Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment Crystallography
Hochgeladen von
Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment Crystallography
Hochgeladen von
Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignments on crystallography
date: 10.11.2014
Theoritical Questions:
I
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
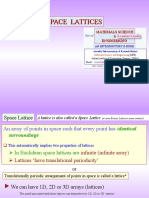
Define the following terms: (i) space lattice (ii) basis (iii) crystal structure (iv) unit cell (v) primitive cell (vi) nonprimitive cell.
Explain how the combination of lattice with a basis forms the crystal structure?
What are Miller indices? Explain with examples. What are their utilities?
Sketch the Miller planes: (100), (010), (001), (110), (101), (011), (111).
Show that in a cubic crystal of side a, the inter-planar spacing between consecutive parallel planes of Miller indices
(hkl) is d hkl
6.
7.
8.
9.
a
2
h k2 l2
Give comparative study of (i) atomic positions (ii) effective number of atoms in a unit cell (iii) co-ordination number
(iv) atomic radius in terms of lattice constant (v) packing fraction (vi) void space of SC, BCC, FCC crystal.
Derive a relation between lattice constant and density of the material of a cubic crystal.
How many crystal structures are there in 3-dimensions? Mention their lattice parameters.
Mention how many Bravais lattices are corresponding to each crystal system.
Numericals:
1
A crystal has FCC structure and its atomic radius is 0.175 nm. What is the volume of the unit cell?
The molecular weight of KBr (FCC) is 119.01 gm-mole-1 and its density is 2.75 gm-cm-3. Calculate the lattice constant of
this crystal.
If the lattice constant for a BCC crystal is 3.57 A and the density of the material of the crystal is 8575 kg-m-3, find its atomic
mass.
A crystal plane cuts at 3a, 4b and 2c along the crystallographic axes. Find Miller indices.
3
4
5
A crystal has lattice constants of 1 A, 2 A and 3 A. A plane (321) cuts an intercept of 1 A along x-axis. Find the intercepts
along other axes.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ElectrostaticsDokument4 SeitenElectrostaticsSyed Raheel AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Dokument10 SeitenPhysics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Puneet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Electricity Question BankDokument5 SeitenCurrent Electricity Question BankAshok PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM20024 Lecture Notes 04 - CrystalsDokument53 SeitenCHEM20024 Lecture Notes 04 - CrystalsEzriel QuantumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Management & Conservation Action PlanDokument24 SeitenEnergy Management & Conservation Action PlanDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classxiiassignment201920Dokument84 SeitenClassxiiassignment201920Dhaval KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- REV12020 PhysicsDokument4 SeitenREV12020 Physicshari kroviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XII Physics AssignmentDokument28 SeitenClass XII Physics AssignmentApex Institute100% (1)
- Physics All IndiaDokument17 SeitenPhysics All IndiahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15A03804 Power Plant EngineeringDokument2 Seiten15A03804 Power Plant EngineeringCharanTheja PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Xi Physics Test PapersDokument14 SeitenCbse Xi Physics Test PapersBhavesh DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Crystal StructureDokument38 SeitenChapter 2 Crystal StructureAbo Abdo100% (1)
- LatticeDokument56 SeitenLatticeCarlos UrregoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB - CFD (U1 & U2) PDFDokument3 SeitenQB - CFD (U1 & U2) PDFGanesh Natarajan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Aurora ClassesDokument21 SeitenPhysics: Aurora ClassesxentrixxNoch keine Bewertungen
- XII NCERT Objective CH 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDokument18 SeitenXII NCERT Objective CH 1 Electric Charges and FieldskarishmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RRB SirDokument1 SeiteRRB Sirprince alok KarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDokument33 SeitenClass 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight Linenick tyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1261 XII Physics Support Material Study Notes and VBQ 2014 15Dokument370 Seiten1261 XII Physics Support Material Study Notes and VBQ 2014 15RajdeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics XII Chapter Wise Question BankDokument87 SeitenPhysics XII Chapter Wise Question BankAdiba khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines-ClassificationDokument21 SeitenIC Engines-ClassificationChintu Santhu0% (1)
- 1.electric Charge & Fields - TestDokument18 Seiten1.electric Charge & Fields - TestArshdeep singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 DeterminantsDokument80 SeitenNCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 4 Determinantskunal vayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperfections in SolidsDokument10 SeitenImperfections in Solidsshubhamgautam56_64970% (1)
- NV MCQ-4 PDFDokument8 SeitenNV MCQ-4 PDFTejas UpadhyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - Defects in Crystalline Solids PDFDokument49 Seiten05 - Defects in Crystalline Solids PDFFRANCESCA SARAZANoch keine Bewertungen
- Defects LatestDokument55 SeitenDefects LatestJaddu MSDNoch keine Bewertungen
- C16 Electrostatic Student1Dokument81 SeitenC16 Electrostatic Student1Faris Izzuddin RoslinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistors Notes 4Dokument13 SeitenTransistors Notes 4Anil Sai100% (1)
