Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
New Revised Project..on Commercial Paper
Hochgeladen von
Akshay MahadikOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
New Revised Project..on Commercial Paper
Hochgeladen von
Akshay MahadikCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
COMMERCIAL PAPER AS A MONEY MARKET
INSTRUMENT
PROJECT REPORT
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of
the
MULUND COLLEGE OF COMMERCE, MULUND-W
By
MS.ARTI ANIL WANKHEDE
TYBCBI
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
DECLARATION
I, Ms. Aarti Anil Wankhede hereby declare that this project report
titled Commercial paper as a money market instrument
submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the
TYBECOM is my original work and it has not formed the basis
for the award of any other degree.
Ms. Arti Anil Wankhede
Place: Mumbai
Date:
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Summary
Commercial paper is available in a wide range of denominations, can
be either discounted or interest-bearing, and usually have a limited
or non-existent secondary market. Commercial paper, in the
global financial market, is an unsecured promissory note with a
fixed maturity of no more than 270 days.The study consists of
various graph of U.S. Commercial Paper types outstanding at
end of each year 2001 to 2007. And Total U.S. CP outstanding.
The study consists of various methods of issues. There are two
methods of issuing credit. The issuer can market the securities
directly to a buy and hold investor such as most money market
funds. Commercial paper is a lower-cost alternative to a line of
credit with a bank. Once a business becomes established, and
builds a high credit rating, it is often cheaper to draw on a
commercial paper than on a bank line of credit. This study also
consists of various advantages and disadvantages of commercial
paper.
There are various credit rating agencies listed in this study. The
types of commercial paper are also broadly classified into this
study. Various chacteristics and features of commercial paper are
finely described in this study.
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Index
Pa
g
Sr
N
Particulars
N
o
Introduction
4-9
9-
History
1
2
13-
Object of Study
Bibliography &
References
3
2
323
8
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
INTRODUCTION:
ABSTRACT
Commercial paper is the most prevalent form of security in the money
market, issued at a discount, with a yield slightly higher
thanTreasury bills. The main issuers of commercial paper are
finance companies and banks, but also include corporations with
strong credit, and even foreign corporations and sovereign issuers.
The main buyers of commercial paper are mutual funds,
banks,insurance companies, and pension funds. Because
commercial paper is usually sold in round lots of $100,000, very
few retail investors buy paper.
Commercial paper are unsecured promissory notes for a specified
amount to be paid at a specified date. They are issued at a discount,
with minimum denominations of $100,000. Terms range from 1 to
270 days.
Finance companies sell 2/3 of the total commercial paper, and sell
their issues directly to the public. But corporations that borrow less
frequently sell their commercial papercalled industrial paper
to paper dealers, who then sell them at a markup to other
investors. A round lot for a paper dealer is $250,000.
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
COMMERCIAL PAPER
Commercial Paper (CP) is an unsecured money market instrument
issued in the form of a promissory note. It was introduced in India
in 1990 with a view to enabling highly rated corporate borrowers to
diversify their sources of short-term borrowings and to provide an
additional instrument to investors. Subsequently, primary dealers
and all-India financial institutions were also permitted to issue CP
to enable them to meet their short-term funding requirements for
their operations. Corporates, primary dealers (PDs) and the AllIndia Financial Institutions (FIs) are eligible to issue CP. The
largest and most creditworthy corporations use commercial paper
as a way to obtain short-term funds. Commercial paper is an
unsecured promissory note or an IOU issued by the corporation.
Corporations will sell commercial paper to finance such things as
short- term working capital or to meet their cash needs due to
seasonal business cycles. Commercial paper maturities range from
one day to a maximum of 270 days. It is issued at a discount to its
face value and has an interest rate that is below what a commercial
bank would typically charge for the funds. Commercial paper is
typically issued in book entry form. There are two types of
commercial paper: direct paper and dealer paper. With direct paper,
the issuer sells it directly to the public without the use of a dealer.
Dealer paper is sold to dealers who then resell the paper to
investors.
6
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note
issued by corporations and foreign governments for many large,
creditworthy issuers. Commercial paper is a low-cost alternative to
bank loans. Issuers are able to efficiently raise large amounts of
funds quickly and without expensive Securities and Exchange
Commission (SEC) registration by selling paper, either directly or
through independent dealers, to a large and varied pool of
institutional buyers. Competitive, market-determined yields in
notes, whose maturity and amounts can be tailored to specific
needs, can be earned by investors in commercial paper.
Commercial paper has become one of Americas most important
debt markets, because of the advantages of commercial paper for
both investors and issuers. Commercial paper outstanding grew at
an annual rate of 14 percent from 1970 to 1991. Commercial paper
totaled $528 billion at the end of 1991.This chapter describes some
of the important features of the commercial paper market. The first
section reviews the characteristics of commercial paper. The second
section describes the major participants in the market, including the
issuers, investors, and dealers. The third section discusses the risks
faced by investors in the commercial paper market along with the
mechanisms that are used to control these risks. The fourth section
discusses some recent innovations, including asset-backed
commercial paper, the use of swaps in commercial paper financing
strategies, and the international commercial paper markets. The
7
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
money market is relevant to the corporate world in terms of shortterm surplus or deficit of funds, which it experience. If a corporate
has a short-term surplus, it invests and if it faces deficit, then it
borrows. A corporate needs short-term funds to manage its working
capital requirements, pay taxes and meet other short-term
commitments. These needs are fulfilled, usually, by obtaining short
term finance from banks, trade credit from creditors, loans from
inter corporate deposits (ICDSs) market, bill discounting and
factoring, etc. corporate are always in search of new instruments to
raise funds that provides them with an optimal combination of low
cost, flexible and desired maturity. One such instrument allowed by
RBI in early 90s .
DEFINITION
COMMERCIAL PAPER
Commercial paper is a short term, unsecured license promissory
note issued at a discount to face value by well known or reputed
companies, who carry a high credit rating and have a strong
financial background. It is an unsecured obligation issued by a
bank or corporation to finance its short-term credit
requirements like accounts receivable and inventories and it
is usually issued at a discount reflecting the prevailing market
interest rates. An unsecured, short-term debt instrument issued by a
corporation, typically for the financing of accounts receivable,
inventories and meeting short-term liabilities. Maturities on
commercial paper rarely range any longer than 270days. The debt
is usually issued at a discount, reflecting prevailing market
interest rate
8
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
HISTORY OF COMMERCIAL PAPER:
The concept of raising funds through commercial paper is new to
Indian corporate. The introduction of CPs is a result of the
suggestions of the Working Group on Monday Market in 1987. The
working group was of the opinion that the CP market had the
advantage of giving high-rated corporate borrowers cheaper funds
than they could obtain from banks, while providing the investors
higher yields than they could obtain from the banking system. In
1989, the RBI announced its decision to introduce CPs. It was
launched with a view to enable highly rated corporate borrowers
to diversify their sources of short-term borrowings and also provide
an additional instrument to investors, by which certain categories
of borrowers could issue CPs in the Indian Money Market. It was
also allowed because the RBI desired to discourage the practice of
lending in the Inter Corporate Deposit (ICD)market. As ICDs were
unsecured and the transactions were not transparent, the RBI felt
that CPs may serve as a good substitute for such funds. Initially,
RBI issued guidelines on issue of CPs in January, 1990, and these
guidelines later were revised many times to facilitate the growth of
the market. It was indicated in April, 2000 policy statement that the
current guidelines to issue the CPs would be modified in the light
9
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
of recommendations made by an Internal Group. Accordingly, a
draft of the revised guidelines as also the Report of the Internal
Group was circulated in July, 2000. Taking in to account the
suggestions received from the participants, the guidelines have now
been finalized. The new guidelines are expected to provide
considerable flexibility to participants and add depth and vibrancy
to the CP market while at the same time ensuring prudential
safeguards and transparency. In particular, the guidelines will
enable companies in the services sector to more easily meet their
short-term working capital needs. At the same time, banks and FIs
will have the flexibility to fix working capital limits duly taking
into account there source pattern of companies finances including
CPs. The changes in the guidelines originally issued are
summarized hereunder. Earlier, a company was eligible to issue CP
only if it had tangible new worth of Rs.10 Crore as per the latest
balance sheet. In April, 90, it was reduced toRs.5 crore and, further
to Rs.4 crore in October, 93.Similarly, the working capital
requirement limit, which was Rs.25 crore, was reduced to Rs.15
crore and later to Rs.4 crore in October, 93. The minimum credit
rating required was A1 and P1 and the same was reduced to A2
andP2 in October, 93. The amount a company was allowed to raise
through CP was limited to 20 percent of its Maximum Permissible
Bank Finance(MPBF) and the same was raised to 75 percent in
October, 93. Since the concept of MPBVF was abolished recently,
now a corporate can raise up to100 percent of its fund-based
working capital (without increasing its overall short-term credit).
The RBI initially stipulated that the company should be listed on
one or more of the stock exchanges. Later, it permitted even
unlisted companies to issue CPs. According to the initial
10
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
guidelines, the maturity period of CP was a minimum of 3 months
and a maximum limit was extended to 1 year in October, 1993 and
the minimum was reduced to 30 days in 1997. However, in later
guidelines, the minimum was further reduced to 15 days. Earlier,
the denomination was Rs.10 lakh and the minimum size of an issue
to a single investor was Rs.50 lakh (face value). In October, 1993
the minimum amount for a single investor was reduced to Rs.25
lakh in multiples of Rs.5 lakh. At present, it is Rs.5 lakh in
multiples of Rs.5 lakh. Earlier, the company which was listed on a
stock exchange was eligible to issue a CP; later this condition was
relaxed. Similarly, the company willing to raise CP had to take
prior approval from the RBI which is not essential now. The
standby facility which was allowed to facilitate redemption has
now been abolished to activate the market. Though the above
conditions were relaxed modified for the growth of CPs, the growth
was not as appreciable as expected. The RBI had taken further
steps to activate the market for CPs as there were hardly any
market makers offering two-way quotes in CPs. The Discount and
Finance House of India (DFHI) was expected to be a market maker
by giving two-way quotes. The RBI permitted the Primary Dealers
(PDs) to raise the funds for their operations by issuing CPs hoping
that this would, in turn, enable the PDs to access greater volumes of
funds thereby enhancing the level of activity in the secondary
market.
First recorded transaction was with The Federal Bank of
New York in 1918. It was estimated at $874 million CP facility.
Commercial paper was first introduced over 100 years ago, when
New York merchants began to sell their short term obligations to
dealers that acted as middlemen. These dealers would purchase the
11
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
notes at a discount from their par value and then pass them on to
banks or other investors. The borrower would then repay the
investor an amount equal to the par value of the note. Marcus
Goldman of Goldman Sachs was the first dealer in the money
market to purchase commercial paper, and his company became
one of the biggest commercial paper dealers in America following
the Civil War. The Federal Reserve also began trading commercial
paper along with treasury bills from that time until World War II to
raise or lower the level of monetary reserves circulating among
banks. After the war, commercial paper began to be issued by a
growing number of companies, and eventually it became the
premier debt instrument in the money market.
CONCEPT OF COMMERCIAL PAPER
For investors in Commercial Paper, increased demand has
emanated from the realization that bank deposits often offer
relatively lower rates in comparison. Money market funds growth
has simultaneously developed with demand for commercial paper.
