Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 11
Hochgeladen von
api-282526559Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 11
Hochgeladen von
api-282526559Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
11.
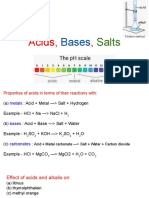
1 Acids and alkalis
Common acids and bases:
Hydrochloric acid
Sulphuric acid
Nitric acid
Ethanoic acid
Phenolphthal
ein
Methyl
orange
HCl
H2SO4
HNO3
CH3COOH
In acid
Colourle
ss
Red
Turns litmus
red
Turns litmus
blue
Sodium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide
Ammonia
NaOH
KOH
Ca(OH)2
NH3
In alkali
Pink
yellow
The pH of any solution can be found using a universal indicator.
11.2 A closer look at acids and alkalis
Solutions of acids contain H+ ions, making them acidic. When an acid is added to water, it
dissociates into ions:
HCl H+ + Cl- (100% of them)
CH3COOH H+ + CH3COO- (only some of them dissociates)
In solutions of strong acids, all the molecules become ions. In the solution of weak acids, only some
molecules become ions. The stronger the acid, the better the conductivity. The higher the concentration
of hydrogen ions, the lower the pH, the stronger the base.
Solutions of alkalis contain OH- ions, making them alkaline. When an alkali is added into water, it
dissolves, and dissociates into ions:
NaOH Na+ + OH- (100% of them)
NH3 H20 NH4+ + OH- (only some of them)
In solutions of strong alkalis, all the molecules become ions. In the solution of weak alkalis, only some
molecules become ions. The stronger the alkali, the better the conductivity. The higher the
concentration of hydroxide ions, the higher the pH, the stronger the base.
11.3 The reaction of acids and bases
Reactions with acids:
Acid + metal salt + hydrogen
Magnesium + sulphuric acid magnesium sulphate + hydrogen. The metal displaces hydrogen, and
takes its place.
Acid + base salt + water
o Acid + metal oxide salt + water
Hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + water
o
Acid + metal hydroxide salt + water
Sulphuric acid + copper oxide copper sulphate + water
Acid + carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide
Calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid calcium chloride + water + carbon dioxide
Reaction with bases
Bases react with acids to get salt and water.
Shown in reactions above.
Sodium, potassium and calcium hydroxides react with ammonium salts, giving out salt,
water and ammonia gas.
Calcium hydroxide + ammonium chloride calcium chloride + water + ammonia
Neutralisation is the reaction with an acid that gives water as well as salt. Farmers use neutralisation to
reduce the acidity in soils, by adding limestone (calcium carbonate), lime (calcium oxide) or slakes lime
(calcium hydroxide). To neutralise a bee sting, which is acidic, baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate)
or calamine lotion (zinc carbonate), can be rubbed.
Neutralisation reactions are not redox, as no electrons are transferred. The reaction of metals with acids
are redox reactions.
11.4 A closer look at neutralisation
When an acid and a base are put together, the hydrogen ions and the hydroxide ions join to form water
molecules. Then the rest of the molecules of the reactants join together to form a salt.
To write an ionic equation:
Write all the ions present in the reaction
Cross out the ions that appear unchanged on both sides of the reaction
What is left is the ionic equation
The hydrogen atom is just a proton. So acids are proton donors, and bases are proton acceptors.
The neutralisation of an insoluble base:
The acid donates a proton
The oxide ions accept them
The lattice breaks down
The positive ions of the base and the negative ions of the acid join together to form the salt
11.5 Oxides
Basic oxides:
Magnesium and oxygen:
Magnesium ribbon lit
Plunged into jar of oxygen
Burns with brilliant white flame
Leaves white ash magnesium oxide
Iron and oxygen:
Hot iron wool plunged into gas jar of oxygen
Glows bright
Throws out shower of sparks
Black solid left iron oxide
Copper and oxygen:
Too unreactive to catch fire in oxygen
When heated in oxygen steam, surface turns black
Black substance copper oxide
The more reactive the metal, the more vigorously it reacts.
How to check if copper oxide is basic:
Insoluble in water
But soluble in dilute acid
Copper oxide mixed with dilute HCl, and warmed
This turns litmus blue
So copper is a basic oxide
Metal oxides are basic.
