Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Question 3
Hochgeladen von
Carlos AlbertoCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Question 3
Hochgeladen von
Carlos AlbertoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
error
10
10
10
10
-5
-10
-15
first order
second order
fourth order
-20
10
-5
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
10
delta x
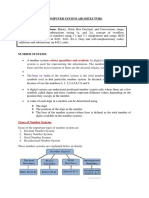
Figure 1 - Numerical error of the finite difference method with different orders of accuracy
The chart above shows how the error of the first derivative of the given function is affected by the x size
and the order of the finite difference used. As we can see the fourth order always presented the small error,
but it has some fluctuations for small x due the fact that calculations performed to compute the
approximation for the derivative requires more algorisms than the actual numerical precision. For x
relatively large the first order scheme is actually better than the second order; mainly because the point
being analyzed (as shown in the figure below) information of the function in the x = 2 and x = 3 is taken to
calculate the derivative when using 2nd order accurate method, this introduce a considerable error in the
calculations, because the derivative at x = 2 is quite different that x = 4. On the other side, in the first order
scheme only the information in the nodes at x = 3 and x = 5 is taken in account, and in this range the
derivative is not so different than x = 4. For x between 103 and 101 the results are like expected, the
first order has the larger error, followed by the second order scheme and the fourth order discretization.
Figure 2 - Plot of the analyzed function
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reza Dianofitra - Lab Report - Convection Diffusion Problem PDFDokument17 SeitenReza Dianofitra - Lab Report - Convection Diffusion Problem PDFReza DianofitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffusion Simulation by The FDM in ExcelDokument3 SeitenDiffusion Simulation by The FDM in ExcelrodwellheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Am 585 HW 4Dokument21 SeitenAm 585 HW 4Jennifer HansonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 130 Numerical Solution To Ce ProblemsDokument10 SeitenMath 130 Numerical Solution To Ce ProblemsMia ManguiobNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAT005 Lab Exercise 3Dokument3 SeitenMAT005 Lab Exercise 3junalynnerosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework # 1: 1 Problem # 1Dokument10 SeitenHomework # 1: 1 Problem # 1Nadihah WahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical MethodsDokument72 SeitenNumerical MethodsAndreas NeophytouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial SimplexDokument17 SeitenTutorial SimplexLuis Angel BNoch keine Bewertungen
- A3 110006223Dokument7 SeitenA3 110006223Samuel DharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accuracy, Condition Numbers and Pivoting: The Effect of RoundingDokument4 SeitenAccuracy, Condition Numbers and Pivoting: The Effect of RoundingaleyhaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument6 SeitenAssignment 1Matkabhai Bhai100% (1)
- Computer Programming Week 4: OperatorsDokument36 SeitenComputer Programming Week 4: Operatorstt_kobraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS450 HW 1Dokument2 SeitenCS450 HW 1Benjamin ChiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical MethodsDokument10 SeitenNumerical MethodsflprietotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Error3 PDFDokument6 SeitenError3 PDFHamza MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter6 (MBI) ElDokument51 SeitenChapter6 (MBI) Eljokowi123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Non-Linear Curve Fitting: 1.1 LinearizationDokument3 Seiten1 Non-Linear Curve Fitting: 1.1 LinearizationflgrhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 01 Bisection Regula-Falsi and Newton-RaphsonDokument12 SeitenLab 01 Bisection Regula-Falsi and Newton-RaphsonUmair Ali ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simultaneous EquationsDokument5 SeitenSimultaneous EquationsBernard BraingixNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2 Written Algorithms For Whole-Number OperationsDokument12 Seiten4.2 Written Algorithms For Whole-Number OperationsAhmad Farid HaebahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Ii: Beyond Binary Classification: Handling More Than Two Classes, Regression, UnsupervisedDokument22 SeitenUnit Ii: Beyond Binary Classification: Handling More Than Two Classes, Regression, UnsupervisedChrsan RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Errors PDFDokument6 SeitenErrors PDFJuan Karlos BalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 138794Dokument42 Seiten138794Jackson Lam0% (1)
- L-6 Computer ArithmeticDokument37 SeitenL-6 Computer Arithmeticbabulkarim194Noch keine Bewertungen
