Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
24.air Interface Channels
Hochgeladen von
deepak19mOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
24.air Interface Channels
Hochgeladen von
deepak19mCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
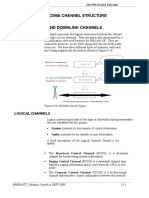
AIR INTERFACE CHANNELS
The path used to carry information between a Mobile Station and a Base Transceiver
Station is known as the Physical Channel. The Control and Traffic Channels are further
subdivided, there are two types of Traffic Channels and three categories of Control
Channels with a total of nine different types
PHYSICAL CHANNEL
Each timeslot on a TDMA frame is called a physical channel. Therefore, there are 8
physical channels per carrier frequency in GSM. Physical channels can be used to
transmit speech, data or signaling information
A physical channel may carry different messages, depending on the information which is
to be sent. These messages are called logical channels. For example, on one of the
physical channels used for traffic, the traffic itself is transmitted using a Traffic CHannel
(TCH) message, while a handover instruction is transmitted using a Fast Associated
Control CHannel (FACCH) message.
LOGICAL CHANNELS
There are 12 logical channels in the system. Two are used for traffic, nine for control
signaling and one for message distribution.
Many types of logical channels exist, each designed to carry a different message to or
from an MS. All information to and from an MS must be formatted correctly, so that the
receiving device can understand the meaning of different bits in the message. For
example, as seen previously, in the burst used to carry traffic, some bits represent the
speech or data itself, while others are used as a training sequence
CONTROL CHANNELS
When an MS is switched on, it searches for a BTS to connect to. The MS scans the entire
frequency band, or, optionally, uses a list containing the allocated carrier frequencies for
this operator. When the MS finds the strongest carrier, it must then determine if it is a
control channel. It does so by searching for a particular logical channel called Broadcast
Control CHannel (BCCH). A frequency carrying BCCH contains important information
for an MS, including e.g. the current LA identity, synchronization information and
network identity. Without such information, an MS cannot work with a network. This
information is broadcast at regular intervals, leading to the term Broadcast CHannel
(BCH) information.According to their functions, four different classes of control
channels are defined: 1. Broadcast channels.
2. Common control channels.
3. Dedicated control channels.
4. Associated control channels
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- GSM Channels1 PDFDokument46 SeitenGSM Channels1 PDFNutan Prakash SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data-Driven Traffic Engineering: Understanding of Traffic and Applications Based on Three-Phase Traffic TheoryVon EverandData-Driven Traffic Engineering: Understanding of Traffic and Applications Based on Three-Phase Traffic TheoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIM: To Study GSM Channels. TheoryDokument2 SeitenAIM: To Study GSM Channels. TheoryAnonymous w74p4iNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesVon EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- LTE ChannelsDokument5 SeitenLTE ChannelsBromand TurkmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Access Networks for UMTS: Principles and PracticeVon EverandRadio Access Networks for UMTS: Principles and PracticeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- 13.1 WCDMA Channel StructureDokument3 Seiten13.1 WCDMA Channel StructureKamal ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Communications Networks and SystemsVon EverandPrinciples of Communications Networks and SystemsNevio BenvenutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.GSM ChannelsDokument24 Seiten7.GSM Channelsmanthasaikarthik100% (1)
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 ChannleDokument5 Seiten3 Channlemohammed aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The International Telecommunications Regime: Domestic Preferences And Regime ChangeVon EverandThe International Telecommunications Regime: Domestic Preferences And Regime ChangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7GSM ChannelsDokument24 Seiten7GSM ChannelsNishant Amit MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisVon EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAYERS & LTE ChannelsDokument13 SeitenLAYERS & LTE ChannelsDhyanendra SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDokument19 SeitenWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaaslamsatnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 - LTE FDD and TDD Mode - Radio Channel Types - PPT PDFDokument14 Seiten05 - LTE FDD and TDD Mode - Radio Channel Types - PPT PDFAhmed GadNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Channels - P-WPS OfficeDokument5 SeitenLTE Channels - P-WPS OfficeEsam SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Channels: Channel Name Acronym