapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccot Essay & Thesis FormatDokument1 SeiteCcot Essay & Thesis Formatapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Globalization Visual Sources CH 23Dokument6 SeitenGlobalization Visual Sources CH 23api-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- A-Bomb SWDokument5 SeitenA-Bomb SWapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vanguard Video Guide - Chinese Development in AngolaDokument1 SeiteVanguard Video Guide - Chinese Development in Angolaapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rise of StalinDokument24 SeitenRise of Stalinapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apwh Period 5 ReviewDokument3 SeitenApwh Period 5 Reviewapi-230184052Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Mystery of Why Portugal Is So Doomed - Matthew O'Brien - The AtlanticDokument18 SeitenThe Mystery of Why Portugal Is So Doomed - Matthew O'Brien - The AtlanticLuis C. OlivalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monster Industrial Shred Series - North AmericaDokument8 SeitenMonster Industrial Shred Series - North AmericaJames DonaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-10664Dokument10 SeitenISO-10664Daniel Quijada LucarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Head'S Application: Project Implementation PaperDokument27 SeitenSchool Head'S Application: Project Implementation PaperEd ManalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economic growth with endogenous saving behavior and Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans modelDokument8 SeitenEconomic growth with endogenous saving behavior and Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans modelMihaela PisoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Analysis of CEAT LTDDokument5 SeitenFinancial Analysis of CEAT LTDSikander KalraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost ObjectiveDokument5 SeitenCost ObjectiveKarmen ThumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambuja CementDokument20 SeitenAmbuja CementArvindYadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement - THABANI 3 MONTHSDokument14 SeitenStatement - THABANI 3 MONTHSvelyassetsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policy Brief: India and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS)Dokument12 SeitenPolicy Brief: India and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGS)Nishat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Data AnalysisDokument54 SeitenChapter 4 Data AnalysisCheng YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument5 Seiten1kawishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Economics Set 8Dokument5 SeitenBusiness Economics Set 8SUNIL SONAWANENoch keine Bewertungen
- Benaglia V CIR PDFDokument4 SeitenBenaglia V CIR PDFGlenn caraigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas YojanaDokument32 SeitenPradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas YojanaTQUAD ADVENTURENoch keine Bewertungen
- SBFC CharterDokument5 SeitenSBFC CharterEmmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Costs of Doing Business in Thailand: Utility RatesDokument5 SeitenCosts of Doing Business in Thailand: Utility RatesColin HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gap Analysis: Presented by You ExecDokument11 SeitenGap Analysis: Presented by You ExecJuan Gómez100% (1)
- American Victory The Real Story of Todays AmwayDokument244 SeitenAmerican Victory The Real Story of Todays AmwayAutodidático Aulas100% (1)
- Donation Bathan JMMDokument9 SeitenDonation Bathan JMMJim M. MagadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP PROJECT Econ FinalDokument28 SeitenGROUP PROJECT Econ FinalHazelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microeconomics: Chapter 5 ChoiceDokument4 SeitenMicroeconomics: Chapter 5 ChoiceRulojy100% (1)
- Glossary of Banking ServicesDokument6 SeitenGlossary of Banking ServicesKarthik GottipatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Feasibility Study for Dermatology Hospital in Jordan's Dead SeaDokument52 SeitenPre-Feasibility Study for Dermatology Hospital in Jordan's Dead SeaKlare MontefalcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCGDokument138 SeitenBCGANKUSHSINGH2690Noch keine Bewertungen
- European Central BankDokument51 SeitenEuropean Central BankJunwil TorreonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SW DirDokument104 SeitenSW DirFahad Ashfaq KhattakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modular KitchenDokument24 SeitenModular KitchenHarsh ThakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ABC's of VSADokument21 SeitenThe ABC's of VSAcarmenyeo80% (5)
- Financial Analysis ProjectionsDokument6 SeitenFinancial Analysis ProjectionsAshish AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen