Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Testing of Hypothesis
Hochgeladen von
shahzaf0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten1 SeiteTesting of hypotheses is based on either interval estimation or comparing means and medians using parametric or non-parametric tests. The null hypothesis (H0) assumes no difference while the alternative hypothesis (HA) assumes a difference. Normal data is compared using means and tests like the t-test, while non-normal data is compared using medians and tests like the Mann-Whitney U test. Hypothesis tests involve comparing one or more groups to determine if their means or medians are equal or different. The appropriate test depends on whether the data is normal and if variances are equal. The null hypothesis is accepted if the p-value is greater than 0.05, otherwise the alternative hypothesis is accepted.
Originalbeschreibung:
QT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenTesting of hypotheses is based on either interval estimation or comparing means and medians using parametric or non-parametric tests. The null hypothesis (H0) assumes no difference while the alternative hypothesis (HA) assumes a difference. Normal data is compared using means and tests like the t-test, while non-normal data is compared using medians and tests like the Mann-Whitney U test. Hypothesis tests involve comparing one or more groups to determine if their means or medians are equal or different. The appropriate test depends on whether the data is normal and if variances are equal. The null hypothesis is accepted if the p-value is greater than 0.05, otherwise the alternative hypothesis is accepted.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten1 SeiteTesting of Hypothesis
Hochgeladen von
shahzafTesting of hypotheses is based on either interval estimation or comparing means and medians using parametric or non-parametric tests. The null hypothesis (H0) assumes no difference while the alternative hypothesis (HA) assumes a difference. Normal data is compared using means and tests like the t-test, while non-normal data is compared using medians and tests like the Mann-Whitney U test. Hypothesis tests involve comparing one or more groups to determine if their means or medians are equal or different. The appropriate test depends on whether the data is normal and if variances are equal. The null hypothesis is accepted if the p-value is greater than 0.05, otherwise the alternative hypothesis is accepted.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
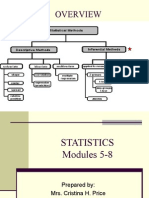
TESTING OF HYPOTHESIS SUMMARY
1.
2.
3.
4.
Testing the hypothesis is based on interval estimation.
Null Hypothesis is represented by H0 and Alternative Hypothesis by HA
The Null Hypothesis is based on concept of equality of the assumption with the actual data estimation
The normal data is compared on the basis of means() and tests are called parametric tests
5.
The non-normal data is compared on the basis of medians(
6.
7.
The hypothesis is also made accordingly i.e. whether you testing on the basis of mean or medians.
Comparing one group with a target
Data is Normal (p> 0.05), H0: 0 = Hypothesized mean and HA: A Hypothesized mean
Data is Non-Normal (p< 0.05) H0: (
8.
)and tests are called non-parametric tests
) = Hypothesized Median, HA: (
) Hypothesized Median
One group measure Twice
Data is Normal (p> 0.05) H0: 1 = 2 and HA: 1 2 (Paired Sample T-Test)
Data is Non-Normal (p< 0.05) > Test the difference column with test median = 0 in Signed Rank Test.
H0 :
9.
HA:
Put the test median of the difference column = 0 in Minitab
Comparing two groups
Data is Normal (p> 0.05) H0: 1 = 2 and HA: 1 2, Check for equality of variances and appropriate Test
Data is Non-Normal (p< 0.05) H0:
and HA:
2,
Use Mann Whitney (U) Test based on comparison of average ranks.
10. Comparing more than two groups
Data is Normal (p> 0.05) Check for equality of variances (Levenes Test) and Appropriate Test (Flow)
H0: 1 = 2 = 3 =.... n and HA: At least one group is significantly different from others Check for equality of
variances and Appropriate Test
Data is Non-Normal (p< 0.05) >
H0 :
2 = .