Control Channel Traffic ChannelDokument8 SeitenLogical Channels: Channel Name Acronym Control Channel Traffic ChannelFajar Aditya WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Channel in LTEDokument4 SeitenChannel in LTEkartik sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Channel in LTE: Logical ChannelsDokument4 SeitenChannel in LTE: Logical Channelskartik sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarDokument43 SeitenVarious Interfaces and Their Mapping: Skgochhayat RTTC, BhubaneswarKuldeep BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Channels: Control ChannelDokument13 SeitenPhysical Channels: Control ChannelAnshul GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTS Make-Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Alcatel Etc. 2206,2964 MCC, IMSI (International Subscriber Identity Moduel) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)Dokument4 SeitenBTS Make-Nokia, Ericsson, ZTE, Alcatel Etc. 2206,2964 MCC, IMSI (International Subscriber Identity Moduel) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module)AnujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Channel Mapping LTEDokument24 SeitenChannel Mapping LTEbadal mishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wcdmachannels 130219233911 Phpapp02Dokument19 SeitenWcdmachannels 130219233911 Phpapp02Muhammad JunaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Channel TypesDokument3 SeitenGSM Channel Typessanu81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vikas GSM NotesDokument27 SeitenVikas GSM NotesVicky SehrawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDokument19 SeitenWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaMostafizaktelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDokument19 SeitenWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavakikirnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Channels in GSMDokument10 SeitenLogical Channels in GSMshridon123Noch keine Bewertungen
- MAC in Umts ProtocolsDokument10 SeitenMAC in Umts ProtocolsQasim Abbas AlviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G ChannelsDokument6 Seiten3G ChannelsAmit BasraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lte Communication ChannelsDokument3 SeitenLte Communication ChannelsRoderick OchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logical Channels of GSMDokument7 SeitenLogical Channels of GSMAhmad HusaeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadcast Control ChannelDokument3 SeitenBroadcast Control Channeltelecomstuffs7931Noch keine Bewertungen
- WCDMA Channels & Channel SwitchingDokument26 SeitenWCDMA Channels & Channel SwitchingDee OyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rationale Behind Use of Channels: Channel. Physical Channel Is Specified by Specific Time Slot/carrier FrequencyDokument9 SeitenRationale Behind Use of Channels: Channel. Physical Channel Is Specified by Specific Time Slot/carrier FrequencyEC20B1007 Dheeban Kumar GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G Channels and 3GDokument5 Seiten2G Channels and 3Gkn09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wcdma Channel ConceptDokument18 SeitenWcdma Channel Conceptneelachal100% (1)
- LTE ChannelDokument11 SeitenLTE ChannelNam Song Hau CTONoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G LTE Channel TypesDokument3 Seiten3G LTE Channel TypesAvneesh DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial: Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3G/UMTS Protocol StackDokument10 SeitenTutorial: Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3G/UMTS Protocol StackbyamokeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ChannelsDokument20 SeitenGSM Channelsshashikala kotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Communication ChannelsDokument4 SeitenLTE Communication ChannelsVishwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5 Radio Interface 1.5.1 General CharacteristicsDokument20 Seiten1.5 Radio Interface 1.5.1 General CharacteristicsThomas Daniel HaYfordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadcast Communications Engineering: Lecture 14: Wireless LAN (2) Engr. Cynthia V. Plaza Jan. 4, 2010Dokument74 SeitenBroadcast Communications Engineering: Lecture 14: Wireless LAN (2) Engr. Cynthia V. Plaza Jan. 4, 2010Cynthia PlazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- By - Manish SrivastavaDokument19 SeitenBy - Manish SrivastavaRahul DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDokument20 SeitenGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir Shakeelhi2nazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- WcdmaDokument3 SeitenWcdmaSangeen AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Broadcast Control ChannelDokument3 Seiten1 Broadcast Control ChannelRaafat YounisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G Logical ChannelsDokument14 Seiten2G Logical ChannelsAkhtar Khan100% (1)