- Physics Question BankDokument11 SeitenPhysics Question BankdevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units and MeasurementsDokument13 SeitenUnits and MeasurementsNITHISH KUMAR.GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Book Back One MarkDokument11 SeitenPhysics Book Back One MarkThaddeus MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Metal OperationsDokument52 SeitenSheet Metal OperationsthakruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Favor Calcular Integrales Por Álgebra y Sustitución Tan) : DX X X XDokument1 SeiteFavor Calcular Integrales Por Álgebra y Sustitución Tan) : DX X X XSantiago Javier Casallas HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - IntroductionDokument47 SeitenBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - IntroductionSDO BSNL NALAGARHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 ElectrochemistryDokument49 SeitenChapter 18 ElectrochemistryDwivelia AftikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCM Question Bank 2 MarksDokument22 SeitenUCM Question Bank 2 MarksManivannan JeevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Physics-Important Questions: Shorts UNIT - 1 (Units and Dimensions)Dokument4 SeitenEngineering Physics-Important Questions: Shorts UNIT - 1 (Units and Dimensions)psatyasankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class XI: Physics Chapter 10: Mechanical Properties of FluidsDokument7 SeitenClass XI: Physics Chapter 10: Mechanical Properties of Fluidschandramohan muruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- M-Power Iit and Neet Academy: MV MGHDokument9 SeitenM-Power Iit and Neet Academy: MV MGHVenu GopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 1 Formulae Ray OpticsDokument14 Seiten6 1 Formulae Ray OpticsNathanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- SO9 BinaryPD-1Dokument13 SeitenSO9 BinaryPD-1Muhammad Tanweer Khan YousafzaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rapid Prototyping and ToolingDokument3 SeitenRapid Prototyping and Toolingappuanandh7811Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Technology-I - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument4 SeitenManufacturing Technology-I - Department of Mechanical EngineeringSoma SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions Bank On ELECTROSTATICSDokument3 SeitenQuestions Bank On ELECTROSTATICSAlok ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 - Respiration and Gas ExchangeDokument64 SeitenChapter 11 - Respiration and Gas ExchangeKareem DmourNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 Part - 1Dokument122 SeitenUNIT 1 Part - 1Ysv PavuluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEC361 2019 Question BankDokument10 SeitenAEC361 2019 Question BankVenky GollavelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board QuestionsDokument50 SeitenElectric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board Questionsgurveer sainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Regenerative Rankine Cycle PDFDokument1 Seite3.1 Regenerative Rankine Cycle PDFsubyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 12 Hot PhysicsDokument50 SeitenPhysics 12 Hot PhysicsdhirendrasisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics & Machinery Question PaperDokument4 SeitenFluid Mechanics & Machinery Question PaperaadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveDokument16 SeitenXii Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju Hssliveapi-3487796590% (1)
- Types of PatternDokument12 SeitenTypes of PatternadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 - Egm 241Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 3 - Egm 241king100% (1)
- Solid State Physics Midterm ExamDokument3 SeitenSolid State Physics Midterm ExamToqa ShweikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MatSci Assignment 1Dokument1 SeiteMatSci Assignment 1Harpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Sciences and EngineeringDokument15 SeitenMaterial Sciences and EngineeringSuraj RarathNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch03 과제Dokument7 Seitench03 과제ks kNoch keine Bewertungen
- VLSI TechnologyDokument89 SeitenVLSI TechnologyRaj PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 - Simple Harmonic MotionDokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 - Simple Harmonic MotionDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment ElectrostaticsDokument3 SeitenAssignment ElectrostaticsDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2 - Damped VibrationDokument1 SeiteAssignment 2 - Damped VibrationDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - Module 3Dokument2 SeitenAssignment - Module 3Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus - PH 101Dokument2 SeitenSyllabus - PH 101Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st YEAR - 2nd SEM 2014-2015 Book ListDokument1 Seite1st YEAR - 2nd SEM 2014-2015 Book ListDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nicol PrismDokument4 SeitenNicol PrismDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Physics Association: Membership Application FormDokument1 SeiteIndian Physics Association: Membership Application FormDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 2005 Physics 2Dokument5 Seiten12 2005 Physics 2Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI - Chapter 2 - TestDokument1 SeiteXI - Chapter 2 - TestDr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen