Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is A Static Switch
Hochgeladen von
Mary HarrisonOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is A Static Switch
Hochgeladen von
Mary HarrisonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What is a Static Switch?
Posted on January 11, 2012 by admin
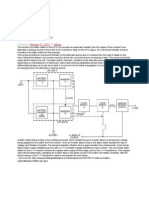
The function of a static switch in the UPS is to provide an automatic transfer from the output of the inverter to an
alternate or backup source in the event of an overload or fault on the UPS output. An overcurrent transfer circuit is
included in the static switch for this purpose.
This circuit provides an overcurrent transfer to the alternate source due to inrushes from the load or faults on the
load. Without this feature, the inverter could be driven into current limit prior to clearing a fault. This would most likely
cause all the loads to be lost. The static switch, therefore, transfers to the alternate source at 110% to 125%
(depending on manufacturer) of rated load, where fault clearing capabilities should exist. Because this circuit cannot
differentiate between an inrush and a fault, it is common for the initial energisation of a load to cause a transfer and
be energized from the alternate or backup source.
A static switch that provides a four-millisecond break when transferring upon inverter failure is sensing the voltage
being supplied to the switch from the inverter. Once an inverter failure occurs, the static switch senses the loss of
voltage and initiates a transfer. The sense-to-transfer initiation time is approximately four milliseconds. A zero-break
static switch is also available but only with a CVT (constant voltage transformer) type inverter. The zero-break static
switch on the CVT inverter monitors the square wave output of the bridge, prior to the CVT transformer. If the square
wave should deteriorate, indicating an inverter failure; the sense circuit in the switch will initiate a transfer, with the
stored energy in the CVT transformer used to accomplish the zero-break.
- See more at: http://www.joneslanglasallesites.com/theengineroom/2012/01/11/what-is-a-staticswitch/#sthash.3MBiqVqE.dpuf
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Application UpsDokument8 SeitenApplication UpsAerwin BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsVon EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesVon EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benchmark Systems For Digital Computer Simulation of A Static Transfer SwitchDokument8 SeitenBenchmark Systems For Digital Computer Simulation of A Static Transfer SwitchArturo Isidro Conde PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Phase Current - Simple CalculationDokument7 SeitenThree Phase Current - Simple CalculationRinda_RaynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Load Dump AnalysisDokument17 SeitenLoad Dump Analysisascvgh20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Current MeasurementDokument7 SeitenCurrent Measurementmuhd_paehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow Part 4Dokument4 SeitenElectrical Thumb Rules You MUST Follow Part 4shaikhsajid242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting Fusing Time of Overloaded PCB Traces Can We Predict It at All - With Douglas Brooks, PHD and Dr. Johannes Adam - ARTECH HOUSE INSIDERDokument12 SeitenPredicting Fusing Time of Overloaded PCB Traces Can We Predict It at All - With Douglas Brooks, PHD and Dr. Johannes Adam - ARTECH HOUSE INSIDERGanesan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- DMX Dimmer PackDokument6 SeitenDMX Dimmer PackcdvsolucionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Murphy's Laws of Combat OperationsDokument4 SeitenMurphy's Laws of Combat OperationsPaul ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecom Battery PDFDokument2 SeitenTelecom Battery PDFAq MwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverter Battery Sizing FaqDokument3 SeitenInverter Battery Sizing FaqFull DocumentaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Industrial Electrical Safe Work Practices: Paper No. ESW-39 Sal Sferrazza Heath GarrisonDokument5 SeitenNew Industrial Electrical Safe Work Practices: Paper No. ESW-39 Sal Sferrazza Heath GarrisonmjimenezgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Phase Conditions in Transformers - Analysis and Protection AlgorithmDokument14 SeitenOpen Phase Conditions in Transformers - Analysis and Protection AlgorithmMaximo Gomez GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue PDFDokument102 SeitenCatalogue PDFhakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- FusingDokument2 SeitenFusingsusanta2uNoch keine Bewertungen
- UN Test Manual Lithium Battery RequirementsDokument10 SeitenUN Test Manual Lithium Battery Requirementsvenkata_gaddamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Flash Faults Calculations Hazard AnalysisDokument10 SeitenArc Flash Faults Calculations Hazard AnalysisMuhammad ShahzaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Wire Gauge PDFDokument5 SeitenAmerican Wire Gauge PDFHarshal VaidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ampacity of Cables in Single Covered Trays - IEEEDokument12 SeitenAmpacity of Cables in Single Covered Trays - IEEEBoris CalderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hawkin Electrical Guide No.8Dokument360 SeitenHawkin Electrical Guide No.8clive ellisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Flash Hazard Calculations in DC Systems R1Dokument36 SeitenArc Flash Hazard Calculations in DC Systems R1DEVI PRASAD GREENSECURENoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic PPT For PFDokument39 SeitenBasic PPT For PFsrichander50% (2)
- Battery Discharge Current CalcDokument2 SeitenBattery Discharge Current CalcSteven MarksNoch keine Bewertungen
- American Wire GaugeDokument5 SeitenAmerican Wire GaugeCunniah DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inrush Current Calculation PDFDokument7 SeitenInrush Current Calculation PDFGilberto MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Electrical LoadsDokument2 SeitenTypes of Electrical LoadsChandaKunda100% (1)
- Fault Current and The Effects On Clampstar®: Test At)Dokument4 SeitenFault Current and The Effects On Clampstar®: Test At)Dante FilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unified Power Quality ConditionerDokument19 SeitenUnified Power Quality ConditionerShameer Sr S RNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPS Presentation Ppt290721Dokument57 SeitenUPS Presentation Ppt290721Aakanksha GahlautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Short Current of TransformerDokument18 SeitenCalculating Short Current of TransformerZaferullah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWG SWG Wire Gauge TableDokument0 SeitenAWG SWG Wire Gauge TableuumpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate The Suitable Capacitor Size in Farads & kVAR For PF ImprovementDokument4 SeitenCalculate The Suitable Capacitor Size in Farads & kVAR For PF ImprovementmaungsoekhinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Control of DC Microgrid With Variable Generation and Energy StorageDokument5 SeitenPower Control of DC Microgrid With Variable Generation and Energy StorageSEP-PublisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulation Test SystemDokument12 SeitenInsulation Test SystemYi Fang YueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection According To The ANSI - IEEE 946 - Open ElectricalDokument8 SeitenProtection According To The ANSI - IEEE 946 - Open ElectricalDoly DamanikNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Design Multi-Kw Converters For Electric Vehicles Part 4 - Power Factor Correction PDFDokument9 SeitenHow To Design Multi-Kw Converters For Electric Vehicles Part 4 - Power Factor Correction PDFoszemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelling of LithiumDokument18 SeitenModelling of LithiumSaumya SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE UPS SLD 225-500kvaDokument1 SeiteGE UPS SLD 225-500kvashivaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- The RS-485 Design GuideDokument9 SeitenThe RS-485 Design GuideZoran FabekovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Phase AC Calculations Revisited: AN110 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 6Dokument6 Seiten3-Phase AC Calculations Revisited: AN110 Dataforth Corporation Page 1 of 6arunmozhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- c1 PDFDokument43 Seitenc1 PDFMadhushan DassanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medium-Voltage High-Speed Source-Transfer Switching Systems A New Tool To Solve Power Quality ProDokument6 SeitenMedium-Voltage High-Speed Source-Transfer Switching Systems A New Tool To Solve Power Quality Proue06037Noch keine Bewertungen
- Example:-: How To Calculate How Much Battery Capacity (SLA Battery) You NeedDokument12 SeitenExample:-: How To Calculate How Much Battery Capacity (SLA Battery) You Needyeo_wh8977Noch keine Bewertungen
- VFD Harmonic MitigationDokument17 SeitenVFD Harmonic Mitigationbirmaduu100% (1)
