Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tensile Testing Sheet1310
Hochgeladen von
Yusuf SahinOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tensile Testing Sheet1310
Hochgeladen von
Yusuf SahinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
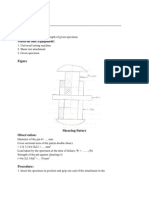
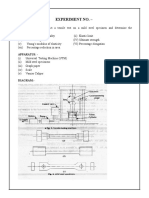
ME 215 MATERIALS LABORATORY
TEST_1
TENSILE TEST
1. Read the theory of tensile behaviour of materials in your notes.
2. Repeat the following procedure for testing each specimen:
(a) Measure and note the gauge length and gauge diameter of the specimen
(b) Set the direct measurement tools for the % elongation and %reduction in diameter for
this specimen.
(c) Set the tensile testing machine,
i. Select the maximum load and assemble the spring and scale for this maximum
load.
ii. Assemble specimen and chucks.
iii. Position the graph paper.
iv. Check the magnification ratio.
v. Turn the handle until the specimen just tightens. Do not apply too much load
while doing this.
vi. Adjust the mercury level to zero load.
(d) Start the testing procedure slowly and gradually increase the load until specimen
fractures.
(e) Using the direct mesuring tools, read the % elongation and % reduction in diameter of
the fractured specimen and note these values.
(f) Measure and note the gauge length and diameter of the necked region of the fractured
specimen.
(g) Using the measurements taken in step (a), calculate the % elongation and % reduction
in diameter.
(h) Then,
i. Compare the measurement in (e) and (g) for each specimen.
ii. Construct a stress versus strain and true stress versus true strain diagram by
using the load-extension diagram.
iii. Calculate the yield strength and ultimate tensile strength (use off-set yield
strength if necessary).
iv. Calculate:
a. Youngs modulus of elasticity.
b. Resilience.
c. Toughness index number.
NOTE THAT TESTING MACHINES OVERALL DEFLECTION IS 41mm PER 2000 KG
IF 2000KG SPRING SCALE IS USED.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Wiring Ecu CalyaDokument22 SeitenWiring Ecu Calyakurnia wan100% (4)
- Kawasaki 1100 STX DI Service ManualDokument288 SeitenKawasaki 1100 STX DI Service Manualnoname618483% (12)
- Edexcel IAL Physics Unit 3 NotesDokument46 SeitenEdexcel IAL Physics Unit 3 Notessshyam3100% (2)
- Cessna Citation XLS+ ReviewerDokument14 SeitenCessna Citation XLS+ ReviewerMK Lariosa100% (2)
- Strength of Materia Lab Manual UET, LahoreDokument14 SeitenStrength of Materia Lab Manual UET, LahoreRizwan Khurram100% (3)
- HendrixACS - 5. B. 15kV 3 Phase-With Logo CABLE ECOLOGICODokument47 SeitenHendrixACS - 5. B. 15kV 3 Phase-With Logo CABLE ECOLOGICOJaime Orlando Santamaria0% (1)
- AASHTO Shear Calculator, No Stirrups: Code Values of Beta and ThetaDokument6 SeitenAASHTO Shear Calculator, No Stirrups: Code Values of Beta and ThetaAnantPawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elongation Index TestDokument2 SeitenElongation Index TestBibhuti B. Bhardwaj60% (5)
- Bending Stiffness of FabricsDokument5 SeitenBending Stiffness of FabricsCasey DeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual HaulotteDokument82 SeitenManual HaulotteRock Saybolt100% (3)
- Magnetic MaterialsDokument11 SeitenMagnetic MaterialsYusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deflection of A Simply Supported BeamDokument6 SeitenDeflection of A Simply Supported BeamZhao Xian Lai20% (5)
- Module 3. Mechanical TestingDokument13 SeitenModule 3. Mechanical TestingPearl Alexandra FabitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD6694-1 - NA To BS EN 1991-2 Cl. NA.2.34.2Dokument142 SeitenPD6694-1 - NA To BS EN 1991-2 Cl. NA.2.34.2stavros_stergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry-Problems and Solutions-1 - MiesslerDokument836 SeitenPhysical Chemistry-Problems and Solutions-1 - MiesslerAKHILA MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sokoine University of Agriculture: Department of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyDokument16 SeitenSokoine University of Agriculture: Department of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual: International Islamic University Malaysia Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument36 SeitenLab Manual: International Islamic University Malaysia Department of Mechanical EngineeringMuhamad HilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deflection of BeamDokument6 SeitenDeflection of BeamNurul Nadhirah50% (2)