Banks also form a significant portion of demand to fulfill its
portfolio diversification need. Another feature making commercial
paper attractive to investors is its availability in different tenors
that are characteristically short-term in nature. This often provides
an opportunity for profit taking particularly for cash rich
individuals and organizations. Amongst the list of investors in
commercial paper, the largest proportion of investors is composed
of fund managers then followed by banks and last but not least,
individuals. The rates offered by commercial paper are pegged on
Treasury bill rates plus a premium of three to five percent
12
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
depending on the quality of the issue, the credit rating and the
issuers current overdraft facility rate. It has been observed that
subscriptions to various commercial paper issues are high when the
treasury bill rates are high.(Dry and Specer,2004).It must however
be noted that when the Treasury Bill e and Central Bank Rates are
high, there are notably fewer issues of CP and available programs
are reluctant to get money through the facility.
MONEY MARKET:
The money market is used by a wide array of participants, from a
company raising money by selling commercial paper into the
market to an investor purchasing CDs as a safe place to park money
in the short term. The money market is typically seen as a safe
place to put money due the highly liquid nature of the securities
and short maturities, but there are risks in the market that any
investor needs to be aware of including the risk of default on
securities such as commercial paper.
Definition:
A segment of the financial market in which financial instruments
with high liquidity and very short maturities are traded. The money
market is used by participants as a means for borrowing and
lending in the short term, from several days to just under a year.
Money market securities consist of negotiable certificates of
deposit (CDs), bankers acceptances, U.S. Treasury bills,
commercial paper, municipal notes, federal funds and repurchase
agreements (repos).
13
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
MONEY MARKET INSTRUMENTS:
The money market is the arena in which financial institutions make
available to a broad range of borrowers and investors the
opportunity to buy and sell various forms of short-term securities.
There is no physical "money market." Instead it is an informal
network of banks and traders linked by telephones, fax machines,
and computers. Money markets exist both in the India and abroad.
The money market is important for businesses because it allows
companies with a temporary cash surplus to invest in short-term
securities; conversely, companies with a temporary cash shortfall
can sell securities or borrow funds on a short-term basis. In essence
the market acts as a repository for short-term funds. Large
corporations generally handle their own short-term financial
transactions; they participate in the market through dealers. Small
businesses, on the other hand, often choose to invest in money-
14
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
market funds, which are professionally managed mutual funds
consisting only of short-term securities.
TYPES OF MONEY MARKET INSTRUMENTS:
TREASURY BILLS
o Treasury bills (T-bills) are short-term notes issued by the U.S.
government. They come in three different lengths to maturity: 90,
180, and 360 days. The two shorter types are auctioned on a weekly
basis, while the annual types are auctioned monthly. T-bills can be
purchased directly through the auctions or indirectly through the
secondary market. Purchasers of T-bills at auction can enter a
competitive bid (although this method entails a risk that the bills
may not be made available at the bid price) or a noncompetitive
bid. T-bills for noncompetitive bids are supplied at the average
price of all successful competitive bids.
FEDERAL AGENCY NOTES
o Some agencies of the federal government issue both short-term and
long-term obligations, including the loan agencies Fannie Mae and
15
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Sallie Mae. These obligations are not generally backed by the
government, so they offer a slightly higher yield than T-bills, but
the risk of default is still very small. Agency securities are actively
traded, but are not quite as marketable as T-bills. Corporations are
major purchasers of this type of money market instrument.
SHORT-TERM TAX EXEMPTS
o These instruments are short-term notes issued by state and
municipal governments. Although they carry somewhat more risk
than T-bills and tend to be less negotiable, they feature the added
benefit that the interest is not subject to federal income tax. For this
reason, corporations find that the lower yield is worthwhile on this
type of short-term investment.
CERTIFICATES OF DEPOSIT
o Certificates of deposit (CDs) are certificates issued by a federally
chartered bank against deposited funds that earn a specified return
for a definite period of time. They are one of several types of
interest-bearing "time deposits" offered by banks. An individual or
company lends the bank a certain amount of money for a fixed
period of time, and in exchange the bank agrees to repay the money
with specified interest at the end of the time period. The certificate
constitutes the bank's agreement to repay the loan. The maturity
rates on CDs range from 30 days to six months or longer, and the
amount of the face value can vary greatly as well. There is usually
a penalty for early withdrawal of funds, but some types of CDs can
be sold to another investor if the original purchaser needs access to
the money before the maturity date.
16
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
COMMERCIAL PAPER
o Commercial paper refers to unsecured short-term promissory notes
issued by financial and nonfinancial corporations. Commercial
paper has maturities of up to 270 days (the maximum allowed
without SEC registration requirement). Dollar volume for
commercial paper exceeds the amount of any money market
instrument other than T-bills. It is typically issued by large, creditworthy corporations with unused lines of bank credit and therefore
carries low default risk.
o Standard and Poor's and Moody's provide ratings of commercial
paper. The highest ratings are A1 and P1, respectively. A2 and P2
paper is considered high quality, but usually indicates that the
issuing corporation is smaller or more debt burdened than A1 and
P1 companies. Issuers earning the lowest ratings find few willing
investor.
BANKERS' ACCEPTANCES
o A banker's acceptance is an instruments produced by a nonfinancial
corporation but in the name of a bank. It is document indicating
that such-and-such bank shall pay the face amount of the
instrument at some future time. The bank accepts this instrument,
in effect acting as a guarantor. To be sure the bank does so because
it considers the writer to be credit-worthy. Bankers' acceptances are
generally used to finance foreign trade, although they also arise
when companies purchase goods on credit or need to finance
inventory. The maturity of acceptances ranges from one to six
months.
REPURCHASE AGREEMENTS
o Repurchase agreementsalso known as repos or buybacksare
Treasury securities that are purchased from a dealer with the
17
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
agreement that they will be sold back at a future date for a higher
price. These agreements are the most liquid of all money market
investments, ranging from 24 hours to several months. In fact, they
are very similar to bank deposit accounts, and many corporations
arrange for their banks to transfer excess cash to such funds
automatically.
PURPOSE OF ISSUANCE
While creditworthy corporations can borrow from banks for the prime
rate of interest, they may be able to borrow at a lower rate by
selling commercial paper. Commercial paper is also sold to provide
seasonal and working capital for corporations, to provide bridge
financing until longer term securities are sold or until money is
expected to be received, such as tax receipts, and to finance the
purchase of other securities. CDOs and SIVs, for instance, use
commercial paper to finance the purchase of mortgage-backed
securities (MBS), profiting from the difference of receiving the
higher yield of MBS securities, and paying the lower yield of
commercial paper.
18
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
As an example of bridge financing, a corporation may project that
interest rates will be lower in the future, but, for business reasons,
may want to finance a project immediately. It can finance the
project immediately by issuing commercial paper with a maturity
that coincides with the projected lower interest rates. Then it can
issue long-term bonds, and use the proceeds to pay for the
redemption of the commercial paper
PARTICIPANTS
1.ISSUERS:
Any private sector companies, public sector units, non-banking
companies, primary dealers (PD), satellite dealers (SDs) etc, can
raise funds through the Commercial papers. But the companies
have to satisfy the eligibility criteria prescribed by RBI as
discussed later. The condition laid by RBI restrict the entry of
issuers into the CP market.
19
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
2.INVESTORS
CPs are generally open to all investors-individuals, banks,
corporates and also Non-resident Indians (NRIs). But NRIs can
only invest on a non-reportable and non transferable basis. SEBI
has permitted Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) also to invest in
corporate debts instruments like CPs. FIIs were allowed to invest
their short-term funds in such instruments too. Within a ceiling of
the $ 1.5 billions of the total FIIs were inflows for debt funds set
down by the RBI. Though the market is open to the above
segments, usually, banks, large corporate bodies, public sector units
with investible funds functions in the market.
Source :- (http://www.indianmoney.com/)
Commercial papers favor both borrowers and investors. It is
considered as an optimal combination of liquidity and returns in the
short-term market. To borrowers it implies low cost of funds, and to
investors it implies liquidity, marketability and returns .I)
Commercial papers does not originate from a specific self
liquidating transaction like normal commercial bills, which
generally arise out of specific trade transaction. II) CPs is backed
by the liquidity and earning powers of the issuer, but is not backed
by any assets, and hence they are unsecured. III) The CP market
provides the borrower a cheaper source of funds witless paper work
and formalities when compared to bank finance. Corporate prefer
this mode of finance as they can determine the cost and maturity.
Similarly, CP involves less paper work formalities, as it an
unsecured liability, unlike bank finance, which is secured. IV)
Investors prefer to invest in CPs due to high liquidity, varied
20
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
maturity and high yield (when compared to bank deposits). The
liquidity is high because it can be transferred by endorsement and
delivery.
ISSUE PRICE
The CPs are issued to the investors at a discount to the face value.
The discount actually is the effective interest rate. The issue prices
determine by the corporate issuing it in the following manner.
Generally the merchant bankers (Issuing and Paying Agent) IPA on
behalf of the corporate client, approaches various investors and
takes quotes, and expected amount of investment for the proposed
CP for various maturity. After obtaining the quotas, the merchant
bankers and issuing company compile the data and arrive at an
optimal discount rate with a feasible maturity date of paper. While
determining the discount rate, it considers factors such s
prevailing call money rates, prime lending rates, T-bill rates,
maturity of the papers and other relevant expenses (such as
brokerage, rating agencys fees, stamp duty, etc). Once the issue
price and maturity are decided, the IPA places the CP with the
investors.
FACTORS AFFECTING PRICING
CP being a short term instrument, its primary and secondary
markets determination of the interest rates, i.e.; the discount rates,
depends upon condition in short-term money market. The following
are the principle factors in pricing the CPs
1. INTERBANK CALL RATES
21
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Since call rates affect all the other short-term rates and banks are
the most important investors in CPs, its pricing is affected very
much by call rates. Also, as the lenders in the CPs market are
predominantly bank, call market affects the CP market rates; lower
call rates means cash surplus. Banks thus view CPs as an
alternative investment route
2. COMPETING MONEY MARKET INVESTMENT
PRODUCTS
Interests rate son CPs are determine by the demand and supply
factors in the money market and the interest rates on the other
competing money market instrument such as Certificate of
Deposits, Commercial Bills, Short term Forward premium and
Treasury Bills, the investment in CPs give comparably higher yield
than those obtained in banks deposits of similar maturity.
TYPES OF COMMERCIAL PAPER
There are two major types of commercial paper 1. Direct Paper 2.
Dealer Paper
Direct Paper:
The Direct Paper is issued by large finance companies and bank
holding companies deal directly with the investor rather than use a
dealer as an intermediary. Though the issuers of direct paper do not
22
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
have to pay any dealers commission, these companies must
operate a marketing division to maintain constant interaction with
active investors. And also these companies need to pay fees to
banks for supporting lines of credit, to the rating agencies and to
agents (i.e. bank trust departments). Hence, this paper must be sold
in large volumes to cover the substantial costs of distribution and
marketing.
Dealer Paper:
The Dealer Paper is issued by dealers on behalf of their corporate
customers. It is mainly issued by non-financial companies and
finance companies. The issuing company sells the paper directly to
the dealer at a discount and commission. The dealer will resell it at
the highest possible price in the market. Companies using dealers
to place their paper are generally smaller, less frequent borrowers
than issuers of direct paper. An open rate method is followed by
which the company receives some money in advance but the
balance depends on the performance of the issue in the open
market.
Source : - (http://www.helium.com)
Commercial Papers can be issued either directly or through a
dealer. If the company issues the paper directly to the investors
without dealing with an intermediary, it is referred to as direct
papers. The companies going for direct paper will announce the
current rates of CPs with various maturities so that the investors
can choose the CPs with various maturities so that the investors can
choose the CPs based on the requirement. If a CP is issued by an
intermediary (i.e.; dealer/merchant banker) on behalf of its
corporate client, it is known as dealer paper. The role of dealer in
23
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
the CP market is to arrange for the private placement of the
instrument. Generally, dealers also play advisory roles in timing the
issue, determining discount rate and appropriate maturity period. In
India, the CPs is usually placed with the investors with the help of
issuing and paying agent. Market making in CPs has not reached
the desirable levelers. However, it is possible for any dealers to
pick up the entire issue of CP of a company and then sell it in the
market.
GENESIS OF CP MARKET IN INDIA
CP is an unsecured money market instrument issued in the
form of a promissory note and transferable by endorsement and
delivery. Commercial Paper was introduced in India in 1990 with a
view to enabling highly rated corporate borrowers to diversify their
sources of short-term borrowings as also to provide an additional
24
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
instrument to investors. Issue of CP is governed by the Nonbanking Companies (Acceptance of deposits through Commercial
Paper) Directions 1989. Acceptance of funds through issue of CP
has been exempted from the provisions of Section 58A of the
Companies Act 1956 and brought within the overall purview of the
Directions issued by the Reserve Bank of India under Section 45K
of the RBI Act, 1934. Under these Directions, CP can be issued
only for raising working capital finance. The aggregate amount to
be raised by issuance of CP cannot exceed the working capital
(fund-based) limit sanctioned by bank/s to an issuer company and
to the extent of CP issued, a corresponding reduction has to be
made in the working capital limit. It was felt that with the
introduction of CP, funds flowing through the inter-corporate
deposit market would shift to the CP market. The eligibility
conditions prescribed for issue of CP have been amended from time
to time and the present guidelines are set out in Annexure I.
Initially only corporates were permitted to issue CP. Subsequently,
primary dealers (PDs) were permitted to issue CP in September
1996 and satellite dealers (SDs) in June 1998.
GROWTH OF THE CP MARKET
CP market in India has witnessed sharp ups and downs. Since
its inception in 1990 and until the end of the financial year 199293, the activity in the CP market in India was minimal and volumes
were very small. The amount outstanding at the end of the year
1992-93 rose to Rs.578 crore from Rs.86 crore as at the end of
financial year 1989-90. Following the various relaxations in the
25
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
terms and conditions for issue of CP (viz., eligibility criteria,
denomination of CP, quantum of CP, etc.) and decline in discount
rates, CP market witnessed a strong growth thereafter. During
1993-94, on an average around Rs.460 crore was mobilised through
CP in a fortnight and the outstanding CP amount as at the end of
March 1994 was Rs.3,264 crore. However, following the
withdrawal of the stand-by facility for CP in October 1994, coupled
with rising discount rates and a shrinking of short-term surplus
funds with banks, there was a sharp decline in the amount raised
through CP. During the period, from October 1994 to March 1995,
fresh issues of CP ranged between Rs.75 - 495 crore during various
fortnights. The outstanding amount of CP declined sharply by
Rs.2,660 crore and stood at Rs.604 crore at end-March 1995.
There was a further decline in the volume of CP to Rs.76 crore by
end-March 1996. However, with the fall in the discount rates,
coupled with further relaxations such as permission to company to
issue CP upto 100 per cent of MPBF, there was a revival in the CP
market and outstanding amount of CP touched Rs.646 crore by the
end of March 1997.
CP issuance gathered momentum thereafter, and witnessed a
pronounced increase since May 1997. During the year 199798,fortnightly issue of CP ranged between Rs.83 - 1,880 crore and
amount outstanding at the end of March 1998 was Rs.1,500 crore,
end-March 1999 was Rs.4,770 crore and at end-January 2000 was
Rs.7,814 crore. The unprecedented and steep rise in CP issuance in
the last two years has been on account of the following factors :
26
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
(a) In October 1997, the stipulation that the request for restoration
of working capital (fund based) credit limit (on repayment of
Commercial Paper) should be considered by banks on the lines of
enhancement of limit was withdrawn and banks were given the
freedom to decide the manner of restoration of the working capital
limit.
(b) There had been sluggishness in the off-take of non-food credit
during this period and banks therefore, deployed their resources in
short-term instruments.
(c) Highly rated blue chip corporates have been issuing CP as an
effective instrument for reducing the funding cost of their working
capital during periods when money market interest rates have ruled
low.
Investors in CP have been banks, financial institutions and to some
extent other corporates. Except for the period when demand for
bank credit had been very high (such as 1995-96), an
overwhelming proportion (more than 80 per cent) of CP amount
has been subscribed to by commercial banks only.
Chart - 1
Demat Procedure For CP - Tentative Scheme
27
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Steps :
1.
After the deal is struck between issuer and investor, deal
confirmations are exchanged.
2.
Issuer enter into agreement with IPA.
3. IPA verify all the documents and issue certificates to that effect.
4. Issuer send IPA certificates to Investor.
5. Issuer request depository to credit the CP to the investor's account.
6. Investor request depository through depository participant for the
credit of CP.
7. Depository matches the request from issuer and depository
participant and give credit to the investor and send confirmation to
issuer and depository participant.
8.
Depository participant give statement of account to investor.
Chart 2
Dematerialisation of Physical CP Certificates
28
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Request
Depository
Issuer
Confirmation
Request
Confirmation
Physical
Certificate
Depository
Participant
Certificate
Statement of
Holding
Investor
Steps :
1.
Investor surrender physical certificates to Depository Participant
(DP).
29
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
2.
DP make request for dematerialisation to depository which in turn
request the issuer for the same.
3.
Issuer confirm to depository certificate may demateralised and
receive physical certificate from DP.
4.
DP gives statement of holding to investor.
FEATURES OF COMMERCIAL PAPER
Commercial paper is the most prevalent form of security in the
money market, issued at a discount, with a yield slightly higher
30
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
than Treasury bills. The main issuers of commercial paper are
finance companies and banks, but also include corporations with
strong credit, and even foreign corporations and sovereign issuers.