- Estimation of Power System Inertia Constant and Capacity of Spinning-Reserve Support Generators Using Measured Frequency TransientsDokument8 SeitenEstimation of Power System Inertia Constant and Capacity of Spinning-Reserve Support Generators Using Measured Frequency TransientsadinamartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notifier Battery Calculations-Readme PDFDokument13 SeitenNotifier Battery Calculations-Readme PDFvictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Automotive Battery Monitoring System - ReportDokument30 SeitenReal Time Automotive Battery Monitoring System - ReportOmkar MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distributed Energy StorageDokument3 SeitenDistributed Energy StoragejuevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Load ModelingDokument15 SeitenIndustrial Load ModelingSandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Best of Bob PeaseDokument338 SeitenThe Best of Bob PeaseCARROUCHO62Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage Drop Calculations For Engineers BeginnersDokument6 SeitenVoltage Drop Calculations For Engineers BeginnersAbdul Rawoof ShaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enclosure Heat Load PDFDokument55 SeitenEnclosure Heat Load PDFdexiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bob Pease Booke Let Ron Analog MasterDokument334 SeitenBob Pease Booke Let Ron Analog MasterTEEHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityVon EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems: A Problem-Based ApproachVon EverandModern Control of DC-Based Power Systems: A Problem-Based ApproachNoch keine Bewertungen
- en Rolling Bearings and Seals in Electric Motors and GeneratorsDokument146 Seitenen Rolling Bearings and Seals in Electric Motors and Generatorseakkachai_tNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 6Dokument8 SeitenArticle 6Mary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Power Plant DesignDokument15 SeitenBasic Power Plant DesignMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Motor Selection and Application GuideDokument32 SeitenAC Motor Selection and Application GuideDanilo Jose GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DECS-100 Digital Excitation Control System: Eatures EnefitsDokument2 SeitenDECS-100 Digital Excitation Control System: Eatures EnefitsMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5kva DG SetDokument1 Seite5kva DG SetMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cho PapDokument27 SeitenCho PapMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auxiliary & Tertiary LoadingDokument2 SeitenAuxiliary & Tertiary LoadingMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compact AVRDokument3 SeitenCompact AVRMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pentium ArchitectureDokument18 SeitenPentium ArchitectureMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substation AutomationDokument83 SeitenSubstation AutomationMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Syn Woodward ManualDokument71 SeitenAuto Syn Woodward ManualMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Static SwitchDokument1 SeiteWhat Is A Static SwitchMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM32xx UserManualDokument108 SeitenPM32xx UserManualMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 6Dokument8 SeitenArticle 6Mary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intel 80x86Dokument13 SeitenIntel 80x86Mary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Power Plant DesignDokument15 SeitenBasic Power Plant DesignMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Motor Selection and Application GuideDokument32 SeitenAC Motor Selection and Application GuideDanilo Jose GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA Standard 71.04Dokument12 SeitenISA Standard 71.04Luis Alberto Chable GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDokument101 Seiten2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Chargers and Charging MethodsDokument4 SeitenBattery Chargers and Charging MethodsMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Motor Selection and Application GuideDokument32 SeitenAC Motor Selection and Application GuideDanilo Jose GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Charging 14-22Dokument9 SeitenBattery Charging 14-22Anonymous U7bJ4KANoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Thermal Overload RelaysDokument6 SeitenABB Thermal Overload RelaysoctaviovalenciacNoch keine Bewertungen
- An II - DG 250KVA Tech SpecificationsDokument19 SeitenAn II - DG 250KVA Tech SpecificationsMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esp OperationDokument11 SeitenEsp OperationMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- C & SDokument24 SeitenC & SthavaselvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HWX Leaflet NewDokument8 SeitenHWX Leaflet NewMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 TypeDokument5 Seiten05 TypeMary HarrisonNoch keine Bewertungen