Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
35 - 42 Applications Mechanical Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Julio Alberto Paz CorderoOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
35 - 42 Applications Mechanical Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Julio Alberto Paz CorderoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
hp calculators
hp calculators
HP 35s Applications in Mechanical Engineering
Applications in mechanical engineering
Practice solving problems in mechanical engineering
- Application 1: Stress on an element (Mohr circle)
hp calculators
HP 35s Applications in Mechanical Engineering
Applications in mechanical engineering
This training aid will illustrate the application of the HP 35s calculator to several problems arising in mechanical
engineering. These examples are far from exhaustive, but do indicate the incredible flexibility of the HP 35s calculator.
Practice solving problems in mechanical engineering
Application 1: Stress on an element (Mohr circle)
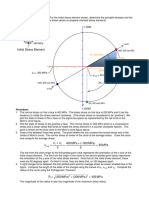
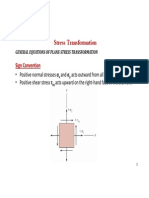
The Mohr circle equations convert an arbitrary stress configuration to principal stresses, maximum shear
stress, and rotation angle. It is then possible to calculate the state of stress for an arbitrary orientation '.
Figure 1
The Mohr circle formulas are shown below, where s is the normal stress, is the shear stress, sx is the
stress in the x direction for Mohr circle input, sy is the stress in the y direction for Mohr circle input, xy is the
shear stress on the element for the Mohr circle input, s1 and s2 are the principal stresses, is the rotation
angle, and max is the maximum shear stress. Note that is the angle of rotation from the specified axis to
the principal axis, and so should be thought of as a negative angle. This is opposite to the normal Mohr
circle convention.
2
Maximum shear stress
sx - sy
+ xy 2
=
2
max
Principal stress
s1 =
Principal stress
s2 =
Rotation angle
sx + sy
2
sx + sy
2
+ max
Figure 3
max
Figure 4
2 xy
1
= tan -1
2
sx sy
Figure 2
Figure 5
Example:
If sx = 25,000 psi, sy = -5,000 psi, and xy = 4,000 psi, compute the principal stresses, the angle of
rotation , and the maximum shear stress.
Solution:
Solve for the maximum shear stress, max.
hp calculators
-2-
HP 35s Applications in Mechanical Engineering - Version 1.0
hp calculators
HP 35s Applications in Mechanical Engineering
In RPN mode:
250005000z2=4000
=?eT
In algebraic mode:
?=4250005000z2
=4000eT
Figure 6
Solve for the principal stress, s1.
In RPN mode:
250005000z2hT
In algebraic mode:
4250005000z2hT
Figure 7
Solve for the principal stress, s2.
In RPN mode:
250005000z2hT
In algebraic mode:
4250005000z2hT
Figure 8
Solve for the rotation angle, .
In RPN mode:
24000250005000z
o2
In algebraic mode:
o240004250005000z
2
Figure 9
Answer:
hp calculators
The principal stresses, s1 and s2, are 25,524 psi and -5,524 psi. The angle of rotation, , is 7.4657 degrees.
The maximum shear stress is 15,524 psi.
-3-
HP 35s Applications in Mechanical Engineering - Version 1.0
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Stress6 ht08 2Dokument26 SeitenStress6 ht08 2fredrikalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohr's CircleDokument13 SeitenMohr's Circleaap1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBE2027 Structural Analysis I Chapter 7 - Mohr's CircleDokument28 SeitenCBE2027 Structural Analysis I Chapter 7 - Mohr's CircleManuelDarioFranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resistencia de MaterialesDokument141 SeitenResistencia de MaterialesOscar GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH1641 - W2008 Lecture 04 - Fatigue IIIDokument31 SeitenMECH1641 - W2008 Lecture 04 - Fatigue IIIShannon WolfeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6177-4 Press and Shrink FitsDokument11 Seiten6177-4 Press and Shrink FitsRajesh RajwadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Mechanics: Stress Mohr's Circle For Plane StressDokument22 SeitenSolid Mechanics: Stress Mohr's Circle For Plane Stressindula123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 13.ch14.transformation 22Dokument49 Seiten13.ch14.transformation 22sidsridhar89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mohr's Circle: Academic Resource CenterDokument23 SeitenMohr's Circle: Academic Resource CentersyedamiriqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohrs Circle Construction ExampleDokument2 SeitenMohrs Circle Construction ExampleCarlos Alquinta PNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME328 Introduction to Design Cylinder Stresses: ldr + 2σ lr − 2l (σ dr term because it's theDokument3 SeitenME328 Introduction to Design Cylinder Stresses: ldr + 2σ lr − 2l (σ dr term because it's theAndri IndriawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin CylinderDokument16 SeitenThin CylinderPranksterz StarzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle Stress ExamplesDokument36 SeitenPrinciple Stress ExamplesPaldexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohrs Circle Construction ExampleDokument2 SeitenMohrs Circle Construction ExampleTesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-4 Moher CircleDokument37 SeitenLecture-4 Moher CircleAbhishek BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEP - SM (Theory) - 19-CLE-48Dokument8 SeitenCEP - SM (Theory) - 19-CLE-48Zain ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 307 Tutorial2 2014 PDFDokument9 Seiten307 Tutorial2 2014 PDFNusret MeydanlikNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 207 - Stresses On Inclined Plane-UpdatedDokument26 SeitenME 207 - Stresses On Inclined Plane-Updatedjintellibya100% (1)
- Principal StressesDokument5 SeitenPrincipal Stressesavinashn1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2: Analysis of Stress: 2.3.1 GENERAL S S T D C C SDokument21 SeitenModule 2: Analysis of Stress: 2.3.1 GENERAL S S T D C C SManish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principal Stresses, Maximum Shear Stresses & Mohr's CircleDokument36 SeitenPrincipal Stresses, Maximum Shear Stresses & Mohr's CircleRyanWongJiaHanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial: Combined Stresses, Mohr's Circle Diagram and Principal StressesDokument10 SeitenTutorial: Combined Stresses, Mohr's Circle Diagram and Principal StressesFidhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - COMPLEX STRESSDokument33 SeitenChapter 6 - COMPLEX STRESSNurul Raihan Shahizan100% (1)
- 8a-Ex. Stress Transformation Examples: GivenDokument3 Seiten8a-Ex. Stress Transformation Examples: GivenadnandjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elliptic and Incompressible PDFDokument27 SeitenElliptic and Incompressible PDFAnonymous x4uYEUMjKxNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 4 - Plane Stress Transformation PDFDokument66 SeitenWEEK 4 - Plane Stress Transformation PDFRichie BobbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background Notes: Xy Yx X y Xy XyDokument6 SeitenBackground Notes: Xy Yx X y Xy Xybridge14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plane Stress TransformDokument24 SeitenPlane Stress Transformsandrock92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mohr Circle1 PDFDokument5 SeitenMohr Circle1 PDFFatima KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Null 1 1Dokument13 SeitenNull 1 1Mohameb BabkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Mohr's CircleDokument22 SeitenApplication of Mohr's CircleMohit ShivaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project A: Yamil G. Brunet Yordano Lopez Omar SanchezDokument21 SeitenProject A: Yamil G. Brunet Yordano Lopez Omar SanchezLuis PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Stress Tutorial 3 Complex Stress and Strain: © D.J.Dunn 1Dokument22 SeitenComplex Stress Tutorial 3 Complex Stress and Strain: © D.J.Dunn 1Php TutorialsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix D Basic Basic Engineering Engineering Calculations CalculationsDokument25 SeitenAppendix D Basic Basic Engineering Engineering Calculations CalculationsaakashtrivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical DesignDokument51 SeitenMechanical DesignsafaozhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Strip Rolling - 2:: R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401Dokument7 SeitenAnalysis of Strip Rolling - 2:: R. Chandramouli Associate Dean-Research SASTRA University, Thanjavur-613 401Devlina GaharwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEP - SM (Theory)Dokument7 SeitenCEP - SM (Theory)Zain ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas 0001Dokument7 SeitenProblemas 0001Luis Piruca MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3d Stress TutDokument6 Seiten3d Stress TutUpender DhullNoch keine Bewertungen
- W2009 Assignment 11 SolutionDokument10 SeitenW2009 Assignment 11 Solutionyuyuhuhu789Noch keine Bewertungen
- BFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2: Stress and Strain TransformationDokument27 SeitenBFC 20903 (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 2: Stress and Strain Transformationhamierul mohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWDokument22 SeitenMEC 3611: Structural Mechanics: Lecture 3: REVIEWhellolover0% (1)
- 6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Dokument49 Seiten6-Transformation of Stress & Strain (Jan2013)Mohammad HanafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 05 Compound StressesDokument7 SeitenChapter 05 Compound StressesAshish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Linear Regression and CorrelationDokument52 SeitenSimple Linear Regression and CorrelationMajmaah_Univ_Public100% (1)
- LabDokument9 SeitenLabKin Wai HongNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionDokument13 SeitenCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology:: Course Title: Course Number: Course DescriptionEdmil Jhon AriquesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor Performance AnalysisDokument30 SeitenCompressor Performance Analysisdnageshm4n244100% (2)
- Plane and Principal Stress - 2Dokument32 SeitenPlane and Principal Stress - 2adnankhan1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Fatigue SpreadsheetsDokument73 SeitenMetal Fatigue SpreadsheetsKishore BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesVon EverandMathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Kieselkalk: Susceptibility To Alkali Silica ReactionDokument1 SeiteKieselkalk: Susceptibility To Alkali Silica ReactionAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali-Silica ReactionDokument9 SeitenAlkali-Silica ReactionAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foreshock: Occurrence Mechanics Earthquake Prediction Examples of Earthquakes With Foreshock Events ReferencesDokument3 SeitenForeshock: Occurrence Mechanics Earthquake Prediction Examples of Earthquakes With Foreshock Events ReferencesAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blind Thrust EarthquakeDokument2 SeitenBlind Thrust EarthquakeAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- AftershockDokument5 SeitenAftershockAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkali-Silica ReactionDokument9 SeitenAlkali-Silica ReactionAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRE Word ThesaurusDokument137 SeitenGRE Word ThesaurusPhanidhar GubbalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EarthquakeDokument6 SeitenEarthquakeAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prestressed ConcreteDokument15 SeitenPrestressed ConcreteAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damping RatioDokument4 SeitenDamping RatioAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akashi BridgeDokument6 SeitenAkashi BridgeAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precast ConcreteDokument1 SeitePrecast ConcreteAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tension ForcesDokument3 SeitenTension ForcesAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater TreatmentDokument6 SeitenWastewater TreatmentAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production (Economics)Dokument9 SeitenProduction (Economics)Alfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactor Mixing - Complete Mix, Plug Flow, & HybridDokument3 SeitenReactor Mixing - Complete Mix, Plug Flow, & HybridAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- WastewaterDokument6 SeitenWastewaterAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer ProgrammingDokument7 SeitenComputer ProgrammingAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prescriptive AnalyticsDokument7 SeitenPrescriptive AnalyticsAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- WastewaterDokument6 SeitenWastewaterAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big DataDokument25 SeitenBig DataAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market EconomyDokument8 SeitenMarket EconomyAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Mix ModelingDokument8 SeitenMarketing Mix ModelingAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- MarketingDokument18 SeitenMarketingAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lean StartupDokument10 SeitenLean StartupAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- SurveyingDokument15 SeitenSurveyingAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Validated