The main buyers of commercial paper are mutual funds, banks,
insurance companies, and pension funds. Because commercial
paper is usually sold in round lots of $100,000, very few retail
investors buy paper.
Commercial paper are unsecured promissory notes for a specified
amount to be paid at a specified date, and are issued by finance
companies, banks, and corporations with excellent credit. They are
issued at a discount, with minimum denominations of $100,000.
The main purchasers are other corporations, insurance companies,
commercial banks, and mutual funds. Terms range from 1 to 270
days.
Finance companies sell 2/3 of the total commercial paper, and sell
their issues directly to the public. But corporations that borrow less
frequently sell their commercial papercalled industrial paper
to paper dealers, who then sell them at a markup to other
investors. A round lot for a paper dealer is $250,000.
Commercial paper can be defined as a short term, unsecured
promissory notes which are issued at discount to face value by well
known companies that are financially strong and enjoy a high credit
rating. Here are some of the features of commercial paper
31
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
1. They are negotiable by endorsement and delivery and hence they
are flexible as well as liquid instruments. Commercial paper can be
issued with varying maturities as required by the issuing company.
2. They are unsecured instruments as they are not backed by any
assets of the company which is issuing the commercial paper.
3. They can be sold either directly by the issuing company to the
investors or else issuer can sell it to the dealer who in turn will sell
it into the market.
4. It helps the highly rated company in the sense they can get
cheaper funds from commercial paper rather than borrowing from
the banks.
However use of commercial paper is limited to only blue chip
companies and from the point of view of investors though
commercial paper provides higher returns for him they are
unsecured and hence investor should invest in commercial paper
according to his risk -return profile.
Following are the characteristics of commercial papers:
1. It is a negotiable instrument.
2. It is an unsecured instrument as it is not backed by any assets of the
company.
3. It can be sold by the issuing company, directly to the investors.
32
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Issuers can be divided into financial and nonfinancial companies, although
most issuers are financial. There are 3 types of finance companies:
1 captive finance companies,
2 bank-related finance companies,
3 independent finance companies.
Captive finance companies are subsidiaries of manufacturers,
with the purpose of providing financing for the manufacturer. The
largest selling of commercial paperGeneral Motors Acceptance
Corporation (GMAC)is also a captive finance company that
provides financing for the customers of General Motors. Other
vehicle manufacturers also have captive finance companies to
promote the sale of their vehicles.
Bank holding companies general use finance companies to cater to
customers with weaker credit. Independent finance companies
are not affiliated with any other company or bankhence, the
name.
Generally, only corporations with the highest credit rating can issue
commercial paper. Some companies with weaker credit can get
credit enhancements, so that they can issue commercial paper.
Asset-backed commercial paper is backed by high quality
collateral. Credit-supported commercial paper is often
guaranteed by an organization with excellent credit, such as a bank.
Often, a letter of credit is used for this purpose, which is referred
to as LOC paper. The bank promises to pay the face value of the
paper if the issuer doesn't. Though the bank generally charges a fee
33
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
equal to 1/2 of 1% of the issue, it is still cheaper than obtaining a
loan from the bank.
Other costs that the issuer must pay are agents' fees to a bank for
doing the paperwork necessary to issue commercial paper, and
thousands of dollars to have the issue rated by a credit rating
organization, such as Standard and Poor's and Moody's.
INVESTMENT CHARACTERISTICS
Most commercial paper has a maturity of about 45 days, and most
are less than 90 days, although some commercial paper has a
maturity of up to 270 days. The terms of the commercial paper is
determined by a number of factors. One factor is the market.
Buyers of commercial paper generally buy the terms that they want
to coincide with their need for money.
The 270-day limit is dictated by the need to register the security
with the SEC if the maturity is longer. This greatly increases the
expense and time to issuehence, commercial paper will rarely
have terms longer than this. If the issuer needs the money longer, it
can usually rollover the issue by issuing new commercial paper to
pay off the maturing paper, which is often done.
There is also a 90-day barrier for the length of terms. When a bank
borrows from the Federal Reserve Bank discount window, it must
provide collateral. The Federal Reserve will only accept
commercial paper as collateral if it has a term of 90 days or less.
This increases the demand for commercial paper with terms of 90
days or less, and, therefore, lowers the interest rate that the issuer
would otherwise have to pay for the same term.
34
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Most commercial paper is sold in round lots of $100,000, although
there is some paper available in $25,000 lots.
COMMERCIAL PAPER MARKET
Most commercial paper is bought in the primary market. The
primary market consists of directly placed and dealer-placed
paper. Directly placed commercial paper is sold directly to the
investor by the issuer without the services of a securities firm. Most
issuers of direct paper are finance companies that sell a large
amount of paper continually, and have salespeople to sell the paper
to investors.
Dealer paper is issued using the services of a securities firm,
usually an investment bank, but, increasingly, large commercial
banks. Commercial banks were prohibited from underwriting
commercial paper by the Glass-Steagall Act, but the Federal
Reserve, in June 1987, allowed subsidiaries of bank holding
companies to underwrite commercial paper, which has significantly
reduced the costs of issuing dealer paper to the issuer.
Although commercial paper is the most prevalent money market
instrument, the secondary market is very small, primarily because
the terms of commercial paper are very short, and because buyers
of commercial paper usually purchase paper with maturities that
coincide with their need for money. Hence, most holders of
commercial paper hold it till maturity. However, in many cases, if
the holder of commercial paper needs the money sooner, the
commercial paper can usually be sold back to the issuer of direct
paper or to the dealer of dealer paper.
35
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
COMMERCIAL PAPER YIELDS
Commercial paper is a discount instrumentthe interest earned is
the difference between the face value and the discounted purchase
price. Yields are calculated using a banker's year of 360 days.