- Mos 2Dokument19 SeitenMos 2Abdullah HaroonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOM Lab ManualDokument32 SeitenSOM Lab ManualMuhammad Junaid100% (1)
- Experiment I Torsion of A Rod 1. AIMDokument7 SeitenExperiment I Torsion of A Rod 1. AIMTshepo MolotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Tensile Test....Dokument3 SeitenSimple Tensile Test....Swayam Tej NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Som Manual-2013 RegDokument26 SeitenSom Manual-2013 RegsugunavidiyadarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile Test UTMDokument4 SeitenTensile Test UTMAman BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 10Dokument6 SeitenExp 10Tayyab AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics As Unit 3Dokument12 SeitenPhysics As Unit 3Muaaz IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SFL3011 Physic Laboratory Report Experiment 1Dokument13 SeitenSFL3011 Physic Laboratory Report Experiment 1Liyana Hamdan85% (13)
- Construction Material Lab Manual2Dokument44 SeitenConstruction Material Lab Manual2VitoPascasioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech of Materials - Lab 1Dokument15 SeitenMech of Materials - Lab 1shihabsultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB MANUAL - Mat Testing - SK SinhaDokument20 SeitenLAB MANUAL - Mat Testing - SK Sinhajodoho3441Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 2019Dokument44 SeitenLab Manual 2019se ruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile Testing - All Activities PDFDokument3 SeitenTensile Testing - All Activities PDFDebbie Diane MarananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating A Test Method in Bluehill 3 SoftwareDokument5 SeitenCreating A Test Method in Bluehill 3 SoftwareDinesh MayagodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mom Practical Theory ContentDokument33 SeitenMom Practical Theory ContentZaky MuzaffarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Papua New Guinea University of Technology CE 261-Engineering Materials Test 2 - Tensile Test of A Steel SpecimenDokument4 SeitenPapua New Guinea University of Technology CE 261-Engineering Materials Test 2 - Tensile Test of A Steel SpecimenIsrael PopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Exercise No. 1 AggregatesDokument11 SeitenLaboratory Exercise No. 1 AggregatesHaha HahahahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual: Strength of Material and Measurement LaboratoryDokument17 SeitenLaboratory Manual: Strength of Material and Measurement LaboratoryPiyuesh GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 - 3pt Bending and Tensile TestingDokument4 SeitenLab 4 - 3pt Bending and Tensile TestingbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp-7 Fatigue TestDokument5 SeitenExp-7 Fatigue TestHanamant Hunashikatti50% (2)
- Tensile TestDokument11 SeitenTensile TestMustafa Ani100% (3)
- Experiments - SOM Strength of Materials Lab ExperimentsDokument38 SeitenExperiments - SOM Strength of Materials Lab ExperimentsSathis KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain GaugeDokument18 SeitenStrain GaugeShannon Hayden0% (1)
- ME 244 SessionalDokument20 SeitenME 244 SessionalShadmanHassinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jresv20n2p241 A1bDokument15 SeitenJresv20n2p241 A1bTaha AbdouNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDokument8 SeitenUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAr Ar ViNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tensile TestDokument4 SeitenTensile TestDanielle PaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report 1Dokument9 SeitenReport 1Faqiroh WajedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 221 Measurement LabDokument4 Seiten1 221 Measurement LabArzu KerimNoch keine Bewertungen
- D 4833 - 00 - Rdq4mzmtmdaDokument4 SeitenD 4833 - 00 - Rdq4mzmtmdaEdy TejedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME - 194 Engineering Materials SessionalDokument45 SeitenME - 194 Engineering Materials SessionalAsif AhnafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Lab-Ahmed AlsharaDokument24 SeitenStrength of Materials Lab-Ahmed AlsharaMṜ ΛßßΛSNoch keine Bewertungen