Kruskal Wallis (H) Test
HA: There is at least one group with the median significantly difference from others
11. Decision Making
1. Data is Normal when p > 0.05 Anderson test is used for checking the normality
2. The Variance are equal when p > 0.05 and the test is Levenes Test
3. Accept the Null Hypothesis when P>0.05 otherwise accept the alternative hypothesis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Duty Manager's ManualDokument30 SeitenDuty Manager's Manualshahzaf50% (4)
- Inferential StatisticsDokument48 SeitenInferential StatisticsNylevon78% (9)
- Parametric Test RDokument47 SeitenParametric Test RRuju VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kruskal Wallis Test PDFDokument2 SeitenKruskal Wallis Test PDFSreya Sanil100% (1)
- Hypothesis Testing by Example Hands On Approach Using RDokument39 SeitenHypothesis Testing by Example Hands On Approach Using RHen IrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 5Dokument28 SeitenActivity 5Hermis Ramil TabhebzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Inference: Dr. Mona Hassan AhmedDokument34 SeitenStatistical Inference: Dr. Mona Hassan Ahmedkareem3456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Esther - Hypo Testing Unit 5 ADokument5 SeitenEsther - Hypo Testing Unit 5 AAdrian FranklinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11 - Small Sample TestDokument8 SeitenCH 11 - Small Sample TesthehehaswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing - Analysis of VarianceDokument19 SeitenHypothesis Testing - Analysis of VarianceaustinbodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Means: 1-One Sample T TestDokument18 SeitenCompare Means: 1-One Sample T Testbzhar osmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premili DefinitionsDokument3 SeitenPremili DefinitionsJayakumar ChenniahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing 15pagesDokument15 SeitenHypothesis Testing 15pagesAravindan RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis TestingDokument45 SeitenHypothesis TestingHerman R. SuwarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project SPSS 2016Dokument18 SeitenProject SPSS 2016alaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument9 SeitenChapter 7storkyddNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Normal MPA Statistics Chapter 2Dokument15 SeitenNew Normal MPA Statistics Chapter 2Mae Ann GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 159 Hyp Tests ConditionsDokument4 Seiten159 Hyp Tests ConditionsSidra AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 How To Analyze Your Data: Nonparametric ParametricDokument18 Seiten5 How To Analyze Your Data: Nonparametric ParametricSubhankar SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic StatDokument35 SeitenBasic StatTaddese GashawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing HypothesisDokument9 SeitenTesting HypothesisUsama IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Inference Hypothesis TestingDokument9 SeitenStatistical Inference Hypothesis TestingTawonga RushambwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explanation For The Statistical Tools UsedDokument4 SeitenExplanation For The Statistical Tools UsedgeethamadhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing - Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)Dokument30 SeitenHypothesis Testing - Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)sakshi tyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sonek Inferential AnalysisDokument25 SeitenSonek Inferential AnalysisAlfredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing General Concept 28102022Dokument21 SeitenHypothesis Testing General Concept 28102022Gourav ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salinan Terjemahan Pengertian Uji NormalitasDokument8 SeitenSalinan Terjemahan Pengertian Uji NormalitasNabila LathifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Statistical Methods in AnachemDokument39 SeitenSome Statistical Methods in AnachemshaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument16 SeitenChapter 2AndreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin534 - Chapter 5Dokument35 SeitenFin534 - Chapter 5Eni NuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing Z and T Tests (CHAPTER 8)Dokument11 SeitenHypothesis Testing Z and T Tests (CHAPTER 8)Hilda Nur Indah LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCSL44 Short NotesDokument2 SeitenBCSL44 Short Notessahil vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps in The Hypothesis Testing: Null Hypothesis. The Null Hypothesis, Denoted by HDokument1 SeiteSteps in The Hypothesis Testing: Null Hypothesis. The Null Hypothesis, Denoted by HJoyce TatumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stats Hypothesis TestingDokument3 SeitenStats Hypothesis TestingLiana BaluyotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing - Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)Dokument14 SeitenHypothesis Testing - Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)Kumar RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sas ProcsDokument8 SeitenSas ProcsPrasad TvsnvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inferential Statistics PDFDokument48 SeitenInferential Statistics PDFBrenda BanderadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inferential Statistics Masters Updated 1Dokument27 SeitenInferential Statistics Masters Updated 1Joebert CalagosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASV CribSheet Hypothesis TestingDokument2 SeitenASV CribSheet Hypothesis TestingvaldesasNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Way AnovaDokument26 SeitenOne Way AnovaSachin JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mann - Whitney Test - Nonparametric T TestDokument18 SeitenMann - Whitney Test - Nonparametric T TestMahiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing Basic Terminology:: PopulationDokument19 SeitenHypothesis Testing Basic Terminology:: PopulationRahat KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRM Unit-3Dokument22 SeitenBRM Unit-3K R SAI LAKSHMINoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes ON Parametric & Non-Parametric Tests FOR Social Scientists/ Participants OF Research Metodology Workshop Bbau, LucknowDokument19 SeitenLecture Notes ON Parametric & Non-Parametric Tests FOR Social Scientists/ Participants OF Research Metodology Workshop Bbau, LucknowDiwakar RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anova MethodologyDokument8 SeitenAnova MethodologyRana AdeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics For College Students-Part 2Dokument43 SeitenStatistics For College Students-Part 2Yeyen Patino100% (1)