The yields on commercial paper are usually 10 to 20 basis points
above Treasury bills of the same maturity, primarily because the
interest earned from commercial paper, unlike T-bills, is not exempt
from state and local taxes. Commercial paper also has lower
liquidity than T-bills, where trading in the secondary market is
more active and bid/ask spreads, narrower.
There is also some credit risk. The main credit risk stems from
rollover risk, when the issuer may not be able to sell new paper to
pay for maturing paper, either because the market has changed, or
the credit rating of the issuer has been downgraded. The best
example of this is the recent downgrades of CDOs and SIVs by the
credit rating agencies. CDOs and SIVs made money from
mortgaged-backed securities that were financed with commercial
paper. Because the commercial paper has much shorter maturities
than the mortgaged-backed securities, the maturing paper has to be
continually rolled over. But because of the subprime mortgage
debacle, the commercial paper market dried up, especially for the
CDOs and SIVs.
36
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
To calculate the investment yield (aka bond equivalent yield) of
commercial paper so as to compare it to the rates of return of other
investments:
1 calculate the interest rate for the period;
2 then compound the rate by the number of periods in a year.
formula for Calculating the Investment Yield or Bond Equivalent Yield
(BEY)
Interest Rate
Number of Terms
Per Term
per Year
Face Value -
Price Paid
Actual Number of
Days in Year
x
Term Length in
Price Paid
Days
37
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
ABOUT COMMERCIAL PAPER
ELIGIBILITY FOR ISSUANCE OF CP
Presently, companies, which satisfy the following requirements,
shall be eligible to issue commercial paper :
The tangible net worth of the company is not less than Rupees four
crore
Working capital (fund-based) limit of the company is not less than
four crore
The minimum credit rating of the company shall be P-2 from
CRISIL or equivalent from other Rating agencies
The borrowal account of the company is classified as a Standard
Asset.
Besides companies, Primary Dealers (PDs) and Satellite Dealers
are also permitted to issue CP.
PERIOD OF CP
CP can be issued for maturities between 15 days to less than
one year.
DENOMINATION AND MINIMUM SIZE OF CP
38
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
CP can be issued in multiples of Rs.5 lakh. Minimum amount to be
invested by single investor - Rs.25 lakh (face value).
Secondary market transaction may be for Rs.5 lakh or multiples
thereof.
CEILING ON AMOUNT OF ISSUE
The aggregate amount to be raised by way of CP shall not exceed
the working capital (fund-based) limit sanctioned by bank/s to an
issuer company.
MODE OF ISSUE
The commercial paper is in the form of usance promissory note
negotiable by endorsement and delivery and issued at discount to
face value.
ELIGIBLE INVESTORS
CP can be issued to individuals, banks, companies, other corporate
bodies registered in India and unincorporated bodies. However, CP
issued to NRIs will not transferable and will be on a nonrepatriable basis.
PROCEDURE FOR ISSUE OF CP
The company which proposes to issue CP has to submit its proposal
to the financing banking company along with a certificate issued by
Credit Rating Agency. The financing banking company, after
satisfying that the issuing company fulfils the eligibility criteria
39
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
takes the proposal on record. The issuing company thereafter
makes arrangements for privately placing the issue and has to
ensure that it shall completes the issue of CP with in the period of
two weeks.
Once the CP is issued, the financing banking company makes
arrangements for reducing the working capital fund based limit to
the extent of the amount of CP issued. The issuing company has to
advise the RBI through its financing company the amount of CP
actually issued with three days from the date of completion of the
issue.
40
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
COMMERCIAL PAPER-ADVANTAGES:
a) Cheaper than a short term business loan from a commercial bank
b) Large amounts may be borrowed conveniently
c) The ability to issue paper gives flexibility to pay for projects as you
go
d) A major benefit of commercial paper is that it does not need to be
registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as
long as it matures before nine months (270 days), making it a very
cost effective means of financing. These securities are actively
a.
e)
f)
g)
traded in secondary market.
High credit ratings fetch a lower cost of capital.
Wide range of maturity provide more flexibility.
It does not create any lien on asset of the company.
Tradability of Commercial Paper provides investors with exit
options.
h) It is quick and cost effective way of raising working capital.
i) Best way to the company to take the advantage of short term
interest fluctuations in the market
j) It provides the exit option to the investors to quit the investment.
k) . They are cheaper than a bank loan.
l) . As commercial papers are required to be rated, good rating
reduces the cost of capital for the company.
m) It is unsecured and thus does not create any liens on assets of the
company.
n) . It has a wide range of maturity
o) It is exempt from federal SEC and State securities registration
requirements.
41
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Commercial Paper Disadvantages:
1) Risk of alienating banks whose loans may be needed when an
emergency develops.
2) May be difficult to raise funds in the paper market at times
3) Commercial paper must generally remain outstanding until
maturity does not permit early retirement without penalty.
4) It is available only to a few selected blue chip and profitable
companies.
5) By issuing commercial paper, the credit available from the banks
may
6) get reduced.
7) Issue of commercial paper is very closely regulated by the RBI
guidelines.
8) Its usage is limited to only blue chip companies.
9) Issuances of commercial paper bring down the bank credit limits.
10)A high degree of control is exercised on issue of Commercial Paper.
11) Stand-by credit may become necessary.
42
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Rates and Pricing
The Federal Reserve Board posts the current rates being paid by
commercial paper on its website. The FRB also publishes the rates
of AA-rated financial and non-financial commercial paper in its
H.15 Statistical Release every Monday at 2:30pm. The data used
for this publication are taken from the Depository Trust & Clearing
Corporation (DTCC), and the rates are calculated based on the
estimated relationship between the coupon rates of new issues and
their maturities. Additional information on rates and trading
volumes is available each day for the previous days activity.
Figures for each outstanding commercial paper issue are also
available at the close of business every Wednesday and on the last
business day of every month.