Acidic oxides:
Carbon and oxygen:
Powdered carbon heated until red hot
Then plunged into a jar of oxygen carbon dioxide
Sulphur and oxygen:
Catches fire over Bunsen burnerblue flame
Brighter flame in pure oxygen sulphur dioxide
Phosphorus and oxygen:
Burns into flame without heating
White solid formed phosphorus pentoxide
When these are dissolved in water they turn litmus red. Non-metal oxides are acidic.
Amphoteric oxides:
React with both acids and alkalis
Aluminium oxide
Zinc oxide
Neutral oxides:
Do not react with acids or bases
Carbon monoxide
Dinitrogen oxide N2O LAUGHING GAS, USED AS ANAESTHETIC
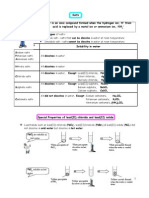
11.5 Making salts
How to make zinc sulphate:
Add zinc to dilute sulfuric acid
It starts to dissolve and hydrogen bubbles off
Bubbling stops when all acid is used up
Excess zinc still left remove by filtering
Heat solution to evaporate some water for saturated solution
Leave to cool
Crystals of zinc sulphate
This method can be used to make salts of magnesium, aluminium, zinc and iron. Not with very reactive
metals.
How to make copper sulphate:
Copper does not react with dilute sulfuric acid
Start with base copper oxide (or even copper carbonate)
Add it to dilute sulphuric acid
Dissolves on warming\solution turns blue
Remove excess solid by filtering
Heat solution to obtain saturated solution
Crystals of copper sulphate will form
To make sodium (or any other very reactive metal) salts:
By titration
Use phenolphthalein as the indicator
Put 25cm3 of sodium hydroxide into flask (use pipette)
Add 2 drops of phenolphthalein
Add acid using burette, bit by bit
When the indicator suddenly turns colourless, stop adding acid as alkali has been used up
Solution is neutral
Find how much acid was added
Repeat without indicator
Heat solution crystals of sodium chloride
11.7 Making insoluble salts by precipitation
Soluble salts:
Sodium salts
Potassium salts
Ammonium salts
All nitrates
All chlorides (except silver chloride, lead chloride)
All sulphates (except calcium sulphate, barium sulphate, lead sulphate)
Sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, ammonium carbonate (All others insoluble)
How to make barium sulphate:
A solution of barium chloride contains barium and chloride ions
Magnesium sulphate contains magnesium ions and sulphate ions
Mix the two solutions together
Barium and sulphate ions bond together
Forming a white precipitate
Filter it and dry it
Equation for the reaction:
Ionic equation:
To precipitate an insoluble salt, you must mix a solution that contains its positive ions with one
that contains its negative ions.
Uses of precipitation:
Used to make coloured pigments for paint
Used to remove harmful substances dissolved in water
Used to make photographic film
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- C CC CCCCCC CCCC CCCCCC CC CCCCCC CCC CC CC CCCCDokument7 SeitenC CC CCCCCC CCCC CCCCCC CC CCCCCC CCC CC CC CCCCAlisha RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 11 - Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument9 SeitenUnit 11 - Acids, Bases and SaltsRaffaella LaxaldeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MetalsDokument9 SeitenMetalsb52352986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Making SaltDokument9 SeitenChemistry Making SaltMaulana Digisel DesainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument8 SeitenAcids and BasesVaijayanthi SaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Bases and Salts Igcse Chemistry 0620Dokument15 SeitenAcid Bases and Salts Igcse Chemistry 0620Aminah ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Organic AcidsDokument7 SeitenExample of Organic AcidsAUDREYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Bases and SaltsDokument9 SeitenAcid Bases and SaltsVenusCrazy 550Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Dokument6 SeitenAcids, Bases and Salts (BBC Site)Ramesh GoldbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and Salts NotesDokument22 SeitenAcids Bases and Salts NotesHaneefah AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and Titration NotesDokument8 SeitenAcids Bases and Titration NotesbritsomaxmillianNoch keine Bewertungen
- When Acids React With Metals, The Outcome Is Very Similar To A Neutralization ReactionDokument2 SeitenWhen Acids React With Metals, The Outcome Is Very Similar To A Neutralization ReactionEduardo ZaldivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec 2 Acids and Bases Notes 2013Dokument11 SeitenSec 2 Acids and Bases Notes 2013Emily TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases NotesDokument10 SeitenAcids and Bases NotesThaarvena RetinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument5 SeitenAcids, Bases and SaltsAmmar RizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases & OxidesDokument22 SeitenAcids, Bases & OxidesMustafa ghazanfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and SaltsDokument8 SeitenAcids Bases and SaltsngaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base and SaltDokument7 SeitenAcid Base and SaltRushikKaretiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid, Bases and Salts (Prashant Kirad) - 1Dokument15 SeitenAcid, Bases and Salts (Prashant Kirad) - 1Ashish Sharma100% (2)
- O-Levels Chapter 8 Acids & BasesDokument3 SeitenO-Levels Chapter 8 Acids & BasesZi Yang LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument27 SeitenChem Acids, Bases and SaltsJun ZheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Base and SaltsDokument20 SeitenAcids, Base and SaltsTapas BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples of Acids: Are Vinegar (Ethanoic Acid) and Lemon Juice (Citric Acid)Dokument44 SeitenExamples of Acids: Are Vinegar (Ethanoic Acid) and Lemon Juice (Citric Acid)Carl Agape DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Bases SaltDokument5 SeitenAcid Bases SaltKeisha DoctorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltDokument37 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Acid Base and SaltRaghav ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and BasesDokument7 SeitenAcids and BasesaquamogolwaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Acid Base ConceptDokument25 SeitenIGCSE Acid Base ConceptawaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases, Salts-IG ChemistryDokument16 SeitenAcids, Bases, Salts-IG ChemistryRashi GhadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OLvlChem Chap11 UploadDokument5 SeitenOLvlChem Chap11 UploaddoullahsaqibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 10Dokument29 SeitenChemistry 10Javed QasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases & SaltsDokument35 SeitenAcids, Bases & SaltsInnocent AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Notes v2Dokument18 SeitenChem Notes v2ehan.ilrnestersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Continuation1Dokument11 SeitenChapter 1 - Continuation1Al Cris BarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Std10 Science EM 3 PDFDokument90 SeitenStd10 Science EM 3 PDFVivek AnandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 7 Chemistry WK 4 L2, 3Dokument3 SeitenYear 7 Chemistry WK 4 L2, 3JennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Subject: Chemistry Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts Following Notes Till Page No: 25 of Science NCERT BookDokument5 SeitenClass X Subject: Chemistry Chapter 2: Acids, Bases and Salts Following Notes Till Page No: 25 of Science NCERT Bookashok pradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Closer Look at Acids: Chapter - 9.2Dokument13 SeitenA Closer Look at Acids: Chapter - 9.2goodboyhokyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Notes Acids, Bases & SaltsDokument6 SeitenChapter Notes Acids, Bases & Saltsmd gayasuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and BasesDokument80 SeitenAcid and BasesMenaga IlangkovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases SaltsDokument24 SeitenAcids Bases SaltsmariamtkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and SaltsDokument14 SeitenAcids Bases and SaltsaarshiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base and SaltDokument24 SeitenAcid Base and Saltmanish100% (1)
- Acid Base and SaltsDokument45 SeitenAcid Base and SaltsPankaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and Salts NotesDokument14 SeitenAcids, Bases and Salts NotesTaryl ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-2 Acids, Bases & Salts NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter-2 Acids, Bases & Salts NotesMohammed RamzanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases 0620Dokument4 SeitenAcids and Bases 0620Gono TakaduuNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument31 SeitenNOTES - Acids, Bases and SaltsKartik ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH2 Acids and SaltsDokument10 SeitenCH2 Acids and SaltsDoc CrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids: Common Acids We Come Across EverydayDokument5 SeitenAcids: Common Acids We Come Across EverydayFarzan ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases & SaltsDokument22 SeitenAcids, Bases & SaltsPiyal ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids Bases and SaltsDokument33 SeitenAcids Bases and SaltsVibi VibesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes Class 10Dokument8 SeitenChemistry Notes Class 10nejihyuga997Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDokument21 SeitenAcids, Bases and SaltsOp bolteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Acids and BasesDokument4 Seiten1 Acids and BasesShawna FisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes Part 2Dokument8 SeitenAcids, Bases and Salts Notes Part 2Dhyan ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11.Dokument45 SeitenChapter 11.HalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACIDS BASES Notes IgcseDokument8 SeitenACIDS BASES Notes IgcsetejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases..Dokument5 SeitenAcids and Bases..rachelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 17Dokument3 SeitenUnit 2 17api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 1-2 3Dokument5 SeitenUnit 2 1-2 3api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 31-2 38Dokument12 SeitenUnit 2 31-2 38api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7Dokument3 SeitenUnit 7api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6Dokument2 SeitenUnit 6api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument3 SeitenUnit 3api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Mixtures, Solutions and Solvents: Solvent It DissolvesDokument6 Seiten2.1 Mixtures, Solutions and Solvents: Solvent It Dissolvesapi-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- DefinitionsDokument5 SeitenDefinitionsapi-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument3 SeitenUnit 1api-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geography Case StudyDokument2 SeitenGeography Case Studyapi-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- SyllDokument5 SeitenSyllapi-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- History NotesDokument22 SeitenHistory Notesapi-282526559100% (1)
- International RelationsDokument13 SeitenInternational Relationsapi-282526559Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial QuestionDokument6 SeitenTutorial QuestionopemipoalakindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 - Acids and Bases: Name: Clas S: Dat eDokument38 SeitenChapter 14 - Acids and Bases: Name: Clas S: Dat e鄭子玄Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry CHP Ter 8Dokument21 SeitenChemistry CHP Ter 8IZIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medio Plantas Carnivoras Atrapa MoscasDokument1 SeiteMedio Plantas Carnivoras Atrapa MoscasLuís G. Murillo VillafañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Barium From Barium Sulphate GravimetricallyDokument4 SeitenEstimation of Barium From Barium Sulphate GravimetricallyMg H67% (15)
- Copper Sulphate Penta HydrateDokument2 SeitenCopper Sulphate Penta HydrateBLi'H'Abiee100% (1)
- Science 20 Make-Up Assignment: Total: Replace: Name: 75Dokument7 SeitenScience 20 Make-Up Assignment: Total: Replace: Name: 75ticoninxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Compounds Handout PDFDokument12 SeitenNaming Compounds Handout PDFLIANNE GEMIMA GIPANoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Chemistry (By Topic)Dokument386 SeitenIB Chemistry (By Topic)aleth100% (10)
- Chemical Equations & ReactionsDokument85 SeitenChemical Equations & ReactionsEsther SparksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 2 TEACHER (Homework 1)Dokument4 SeitenChapter 8 2 TEACHER (Homework 1)Pang Hong HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions: 2H (G) + O (G) 2H O (L)Dokument5 SeitenChemical Reactions: 2H (G) + O (G) 2H O (L)Brooklyn WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis Guide Sheet For Chemistry PracticalDokument4 SeitenQualitative Analysis Guide Sheet For Chemistry PracticalquinzhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfinol PDFDokument25 SeitenSulfinol PDFcandra_zakaria4416Noch keine Bewertungen
- Total Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsDokument1 SeiteTotal Fluorine Chlorine Sulfur Aromatic HydrocarbonsAmol AdsulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1Dokument3 SeitenExperiment 1Myzhel InumerableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flame Test Lab StudentDokument2 SeitenFlame Test Lab StudentMark SakaguchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural Applications of Flame PhotometryDokument2 SeitenAgricultural Applications of Flame PhotometryTasnim Jahan100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Equations-1Dokument14 SeitenChemical Reactions and Equations-1Manwinder Singh GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- AqueousDokument35 SeitenAqueousDevananda R SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and BasesDokument4 SeitenAcid and BasesMika SaldañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goddard Langmuir 1987Dokument7 SeitenGoddard Langmuir 1987corechiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.stoichiometric RelationshipsDokument29 Seiten1.stoichiometric RelationshipsLaraStrbacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4Dokument68 SeitenUnit 4priyata debNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barium Sulphate To Barium SulfideDokument6 SeitenBarium Sulphate To Barium SulfideAsad Abbas AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA Chem GCSE Combined C7 Practice AnswersDokument2 SeitenAQA Chem GCSE Combined C7 Practice AnswersLeslie MasiyandimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aliquat 336: Technical Information Global Mining SolutionsDokument3 SeitenAliquat 336: Technical Information Global Mining SolutionsEduardo OetikerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Chemistry IAL EDEXCEL 2024 Jan PaperDokument20 SeitenUnit 1 Chemistry IAL EDEXCEL 2024 Jan Papersamehsamdi100% (1)
- Practice Problems (Chapter 2) Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds - KEYDokument3 SeitenPractice Problems (Chapter 2) Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds - KEYsarahsarfraz81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Equations Worksheet 1Dokument2 SeitenEquations Worksheet 1jaikovskyNoch keine Bewertungen