- UMTS / WCDMA Channels: - Tutorial, or Overview of The Basics of UMTS / WCDMA Logical, Physical and Transport ChannelsDokument4 SeitenUMTS / WCDMA Channels: - Tutorial, or Overview of The Basics of UMTS / WCDMA Logical, Physical and Transport ChannelsDiwakar MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCDMA ChannelsDokument4 SeitenWCDMA ChannelsBromand TurkmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDokument20 SeitenGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelNguyễn HùngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Interface: 1.5.1 General CharacteristicsDokument17 SeitenRadio Interface: 1.5.1 General CharacteristicsFaran Ul GhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS Channel PDFDokument3 SeitenUMTS Channel PDFlimtiongvi100% (1)
- GSM Physical and Logical ChannelsDokument20 SeitenGSM Physical and Logical ChannelsJamshid IbragimovNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G UMTS Data ChannelsDokument6 Seiten3G UMTS Data ChannelsMark EmakhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HandoffDokument1 SeiteHandoffdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28.traffic ChannelsDokument1 Seite28.traffic Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30.trafic in Interfacing-MocDokument2 Seiten30.trafic in Interfacing-Mocdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 33.benefits From TrainingDokument1 Seite33.benefits From Trainingdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27.dedicated Control ChannelsDokument1 Seite27.dedicated Control Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 23.bursts and FramesDokument1 Seite23.bursts and Framesdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oadcast ChannelsDokument2 SeitenOadcast Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.functioning of HLRDokument2 Seiten16.functioning of HLRdeepak19m100% (1)
- Mon Control ChannelsDokument1 SeiteMon Control Channelsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22.transmission Rate& Channel ConceptDokument1 Seite22.transmission Rate& Channel Conceptdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21.radio ChannelDokument2 Seiten21.radio Channeldeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- DatabaseDokument1 SeiteDatabasedeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18.functions of EirDokument1 Seite18.functions of Eirdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17.authentication CenterDokument2 Seiten17.authentication Centerdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15.functioning of VLRDokument1 Seite15.functioning of VLRdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13.the Base Station ControllerDokument1 Seite13.the Base Station Controllerdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14.functioning of MSCDokument2 Seiten14.functioning of MSCdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.mobile StationDokument1 Seite11.mobile Stationdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.introduction To GSM TechnologyDokument2 Seiten9.introduction To GSM Technologydeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.the SIMDokument1 Seite12.the SIMdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company ProfileDokument2 SeitenCompany Profiledeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.tech. Dept.& Org - StructureDokument2 Seiten8.tech. Dept.& Org - Structuredeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work ElementsDokument1 SeiteWork Elementsdeepak19mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Rebuilding Kits: Kit BulletinDokument2 SeitenApplication Rebuilding Kits: Kit Bulletinhidraulic100% (1)
- Ex-Capt. Harish Uppal Vs Union of India & Anr On 17 December, 2002Dokument20 SeitenEx-Capt. Harish Uppal Vs Union of India & Anr On 17 December, 2002vivek6593Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970Dokument2 SeitenComprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970Bryan AbestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper - 1: Principles & Practice of Accounting Questions True and FalseDokument29 SeitenPaper - 1: Principles & Practice of Accounting Questions True and FalsePiyush GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Flow ProfileDokument5 SeitenWind Flow ProfileAhamed HussanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Forensic Final Project CompilationDokument15 SeitenIntro To Forensic Final Project Compilationapi-282483815Noch keine Bewertungen
- 09 20 17Dokument26 Seiten09 20 17WoodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msds 77211 enDokument13 SeitenMsds 77211 enJulius MwakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pace 349 ScheduleDokument3 SeitenPace 349 Schedulesaxman011100% (1)
- SchlumbergerDokument29 SeitenSchlumbergerAitazaz Ahsan100% (5)
- Daily Price Monitoring: Retail Prices of Selected Agri-Fishery Commodities in Selected Markets in Metro ManilaDokument3 SeitenDaily Price Monitoring: Retail Prices of Selected Agri-Fishery Commodities in Selected Markets in Metro ManilaRio CorralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Is Inventory Turnover Important?: ... It Measures How Hard Your Inventory Investment Is WorkingDokument6 SeitenWhy Is Inventory Turnover Important?: ... It Measures How Hard Your Inventory Investment Is WorkingabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Participation 9 E7-18: Last Name - First Name - IDDokument2 SeitenClass Participation 9 E7-18: Last Name - First Name - IDaj singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCCA Semester New Syllabus Direction 2016-17 PDFDokument76 SeitenBCCA Semester New Syllabus Direction 2016-17 PDFChetana Gorakh100% (1)
