Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rotational Motion: M V O A
Hochgeladen von
PornachandraRaoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rotational Motion: M V O A
Hochgeladen von
PornachandraRaoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
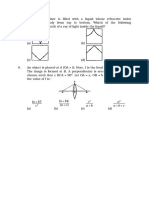
ROTATIONAL MOTION
1) A
2) A
3) A
4) B
B
B
15. A disc of mass M and raduis R is rolling with angular speed
on a horizontal plane as shown in figure.
The magnitude of angular momentum of the disc about the origin O is
Y
3v
2a
M
R
X
1) 1/ 2 MR 2
2) MR 2
3) 3/ 2 MR 2
4) 2MR 2
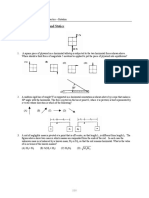
16. A cubical block of side a is moving with velocity v on a horizontal smooth plane as shown in figure. It
hits a ridge at point O. The angular speed of the block after it hits O is
1) 3v 4a
2) 3v 2a
3)
4) zero
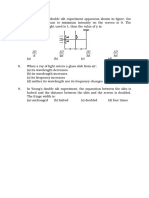
17. A cubical block of side L rests on a rough horizontal surface with co-efficient of friction .A horizontal
force F is applied on the block as shown. if the co-efficient of friction is suffeiciently high so that the
block does not slide before toppling, the minimum force required to topple the block is
1) infinitesimal
2) mg/4
3) mg/2
4) mg (1 - )
18. A thin wire of length L and uniform linear mass density is bent into a circular loop with centre at O as
shown . The moment of inertia of the loop about the axis XX is
1)
23
L
2)
16 3
5L
3)
16
3 L3
4)
8
x'
x
900 O
19. An equilateral triangle ABC formed from a uniform wire has two small identical beads initially located at
A. The triangle is set rotating about the vertical axis AO. Then the beads are released from rest simultaneously and allowed to slide down, one along AB and the other along AC shown . Neglecting frictional
effects, the quantities that are conserved as the beads slide down , are
A
a) angular velocity and total energy (Kinetic and potential)
g
b) total angular momentum and total energy.
c) angular velocity and momentum and moment of inertia about the axis of rotation.
d) total angular momentum and moment of inertia about the axis of rotation
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Dokument311 SeitenUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- 2ForceMotionBasicsStudent TL2Dokument3 Seiten2ForceMotionBasicsStudent TL2Kelvin SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Past IB QuestionsDokument34 Seiten9.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Past IB QuestionsSelim BolekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Rigid Body DynamicsDokument9 SeitenAssignment On Rigid Body DynamicsKaveesh KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT JEE - Rotation Motion (MAINS)Dokument6 SeitenIIT JEE - Rotation Motion (MAINS)yashsodhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irp DPP No3Dokument4 SeitenIrp DPP No3Shivam JaggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - Angular Momentum - ExerciseDokument19 Seiten06 - Angular Momentum - Exercisekenchan0810.kcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)Dokument4 SeitenEr. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)ShreyanshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotation Dynamics and Angular Momentum PDFDokument4 SeitenRotation Dynamics and Angular Momentum PDFTarun GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subjective Questions: Rigid Body DynamicsDokument11 SeitenSubjective Questions: Rigid Body DynamicsDhruv Jyot SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- RotationDokument9 SeitenRotationXtreme VitthalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista 3Dokument4 SeitenLista 3Thales FreireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moving Axis Rotation Cases - 37Dokument6 SeitenMoving Axis Rotation Cases - 37Dhruv KuchhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotation-HomeworkDokument10 SeitenRotation-Homeworksophia.bao20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics PaperDokument17 SeitenPhysics PaperharshanauocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotatory Motion 1Dokument4 SeitenRotatory Motion 1Shiva Ram Prasad Pulagam100% (1)
- Physics (Jee Advanced)Dokument8 SeitenPhysics (Jee Advanced)PranavMachingal100% (1)
- Rotation Dynamics AssigntyrftyugrroooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooomentDokument9 SeitenRotation Dynamics AssigntyrftyugrroooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooomentAnju Sahai100% (1)