- EME1066 Strength of Material Lab Sheet 2016Dokument10 SeitenEME1066 Strength of Material Lab Sheet 2016Vincent FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.MEET 315LA MatScie Engineering ME Lab Module 1Dokument59 Seiten1.MEET 315LA MatScie Engineering ME Lab Module 1Cj TilamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials Laboratory ExperimentsDokument20 SeitenStrength of Materials Laboratory Experimentskenneth iyahenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENG60503 Lecturer 8Dokument5 SeitenENG60503 Lecturer 8Porkkodi SugumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 MaterialsDokument31 SeitenChapter 1 MaterialsFahmi AmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mos Lab Manul by Abhidhesh YadavDokument45 SeitenMos Lab Manul by Abhidhesh YadavabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexural Test by Third Point LoadingDokument2 SeitenFlexural Test by Third Point LoadingMenkar Construction Supplies TradingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Sheet Experiment 2-StrengthDokument2 SeitenLab Sheet Experiment 2-Strengthfaqhrul0% (1)
- CE6411 Strength of MaterialsDokument38 SeitenCE6411 Strength of Materialsamns99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Centripetal Force and Circular Motion Lab CC NGSS Revision 2014Dokument2 SeitenCentripetal Force and Circular Motion Lab CC NGSS Revision 2014bob sagetNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 6315 Strength of Materials LabDokument33 SeitenCE 6315 Strength of Materials LabSenthil SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIV Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenAIV Lab ReportlawvishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Stiffness TestingDokument13 SeitenFabric Stiffness TestingFahima RashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Error AnalysisDokument7 SeitenError Analysiszpoturica569Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion and ConclusionDokument16 SeitenDiscussion and Conclusionzul hilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture37 PDFDokument16 SeitenLecture37 PDFPavana KumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 1Dokument9 SeitenLab Manual 1Hallowfied KawsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biorobotics - Methods & Applications - Barbara Webb & Thomas R. ConsiDokument206 SeitenBiorobotics - Methods & Applications - Barbara Webb & Thomas R. Consijuridoc100% (1)
- Ch13 14 AnovaDokument48 SeitenCh13 14 AnovaYusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus IIDokument379 SeitenCalculus IIAsih Bsi UnissulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 1Dokument3 SeitenPs 1rhusseinpos4765Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 2Dokument1 SeitePs 2Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Compliance Controls: 9.1 Hybrid Position/Force ControlDokument10 SeitenForce and Compliance Controls: 9.1 Hybrid Position/Force ControlmayankfirstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 3Dokument3 SeitenPs 3Yusuf Sahin0% (1)
- Me 215 CH 5 Hardness Part 11310Dokument38 SeitenMe 215 CH 5 Hardness Part 11310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 215 CH 6 Fatigue 21310Dokument39 SeitenMe 215 CH 6 Fatigue 21310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 4Dokument3 SeitenPs 4Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 8Dokument5 SeitenPs 8Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 7Dokument3 SeitenPs 7Roger Salomon QuispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 5Dokument3 SeitenPs 5Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ho9 Magnetic FundamentalsDokument3 SeitenHo9 Magnetic FundamentalsDavid TurnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 215 CH 11310Dokument123 SeitenMe 215 CH 11310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 215 CH 4 Bending 1310Dokument33 SeitenMe 215 CH 4 Bending 1310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties in Shear: (Eg. Ssy 0.5sy)Dokument34 SeitenProperties in Shear: (Eg. Ssy 0.5sy)Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep Properties PDFDokument23 SeitenCreep Properties PDFMehmet Soysal100% (1)