- L7 Hypothesis TestingDokument59 SeitenL7 Hypothesis Testingمصطفى سامي شهيد لفتهNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Hypothesis TestingDokument32 SeitenWhat Is Hypothesis TestingNasir Mehmood AryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypothesisDokument11 SeitenHypothesisMasudur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12 - T-Test IDokument33 SeitenLecture 12 - T-Test Iamedeuce lyatuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- TtestDokument8 SeitenTtestMarvel EHIOSUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Analysis and Hypothesis TestingDokument20 SeitenData Analysis and Hypothesis TestingSatish RAjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing GDokument28 SeitenHypothesis Testing GRenee Jezz LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter5.2-Inferential StatisticsDokument27 SeitenChapter5.2-Inferential StatisticsHoài JangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothesis Testing (MODIFIED)Dokument47 SeitenHypothesis Testing (MODIFIED)Danna ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 HypothesisDokument41 SeitenUnit 3 Hypothesisabhinavkapoor101Noch keine Bewertungen
- SM 38Dokument19 SeitenSM 38ayushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument8 SeitenChapter 10Angelica MijaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parametric Tests: DR Heena SharmaDokument60 SeitenParametric Tests: DR Heena SharmaBhartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Educational QualityDokument17 SeitenMeasuring Educational QualityshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of T-Tests: Test Purpose ExampleDokument5 SeitenTypes of T-Tests: Test Purpose Exampleshahzaf50% (2)
- Input Output Process ExamplesDokument2 SeitenInput Output Process ExamplesshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Quality Management - TQMDokument1 SeiteTotal Quality Management - TQMshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Managemen1Dokument4 SeitenIndustrial Managemen1shahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump TypesDokument1 SeitePump TypesshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Control ValveDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Control ValveshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Human Resource ManagementDokument22 SeitenStrategic Human Resource Managementshahzaf67% (3)
- SMS Symbols and MeaningsDokument3 SeitenSMS Symbols and MeaningsshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIG and TIG WeldingDokument2 SeitenMIG and TIG WeldingshahzafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Componential Analysis and The Study of MeaningDokument23 SeitenComponential Analysis and The Study of MeaningJean-Christophe ChampagneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Culture in Cognitive Development - Class LectureDokument42 SeitenThe Role of Culture in Cognitive Development - Class Lectureangelica agaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1234Dokument1.746 Seiten1234Enrique AmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scraping Instagram With PythonDokument4 SeitenScraping Instagram With PythonSrujana TakkallapallyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PI System Architecture Planning and ImplementationDokument225 SeitenPI System Architecture Planning and Implementationsatish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Module 1-Lesson 1 (Music)Dokument2 SeitenGrade 7 Module 1-Lesson 1 (Music)jennylyn ragosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASEAN Literature-Task 7 - CambodiaDokument4 SeitenASEAN Literature-Task 7 - Cambodiarchellee689Noch keine Bewertungen
- Editorial: TEFL in Morocco: A Succinct OverviewDokument16 SeitenEditorial: TEFL in Morocco: A Succinct OverviewMohammed HassimNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Blueprint of Technology, Applications and Market Drivers Towards The Year 2030 and Performance Target AnalysisDokument45 SeitenA Blueprint of Technology, Applications and Market Drivers Towards The Year 2030 and Performance Target AnalysisJoy DuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cleopatra Finds Her VoiceDokument5 SeitenCleopatra Finds Her Voiceapi-264591964Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - Class INTSO Work Sheet - 1 - Basics On GeometryDokument2 Seiten8 - Class INTSO Work Sheet - 1 - Basics On Geometryyoutuber tanishNoch keine Bewertungen
- " " - Fennel Hudson: Exams Test Your Memory, Life Tests Your Learning Others Will Test Your PatienceDokument2 Seiten" " - Fennel Hudson: Exams Test Your Memory, Life Tests Your Learning Others Will Test Your PatienceJezreel Jezz David Baculna100% (1)
- COS1512 202 - 2015 - 1 - BDokument33 SeitenCOS1512 202 - 2015 - 1 - BLina Slabbert-van Der Walt100% (1)
- GRPC TutorialDokument111 SeitenGRPC TutorialAmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Analysis and Transmission of SignalsDokument53 SeitenChapter 3 - Analysis and Transmission of SignalsIBRAHIM ALFARISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cool Kids 1 SB SampleDokument12 SeitenCool Kids 1 SB SampleBarbara Arenas GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lessons Learned FioriDokument52 SeitenLessons Learned Fiorimayank.cs2478100% (2)
- Unit 2Dokument6 SeitenUnit 2hongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 - Database ConceptsDokument23 SeitenChapter1 - Database Conceptstinishdharan100% (1)
- The Notorious Collatz Conjecture: Terence Tao, UCLADokument63 SeitenThe Notorious Collatz Conjecture: Terence Tao, UCLASaransh Prajapati100% (1)
- 1 - Philippine Pre-Colonial To Modern LiteratureDokument17 Seiten1 - Philippine Pre-Colonial To Modern LiteratureDalene Evangelio100% (1)
- Concurrency Control and RecoveryDokument24 SeitenConcurrency Control and RecoveryTinashe KotaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32Dokument12 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9618/32davieNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaikuDokument25 SeitenHaikuKim HyunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATV Sample: Forward T SoftwareDokument28 SeitenATV Sample: Forward T SoftwareMitic MilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rachana Devara: @bvrit - Ac.inDokument2 SeitenRachana Devara: @bvrit - Ac.inDevara RachanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Realism In American Literature: Group 11: Nguyễn Thái Hà Vi Nguyễn Thị Xuân NhiDokument15 SeitenRealism In American Literature: Group 11: Nguyễn Thái Hà Vi Nguyễn Thị Xuân NhiNgọc Trâm ThiềuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learners With ExceptionalitiesDokument5 SeitenLearners With ExceptionalitiesApril Lanuza100% (3)
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) : in This ChapterDokument34 SeitenSimple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) : in This ChapterSuraj JathannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chaucer's Contribution To English Language and LiteratureDokument13 SeitenChaucer's Contribution To English Language and LiteratureAgustinus Elisabeth78% (9)