- Title IX - Crimes Against Personal Liberty and SecurityDokument49 SeitenTitle IX - Crimes Against Personal Liberty and SecuritymauiwawieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microstrip Antennas: How Do They Work?Dokument2 SeitenMicrostrip Antennas: How Do They Work?Tebogo SekgwamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (English) 362L Stereoselective Wittig Reaction - Synthesis of Ethyl Trans-Cinnamate (#7) (DownSub - Com)Dokument6 Seiten(English) 362L Stereoselective Wittig Reaction - Synthesis of Ethyl Trans-Cinnamate (#7) (DownSub - Com)moNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caso 1 - Tunel Sismico BoluDokument4 SeitenCaso 1 - Tunel Sismico BoluCarlos Catalán CórdovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webdynpro ResumeDokument4 SeitenWebdynpro ResumeAmarnath ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Shop InventoryDokument21 SeitenBook Shop InventoryAli AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- AWS Migrate Resources To New RegionDokument23 SeitenAWS Migrate Resources To New Regionsruthi raviNoch keine Bewertungen
- NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT COMPANY v. CADokument11 SeitenNATIONAL DEVELOPMENT COMPANY v. CAAndrei Anne PalomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 252: Computer Organization and Architecture II: Lecture 5 - The Memory SystemDokument29 SeitenCS 252: Computer Organization and Architecture II: Lecture 5 - The Memory SystemJonnahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Based and Unified StorageDokument12 SeitenObject Based and Unified Storageashu narayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- About FW TaylorDokument9 SeitenAbout FW TaylorGayaz SkNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCRP Wheel Rail Noise ReportDokument220 SeitenTCRP Wheel Rail Noise ReportAnonymous OmwbxkB100% (1)
- Arab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2Dokument7 SeitenArab Open University B326: Advanced Financial Accounting TMA - Spring 2022-2023 V2samiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student ManualDokument19 SeitenStudent ManualCarl Jay TenajerosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquamaster 3 Flow Measurement: Saving Every Drop of Energy and Cost Naturally!Dokument7 SeitenAquamaster 3 Flow Measurement: Saving Every Drop of Energy and Cost Naturally!FIRMANSYAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centaur Profile PDFDokument5 SeitenCentaur Profile PDFChandra MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewVon EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItVon EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (66)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyVon EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (111)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldVon EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (55)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsVon EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (722)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andVon EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (709)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldVon EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyVon EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyVon EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootVon EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreVon EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (76)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderVon EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (399)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumVon EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (12)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceVon EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeVon EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (69)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Von EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (34)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveVon EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsVon EverandEvaluation of Some SMS Verification Services and Virtual Credit Cards Services for Online Accounts VerificationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldVon EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (107)
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesVon EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bitcoin Standard: The Decentralized Alternative to Central BankingVon EverandThe Bitcoin Standard: The Decentralized Alternative to Central BankingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (41)
- 100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziVon Everand100M Offers Made Easy: Create Your Own Irresistible Offers by Turning ChatGPT into Alex HormoziNoch keine Bewertungen