- Design Engineering and Selection of MaterialsDokument58 SeitenDesign Engineering and Selection of MaterialsYusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 215 CH 6 Fatigue 11310Dokument36 SeitenMe 215 CH 6 Fatigue 11310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 215 CH 5 Hardness Part 21310Dokument31 SeitenMe 215 CH 5 Hardness Part 21310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch01 Intro Stat&DataAnalysisDokument106 SeitenCh01 Intro Stat&DataAnalysisYusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch12 MultipleRegression1Dokument46 Seitench12 MultipleRegression1Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me215ch3 New1310Dokument68 SeitenMe215ch3 New1310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 215 Projects Groups 1310Dokument2 SeitenMe 215 Projects Groups 1310Yusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch10 HypothesisTest One AndTwoDokument119 SeitenCh10 HypothesisTest One AndTwoYusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch11 SimpleRegressionDokument50 Seitench11 SimpleRegressionYusuf SahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series 560 & 570: Pressure Safety Valves ASME Section I (560) & VIII (570) NB Certified For Air, Gas and SteamDokument4 SeitenSeries 560 & 570: Pressure Safety Valves ASME Section I (560) & VIII (570) NB Certified For Air, Gas and SteamEdbaac BANoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Partes Gestetner 2751Dokument169 SeitenManual de Partes Gestetner 2751desechableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perancangan Elevator Penumpang Pada Gedung Bertingkat Dengan Kapasitas 500 KG Di Yanglim Plaza MedanDokument11 SeitenPerancangan Elevator Penumpang Pada Gedung Bertingkat Dengan Kapasitas 500 KG Di Yanglim Plaza MedanWin ManikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Oil ViscosityDokument2 SeitenEngine Oil Viscosityjhnbrry21803Noch keine Bewertungen
- SRP 003x PRESSURE TEST PROCEDUREDokument10 SeitenSRP 003x PRESSURE TEST PROCEDURECavid MAMMADOVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission atDokument47 SeitenTransmission atDidier ÁlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFRA Water QMS MIS Report - SEP 2020Dokument57 SeitenINFRA Water QMS MIS Report - SEP 2020Kumar AbhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen Sensor Certification ManualDokument20 SeitenOxygen Sensor Certification ManualSR BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example - Free Vibration of A SDOF Portal FrameDokument3 SeitenExample - Free Vibration of A SDOF Portal FramemehmetNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARI ARMATUREN - Ball Float Steam Trap CONADokument15 SeitenARI ARMATUREN - Ball Float Steam Trap CONArahimi mohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johnson Controls J06Dokument124 SeitenJohnson Controls J06Geovanni Sanchez TrejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sis 2.0Dokument2 SeitenSis 2.0ShaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gates & DampersDokument30 SeitenGates & DampersMaximilianoRodrigoCabestreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutting Edges & End Bits: Bolt-On & Weld-In Cutting Edges For Buckets & BladesDokument32 SeitenCutting Edges & End Bits: Bolt-On & Weld-In Cutting Edges For Buckets & Blades8897477809Noch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Calculations GuideDokument36 SeitenHVAC Calculations GuideAS HASNoch keine Bewertungen
- McQuay WSC WDC Installation Manual EngDokument36 SeitenMcQuay WSC WDC Installation Manual EngCaturkarya BandonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 (Materials & Hardware) SubModule 6.2 (Aircraft Mat PDFDokument13 SeitenModule 6 (Materials & Hardware) SubModule 6.2 (Aircraft Mat PDFJunaid YounusNoch keine Bewertungen
- NES 339 Requirements For Steering and Stabilizer Systems For HM Surface Ships and Royal Fleet Auxiliaries - Category 1Dokument66 SeitenNES 339 Requirements For Steering and Stabilizer Systems For HM Surface Ships and Royal Fleet Auxiliaries - Category 1JEORJENoch keine Bewertungen
- (201 Marks) : (1 Mark)Dokument49 Seiten(201 Marks) : (1 Mark)Manav NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Máy SliceDokument15 SeitenMáy SliceHoang NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weightor & Load Cell ALEDokument2 SeitenWeightor & Load Cell ALEzackysipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tanks: Dosing Tank and AccessoriesDokument10 SeitenTanks: Dosing Tank and AccessoriesNaji OmarNoch keine Bewertungen