Learning: See AlsoDokument1 SeiteValidated Learning: See AlsoAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnalyticsDokument6 SeitenAnalyticsAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Least Squares FittingDokument3 SeitenLeast Squares FittingAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Least SquaresDokument11 SeitenLeast SquaresAlfredo Romero GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson# 9 Irr of Ra 8495Dokument10 SeitenLesson# 9 Irr of Ra 8495Jom NamlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kloppenborgresume 12734631027669 Phpapp01Dokument6 SeitenKloppenborgresume 12734631027669 Phpapp01Seyton123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Forging Die Design For Gear BlankDokument4 SeitenForging Die Design For Gear BlankAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precast Concrete Connections. Issues and Innovative SolutionsDokument87 SeitenPrecast Concrete Connections. Issues and Innovative SolutionsCsongor BiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Guide To ISO-14692Dokument12 SeitenQuick Guide To ISO-14692maninventor100% (5)
- A N Engineering Report On Unit 8: Engineering Design, Assignment 2 - Use of Computer Based Technology in Engineering DesignDokument14 SeitenA N Engineering Report On Unit 8: Engineering Design, Assignment 2 - Use of Computer Based Technology in Engineering DesignTop Engineering SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Strut-And-tie Model For Ultimate Loads of Precast Concrete Joints With Loop Connections in TensionDokument8 SeitenA Strut-And-tie Model For Ultimate Loads of Precast Concrete Joints With Loop Connections in Tensionmanoelj_26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Profile: Using Fuzzy Logic in LogixDokument2 SeitenSolutions Profile: Using Fuzzy Logic in LogixpfalencarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nbs Technical Note 1319Dokument252 SeitenNbs Technical Note 1319asarolicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anish KumarDokument3 SeitenAnish KumarVineet DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column BasesDokument29 SeitenColumn BasesNavi Rengarajan100% (4)
- Identification of Sags and Swells Using Pic MicrocontrollerDokument6 SeitenIdentification of Sags and Swells Using Pic MicrocontrollerijsretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis Report: My Choice My Future (MCMF)Dokument20 SeitenAnalysis Report: My Choice My Future (MCMF)Crazerzz LohithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hermeticity Testing of Mems and Microelectronic Packages: September 2013Dokument2 SeitenHermeticity Testing of Mems and Microelectronic Packages: September 2013Enrique OsorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommercialComplete NFPA 285 BrochureDokument8 SeitenCommercialComplete NFPA 285 BrochureMehmet OzdenNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSE Walls For Support of Highway BridgesDokument28 SeitenMSE Walls For Support of Highway Bridgestalaati50% (2)
- Ansi Sdi RD 2017 StandardDokument12 SeitenAnsi Sdi RD 2017 StandardAlekNoch keine Bewertungen
- EGCE 430 Lecture 01-1 OverallDokument3 SeitenEGCE 430 Lecture 01-1 OverallleandropessiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS 1358-2004 - Bursting Discs and Devices PDFDokument45 SeitenAS 1358-2004 - Bursting Discs and Devices PDFThaiminh VoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telephone Directory (2016)Dokument22 SeitenTelephone Directory (2016)Santhosh AkashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boston Gear Dcx202erp Ratiotrol PDFDokument31 SeitenBoston Gear Dcx202erp Ratiotrol PDFlalo100% (1)
- EE413Dokument4 SeitenEE413bravotolitsNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDAS E-Learning Courses: Sharing Knowledge, Gaining Experience, Making DifferenceDokument43 SeitenMIDAS E-Learning Courses: Sharing Knowledge, Gaining Experience, Making DifferenceFauzan SoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Stage Analysis Reflecting Long-Term DeformationDokument18 SeitenConstruction Stage Analysis Reflecting Long-Term DeformationAshish LoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BN I CatalogDokument120 SeitenBN I CatalogMujjo SahbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holibajoli ARMAC Quotation VidyutDokument3 SeitenHolibajoli ARMAC Quotation VidyutLalit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26 05 43 Underground Ducts and Raceways For Electrical SystemsDokument7 Seiten26 05 43 Underground Ducts and Raceways For Electrical SystemsjopaypagasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Level of Implementation of Building Information Modelling Education in Nigerian UniversityDokument6 SeitenAssessment of Level of Implementation of Building Information Modelling Education in Nigerian UniversityAbdullahi Mohammed AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wbjee Branches Seats WBJEE-2020Dokument22 SeitenWbjee Branches Seats WBJEE-2020Anish MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Software Requirements SpecificationsDokument16 SeitenWriting Software Requirements Specificationskicha0230Noch keine Bewertungen