- In Terp MethodsDokument46 SeitenIn Terp MethodsriccardocozzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math2059 p2Dokument23 SeitenMath2059 p2mecengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number System: Chapter - 3Dokument16 SeitenNumber System: Chapter - 3lvsaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution of Inverse Diffusion Problems in ExcelDokument4 SeitenSolution of Inverse Diffusion Problems in ExcelrodwellheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question: What Do The Empty Cells in Plot With Facet - Grid (DRV Cyl) Mean? How Do This Plot IsDokument5 SeitenQuestion: What Do The Empty Cells in Plot With Facet - Grid (DRV Cyl) Mean? How Do This Plot IsUtkarsh GurjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Circuit Analysis and Design - MalestromDokument32 SeitenDigital Circuit Analysis and Design - MalestromKevin RosadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Downey 07 Rand FloatDokument8 SeitenDowney 07 Rand Floatrose sandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDokument46 SeitenIntroduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsGinu ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDokument46 SeitenIntroduction To Computational Fluid Dynamicsanon_635727152Noch keine Bewertungen
- Raste Rising Lines CirclesDokument11 SeitenRaste Rising Lines CirclesAnish NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week01 - Introduction To NumericalDokument16 SeitenWeek01 - Introduction To NumericalHaziq IzharNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9334 Hood D ExcelodeDokument4 Seiten9334 Hood D ExcelodeRémyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Number SystemDokument18 SeitenNumber SystemJanarthanan SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week01 - Introduction To NumericalDokument48 SeitenWeek01 - Introduction To NumericalInunHazwaniKhairuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Computing - LESSON 1: Computer Arithmetic and Error Analysis 1Dokument10 SeitenScientific Computing - LESSON 1: Computer Arithmetic and Error Analysis 1Lee Hei LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 01: IT1005: Name: Lee Zhi Kang Matric No.: A0088205EDokument5 SeitenLab 01: IT1005: Name: Lee Zhi Kang Matric No.: A0088205ELee Zhi KangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite DifferenceDokument11 SeitenFinite DifferenceAlex IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 1 SolutionsDokument10 SeitenHomework 1 SolutionsRajesh GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELEC3030 Notes v1Dokument118 SeitenELEC3030 Notes v1kosmos3384Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Analysis On Extracting Square and Cube Roots by Aryabhata's MethodsDokument4 SeitenAn Analysis On Extracting Square and Cube Roots by Aryabhata's MethodsPrateekSharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Round-Off Errors and Truncation ErrorsDokument35 Seiten5 Round-Off Errors and Truncation ErrorsEdryan PoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSA Unit 1 NotesDokument46 SeitenCSA Unit 1 Notes6747 mohammedjeelaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arithm CRCDokument12 SeitenArithm CRCsai leenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 142 Experiment #1: Atomic Emission: Deadline: Due in Your TA's 3rd-Floor Mailbox 72 Hours After Your Lab EndsDokument8 SeitenChem 142 Experiment #1: Atomic Emission: Deadline: Due in Your TA's 3rd-Floor Mailbox 72 Hours After Your Lab Endsapi-301880160Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods c1/10Dokument4 SeitenNumerical Methods c1/10Iustin CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1 - 2 IntroductionDokument43 SeitenLec 1 - 2 IntroductionarafatasgharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Point Integration RuleDokument2 SeitenMid-Point Integration RulerodwellheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Numerical Solution MethodsDokument56 SeitenChapter 10 Numerical Solution MethodsmuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nu Taro ContinuousDokument23 SeitenNu Taro ContinuousRavi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ErrorsDokument106 SeitenErrorsapi-375687150% (2)
- 4 Mathematical OperationDokument7 Seiten4 Mathematical OperationsyukzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuous Distributions in RDokument155 SeitenContinuous Distributions in ROfosu AnimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line Drawing Algorithm: Mastering Techniques for Precision Image RenderingVon EverandLine Drawing Algorithm: Mastering Techniques for Precision Image RenderingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Von EverandMatrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (4)
- ME 412 Spring 2015-Project 5Dokument3 SeitenME 412 Spring 2015-Project 5Carlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carlos Nunes Proj5 Me412 BackupDokument29 SeitenCarlos Nunes Proj5 Me412 BackupCarlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carlos Nunes Ae515 PresentationDokument9 SeitenCarlos Nunes Ae515 PresentationCarlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 3Dokument4 SeitenQuestion 3Carlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plots of Question 3.2 and 3.4Dokument4 SeitenPlots of Question 3.2 and 3.4Carlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat: Asdfasdf 1Dokument6 SeitenHeat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat Heat: Asdfasdf 1Carlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodinamica AplicadaDokument13 SeitenAerodinamica AplicadaCarlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MohemDokument6 SeitenMohemdaimon_pNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid FluidDokument6 SeitenFluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid Fluid FluidCarlos AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen