Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Coordinate Transformations
Hochgeladen von
SushitaBethSenobago0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
55 Ansichten24 Seitenmatrix analysis of frames
Originaltitel
LECTURE 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenmatrix analysis of frames
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
55 Ansichten24 SeitenCoordinate Transformations
Hochgeladen von
SushitaBethSenobagomatrix analysis of frames
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 24
COORDINATE
TRANSFORMATIONS
Transformation from Global to Local
Coordinate Systems
T is referred to as the transformation
Transformation from Local to Global
Coordinate Systems
Example: Determine the transformation matrices for the members of
the truss shown
Member 1: the joint 1 is the
beginning joint and joint 2 is the end
joint for member 1.
for any member with the
positive directions of its local x
and y axes oriented in the
positive directions of the global
X and Y axes, respectively, the
transformation matrix always
Example:For the truss shown , the end displacements of member 2 in
the global
coordinate system are
Calculate the end forces for this member in the global coordinate
system. Is the member in equilibrium under these forces?
MEMBER STIFFNESS RELATIONS IN THE
GLOBAL COORDINATE SYSTEM
Local
Stiffness
Q = ku
Force Transformation
Member Stiffness in Global Coordinate
System
a stiffness coefficient Kij represents the force at the
location and in the direction of Fi required, along with
other end forces, to cause a unit value of displacement
vj, while all other end displacements are zero
Solve Example 3.5 by using the member stiffness
relationship in the global coordinate
system, F = Kv.
Member End Forces in the Global
Coordinate System: By applying the
relationship F = Kv
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ce 153 - Lecture 3 Coordinate TransformationDokument25 SeitenCe 153 - Lecture 3 Coordinate TransformationJovan BucolNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Symbols: © Redzuan Abdullah, FKA, UTM Chapter1 Page 1Dokument45 SeitenList of Symbols: © Redzuan Abdullah, FKA, UTM Chapter1 Page 1Nur Anira AsyikinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.formation of Global AnalysisDokument8 Seiten2.formation of Global AnalysisENGINEERING SOFTWARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Analysis For Architect NotesDokument82 SeitenStructural Analysis For Architect NotesALAWI SSEKUBUNGANoch keine Bewertungen
- m4l24 Lesson 24 The Direct Stiffness Method: Truss AnalysisDokument23 Seitenm4l24 Lesson 24 The Direct Stiffness Method: Truss AnalysisVitor ValeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - Analysis of Beams Using Matrix Stiffness MethodDokument43 Seiten04 - Analysis of Beams Using Matrix Stiffness MethodRyiehmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Statically Indeterminate Structures by The Direct Stiffness MethodDokument28 SeitenAnalysis of Statically Indeterminate Structures by The Direct Stiffness Methodgilberthufana446877Noch keine Bewertungen
- Node Nodal Degrees of Freedom: 1. The Definition of The Finite Element Method (FEM)Dokument32 SeitenNode Nodal Degrees of Freedom: 1. The Definition of The Finite Element Method (FEM)KomarudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument12 SeitenLecture 2Syed Hussain Akbar MosviNoch keine Bewertungen
- A (Bold Faced) : by HandDokument79 SeitenA (Bold Faced) : by Handএ. এইচ ফিরোজNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated Complex Theory NotesDokument4 SeitenActivated Complex Theory NotesdeaffobNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE474 Ch5 StiffnessMethodDokument35 SeitenCE474 Ch5 StiffnessMethodRaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2 Flexibility MethodsDokument22 Seiten2.2 Flexibility Methodsyehunzer yeneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05-Bar Elements in 2d SpaceDokument49 Seiten05-Bar Elements in 2d SpaceMohd NasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 Stiffness Method For FrmesDokument26 SeitenLesson 5 Stiffness Method For Frmescriscab12345Noch keine Bewertungen
- DinamicaDokument41 SeitenDinamicaakmadara17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5Dokument28 SeitenChap 5Mï XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Stiffness MethodDokument6 SeitenDirect Stiffness MethodAhmad ThaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 28 - Direct Stiffness Full A MatrixDokument7 SeitenNotes 28 - Direct Stiffness Full A MatrixSadaf NazNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Material Obeys Hooke's Law. 3. Forces Are Applied Only at The Ends of The Bar. 4. The Bar Supports Axial Loading Only Bending, Torsion, and Shear Are NotDokument16 SeitenThe Material Obeys Hooke's Law. 3. Forces Are Applied Only at The Ends of The Bar. 4. The Bar Supports Axial Loading Only Bending, Torsion, and Shear Are NotMuket AgmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trabajo VibracionesDokument17 SeitenTrabajo VibracionesCesar BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Analysis of StructuresDokument57 SeitenDynamic Analysis of StructuresYollanda LorenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F Ma Where F Is The Resultant Unbalanced Force Acting On The Particle, and A Is TheDokument3 SeitenF Ma Where F Is The Resultant Unbalanced Force Acting On The Particle, and A Is TheJhasper FLoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- StiffnessDokument12 SeitenStiffnessBobi PitropNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDokument30 SeitenEngineering Mechanics: StaticsMohammed AL-sharafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Stiffness AnalysisDokument40 SeitenIntroduction To Stiffness AnalysisSiddharth GhorpadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 3Dokument62 SeitenPresentation 3leleparthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Structural Analysis To Finite Element MethodDokument25 SeitenFrom Structural Analysis To Finite Element MethodB S Praveen BspNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6403 PIT FullDokument93 SeitenME6403 PIT Fullsamuelben87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - Analysis of Plane Trusses Using Matrix Stiffness MethodDokument39 SeitenModule 3 - Analysis of Plane Trusses Using Matrix Stiffness MethodVon Tiosing100% (1)
- Stiffness Methods For Systematic Analysis of StructuresDokument35 SeitenStiffness Methods For Systematic Analysis of Structuresjtek01100% (1)
- Finite Element AnalysisDokument9 SeitenFinite Element Analysishas960Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Nigeria, Nsukka: ME 431 - Theory of Elasticity IDokument14 SeitenUniversity of Nigeria, Nsukka: ME 431 - Theory of Elasticity IEmmanuel JustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03b Direct Stiffness Method TrussDokument18 Seiten03b Direct Stiffness Method TrussAnamolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frame Analysis Using Matrix Strutural AnalysisDokument12 SeitenFrame Analysis Using Matrix Strutural AnalysisCarl Chester RagudoNoch keine Bewertungen
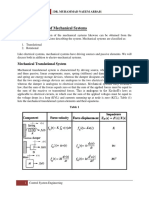
- Mechanical Systems 3Dokument34 SeitenMechanical Systems 3sidkhan1Noch keine Bewertungen
- MS NotesDokument107 SeitenMS Notessrinithims78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Force System and ResultantDokument20 SeitenForce System and ResultantMyra GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bodies or Fluids That Are at Rest or in Motions.: DynamicsDokument23 SeitenBodies or Fluids That Are at Rest or in Motions.: DynamicsJames MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Freedom. For Example A Simple Pendulum Consisting of An Inextensible String That IsDokument37 SeitenOf Freedom. For Example A Simple Pendulum Consisting of An Inextensible String That IsLucia Antonius100% (1)
- Module 4 - Analysis of Beams Using Matrix Stiffness MethodDokument34 SeitenModule 4 - Analysis of Beams Using Matrix Stiffness MethodVon TiosingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Method Chapter 4 - The DSMDokument17 SeitenFinite Element Method Chapter 4 - The DSMsteven_gogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument37 SeitenChapter 2Yordanos AbebawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Lectby VRKDynof MachineryDokument59 SeitenUnit 1 Lectby VRKDynof Machineryrukmini_ramkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UsahaDanEnergi (Kelompok5)Dokument15 SeitenUsahaDanEnergi (Kelompok5)Novitasr AlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics I To III Units PDFDokument143 SeitenEngineering Mechanics I To III Units PDFAnil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goldstein Classical Mechanics Notes (Michael Good 2004)Dokument149 SeitenGoldstein Classical Mechanics Notes (Michael Good 2004)Karan Gupta100% (1)
- Introduction To Matrix Methods For Structural Analysis: Definitions ElementsDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Matrix Methods For Structural Analysis: Definitions ElementsprakharNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Dynamic Analysis of StructuresDokument43 SeitenPDF Dynamic Analysis of StructuresChegue BureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buckling of Thin PlatesDokument11 SeitenBuckling of Thin PlatesEugeniu PrisacariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy 101Dokument4 SeitenPhy 101preciousbukola155Noch keine Bewertungen
- Displacement MethodDokument3 SeitenDisplacement MethodKhen CatayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Is How We Find Our Value in Every Degrees of Freedom and Every ReactionDokument8 SeitenThis Is How We Find Our Value in Every Degrees of Freedom and Every ReactionPatrick AlimuinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic System Modeling and Control - Hugh JackDokument1.016 SeitenDynamic System Modeling and Control - Hugh Jackjiugarte1100% (2)
- Acad ReviewerDokument79 SeitenAcad ReviewerSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comelec Registration FormDokument5 SeitenComelec Registration FormSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loadings For 4 Storey BuildingDokument7 SeitenLoadings For 4 Storey BuildingSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land and Building CostDokument2 SeitenLand and Building CostSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Costs, Revenue, Variable CostDokument1 SeiteFixed Costs, Revenue, Variable CostSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14-OG-0103 PlanDokument1 Seite14-OG-0103 PlanSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- R VesselDokument14 SeitenR VesselSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2500 GRT Slipway: Location: Cabu, Tambler, G.S.C. Owner: Safi Shipyard, Inc. ProjectDokument48 Seiten2500 GRT Slipway: Location: Cabu, Tambler, G.S.C. Owner: Safi Shipyard, Inc. ProjectSushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Break Even Chart: PHP (Million)Dokument1 SeiteBreak Even Chart: PHP (Million)SushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sushita 172 Report (BRIDGE DESIGN)Dokument9 SeitenSushita 172 Report (BRIDGE DESIGN)SushitaBethSenobagoNoch keine Bewertungen