- Rotational MechanicsDokument6 SeitenRotational MechanicsHemant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDokument9 SeitenPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsDokument32 SeitenNEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsSuriyanarayana KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Motion - DinâmicaDokument32 SeitenRotational Motion - DinâmicaRenan OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15A03302 Engineering Mechanics PDFDokument3 Seiten15A03302 Engineering Mechanics PDFAbhi RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of Term 2 s.5 PhyDokument6 SeitenEnd of Term 2 s.5 PhyMubiruIvanSnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELP-01 To 06 - Rotational MotionDokument16 SeitenELP-01 To 06 - Rotational Motionnavy.aulakh11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Motion Part-BDokument25 SeitenRotational Motion Part-Bsmi_santhosh100% (1)
- Mechanics PartDokument2 SeitenMechanics PartPetros JereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational MotionDokument28 SeitenRotational MotionVansh AwasthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lows of MotionDokument20 SeitenLows of MotionSaswata Sundar LagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 JAN 16 Int GT 01 Camp NarmadaDokument8 Seiten30 JAN 16 Int GT 01 Camp Narmadashanakara raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionDokument108 SeitenBB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionSunil DahaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inc Xii Main - 23.07.2022Dokument13 SeitenInc Xii Main - 23.07.2022Dinesh BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys1001 2010Dokument2 SeitenPhys1001 2010LUI MAN KITNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT-JEE 2002 Mains Paper With Answer KeyDokument10 SeitenIIT-JEE 2002 Mains Paper With Answer KeyNarmadha RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 2 (M)Dokument7 SeitenInc. Sr. Co Physics Worksheet - 2 (M)VijayKakarlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual Problems in Physics For IIT-JEEDokument52 SeitenConceptual Problems in Physics For IIT-JEEApex Institute100% (3)
- Fluid MechanicsDokument2 SeitenFluid MechanicsAnkur GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prob Set 5Dokument2 SeitenProb Set 5Debolina DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP1 RotationaldynamicsDokument14 SeitenCPP1 RotationaldynamicsBNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50Dokument22 Seiten50rockingjoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phys 697Dokument19 SeitenPhys 697joseftrihandokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid Body Dynamics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDokument21 SeitenRigid Body Dynamics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGRavi YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of Inertia: I ML I ML I ML I MLDokument17 SeitenMoment of Inertia: I ML I ML I ML I MLvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- RotaionalDokument19 SeitenRotaionalSujay BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 5 - Centre of MassDokument16 SeitenChapter - 5 - Centre of MassMohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Final QPDokument8 SeitenGrade 12 Final QPfazeelm24Noch keine Bewertungen
- MI Practice QuestionDokument3 SeitenMI Practice Questionmalhar366Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On MagnetismDokument4 SeitenProblems On MagnetismRohit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2. Growth-Phase-1 & 2 - JA - 01-10-2023Dokument12 SeitenP2. Growth-Phase-1 & 2 - JA - 01-10-2023Tanay1 MitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpringerDokument10 SeitenSpringerMonico AlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recitation-4: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy and Conservation of EnergyDokument12 SeitenRecitation-4: Work, Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy and Conservation of EnergyAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECTION-I (Single Choice Questions)Dokument6 SeitenSECTION-I (Single Choice Questions)Bhawna SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument2 Seiten1AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Moving Charges & Magnetism Test 2Dokument4 Seiten2 Moving Charges & Magnetism Test 2DevangNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Advanced - 02 (Paper-2) PDFDokument31 SeitenJEE Advanced - 02 (Paper-2) PDFKunal QumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- II IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 14 - SHMDokument6 SeitenII IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 14 - SHMAshwin KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP Nlm-IiDokument8 SeitenDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Ray 59Dokument1 SeiteRay 59PornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Axis. An Object Starts From (2 M, 0, 0) With A Velocity of I JDokument1 SeiteX-Axis. An Object Starts From (2 M, 0, 0) With A Velocity of I JPornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray 31Dokument1 SeiteRay 31PornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Axis. An Object Starts From (2 M, 0, 0) With A Velocity of I JDokument1 SeiteX-Axis. An Object Starts From (2 M, 0, 0) With A Velocity of I JPornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray 6Dokument1 SeiteRay 6PornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray 4Dokument1 SeiteRay 4PornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray 5Dokument1 SeiteRay 5PornachandraRaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Most Cited Papers: Quantum ComputersDokument205 SeitenMost Cited Papers: Quantum ComputersManjunath.RNoch keine Bewertungen
- LINDE Electric-Trucks Schema'xDokument51 SeitenLINDE Electric-Trucks Schema'xAntonio novoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Guidelines For Single Event Transient (SET)Dokument27 SeitenTesting Guidelines For Single Event Transient (SET)tomek_zawistowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 전자기학 1장 솔루션Dokument13 Seiten전자기학 1장 솔루션이재하Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Quantum Mechanics - Lecture2 - DQHDokument78 SeitenIntroduction To Quantum Mechanics - Lecture2 - DQHViệt Hoàng NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE311S: Dynamic Systems and Control Problem Set 2Dokument3 SeitenECE311S: Dynamic Systems and Control Problem Set 2zoeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moisture Buffering Capacity of Hygroscopic Building Materials: Experimental Facilities and Energy ImpactDokument13 SeitenMoisture Buffering Capacity of Hygroscopic Building Materials: Experimental Facilities and Energy ImpactBayang SilamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Project A TitleDokument3 SeitenMaths Project A TitleVenkatram PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering ReferencesDokument122 SeitenEngineering ReferencesRogerio MarczakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prediction of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity From Particle Size DistributionDokument5 SeitenPrediction of Soil Hydraulic Conductivity From Particle Size DistributionGELBER GUTIERREZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary: Activity 1Dokument18 SeitenVocabulary: Activity 1Aurora GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Measurements of Elastic and Viscoelastic Properties With FASTForce Volume CR - AN148Dokument7 SeitenQuantitative Measurements of Elastic and Viscoelastic Properties With FASTForce Volume CR - AN148Fabien CazesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harmonic ElementsDokument6 SeitenHarmonic ElementsSai KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test of Soundness of Hydraulic CementDokument33 SeitenTest of Soundness of Hydraulic Cementmacs_smacNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 BSC Junior (7&8) Paper and AnswersDokument20 Seiten2016 BSC Junior (7&8) Paper and AnswersUmayal Sivanandan100% (1)
- User Manual Casio G-Shock Classic GW-M5610-1ER (English - 6 Pages)Dokument3 SeitenUser Manual Casio G-Shock Classic GW-M5610-1ER (English - 6 Pages)Dénes SimonyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering 374: Fluid MechanicsDokument10 SeitenChemical Engineering 374: Fluid MechanicsFrankie TamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empirical Correlations Drained Shear Strength For Slope Stability AnalysesDokument10 SeitenEmpirical Correlations Drained Shear Strength For Slope Stability AnalysesPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Lecture-8 Shear Strength of Soils Dr. Attaullah ShahDokument5 Seiten1 Lecture-8 Shear Strength of Soils Dr. Attaullah ShahHIMANSHUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Certificate Welding Wire-ModelDokument1 SeiteProduct Certificate Welding Wire-ModelRamona CrangasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Egm 3601 - Exam 1Dokument10 SeitenEgm 3601 - Exam 1smahmood23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hermle Technical Data c12 enDokument4 SeitenHermle Technical Data c12 enSantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 101 - HW34Dokument1 SeitePhysics 101 - HW34Tim JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Episode 220 2 Worked ExamplesDokument4 SeitenEpisode 220 2 Worked ExamplesAno ChasafaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metoda Proracuna MTU SignalaDokument28 SeitenMetoda Proracuna MTU SignalaGoran LevačićNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEMO Test1 2019 SEM1 Electrical Engineering IIIDokument3 SeitenMEMO Test1 2019 SEM1 Electrical Engineering IIImjaji khulehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Assign No 1Dokument8 SeitenSolution Assign No 1OvaisAkhterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit III Stress DistributionDokument23 SeitenUnit III Stress DistributionIlakkya m.sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 吊耳计算Dokument4 Seiten吊耳计算huangjlNoch keine Bewertungen