The Bottom Line
Commercial paper is becoming increasingly available to retail
investors from many outlets. Those who seek higher yields will
likely find these instruments appealing due to their superior returns
with modest risk. For more information on commercial paper,
contact your financial advisor or visit the Federal Reserve Board
website.
43
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Commercial Paper and Credit Rating agencies
All eligible participants shall obtain the credit rating for issuance of
Commercial Paper either from Credit Rating Information Services
of India Ltd. (CRISIL) or the Investment Information and Credit
Rating Agency of India Ltd. (ICRA) or the Credit Analysis and
Research Ltd. (CARE) or the FITCH Ratings India Pvt. Ltd. or
such other credit rating agency (CRA) as may be specified by the
Reserve Bank of India from time to time, for the purpose.
The minimum credit rating shall be A-2 [As per rating symbol and
definition prescribed by Securities and Exchange Board of India
(SEBI)].
The issuers shall ensure at the time of issuance of CP that the rating so
obtained is current and has not fallen due for review.
44
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Introduction to Commercial Paper Structures, Special Report,
January 1998 Pros, Cons and Considerations in Introducing an CP
Conduit, Special Report, October 2002
Commercial Paper: Understanding the Risks, Special Report, April
1997.(Note: this article is the predecessor to The Fundamentals of
CP.)
Moodys Approach to Evaluating Credit Arbitrage CP Programs,
Special Report, August 2002.
An Introduction to Structured Investment Vehicles, Special Report,
January 2002Structured Investment VehiclesRecent
Developments, Special Report, January 2003
Comparing and Contrasting Credit Arbitrage CP Programs and
Structured Investment Vehicles, Special
Report, January 2002
LOC-Backed CP Programs: Structure is Key, Special Report, August
2000.
Rating Commercial Paper Programs Backed by Maturity-Matched
Loans, Special Report, September 1999.
On Being A Prudent Investor: Understanding the Nuts and Bolts of
Australian CP Structures, Special Report, August 1998.
CP Investors
U.S. Money Market Funds Carry a Big Buy-Side Stick with CP,
Special Report, July 2002.
U.S. Money Market Funds Hungry for Asset-Backed Commercial
Paper, Special Report, April 20, 2001.
45
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
The commercial paper market has long been viewed as a bastion of
high liquidity and low risk. But twice during the financial crisis of
20072009, the commercial paper market nearly dried up and
ceased being perceived as a safe haven. Major interventions by the
Federal Reserve, including large outright purchases of commercial
paper, were eventually used to support both issuers of and investors
in commercial paper. Even though the commercial paper market
has experienced disruptions in the past, the financial crisis of 2007
2009 was by far the largest decline in the commercial paper market,
and in contrast to previous turbulent episodes, it mostly affected
commercial paper issued by financial institutions. This crisis has
also shown that the Federal Reserve is likely to respond
aggressively to such a sudden decline of the commercial paper
market. In fact, the scale of the Federal Reserves response was
unprecedentedincluding a blanket guarantee of money market
investment worth $3 trillion and direct purchases of commercial
paper of up to $370 billion. Such large-scale market interventions
raise concerns about future moral hazard of commercial paper
issuers, independent of whether these guarantees will remain
implicit or not. Financial regulation will need to address the
negative incentives generated by the expectation of future
government interventions, either by directly regulating the risk of
commercial paper issuers or by charging issuers or investors for the
insurance provided by the government.
46
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
The commercial paper market is far from being fully restored. In fall
2009,the Federal Reserve is still in the process of unwinding its
purchases of commercial paper, the amount of commercial paper
outstanding is still quite low, and interest When Safe Proved Risky:
Commercial Paper during the Financial Crisis of 20072009 49
rate spreads on asset-backed commercial paper are still at their
historical highs. Issuers of commercial paper will remember for
some time that commercial paper was much riskier than they had
originally believed. And investors in commercial paper will
remember for some time that commercial paper turned out to be
much riskier than they had thought. The high level of skepticism on
both sides of the market for commercial paper suggests that the
market will probably diminish relative to its size before the
financial crisis.
State Bank of India said a further cut in base rate by the lenders will
be possible only if there is a substantial pick up in loan growth,
which it expect from the fourth quarter. SBI Chairman Arundhati
Bhattacharya said although the rates in the commercial papers are
lower, banks can only match those rates once credit growth picks
up. "If we are going to compete on the commercial paper market
front, we have to lower base rate by more than 100 basis points,
which, looking at the credit growth in the market, is something that
cannot be done," she told reporters here after addressing the
shareholders at the 60th AGM here this evening. "I see credit
47
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
growth to improve from the fourth quarter," Bhattacharya said.
Currently, corporates are attracted more towards commercial papers
where rates are lower to the tune of 100-200 bps than what banks
are offering. Earlier, Reserve Bank Governor Raghuram Rajan said
higher competition from lower rates in the money market
instruments may force banks to reduce their lending rates.
"Competition is one of the reasons why transmission takes place
and while you may want to retain profits, competition may not
allow you to retain profit. Banks at some point see competition
from money market, and then they may want to adjust the rates
appropriately because they are not getting credit growth otherwise,"
Rajan told reporters in Chennai after a central bank board meeting.
During the last three months, many large and small public and
private sector banks have reduced their base rates twice but to the
tune of just about 30 bps, against RBI's 75 bps reduction repo rate,
after Rajan blamed them for not passing the benefits of repo rate
cuts to borrowers. The largest lender has reduced its base rate by 30
basis points in the beginning of this fiscal. Its minimum lending
rates stands at 9.70 per cent, which is the lowest amongst the large
lenders. Private sector lenders such as HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank
also offer base rate at 9.70 per cent. When asked whether bank has
put merger of associate banks on the back burner, the SBI chairman
said, "Yes, at this point." SBI has five associate banks- State Bank
of Bikaner & Jaipur , State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of
Patiala, State Bank of Travancore and State Bank of Mysore .
Bhattacharya said the bank has also written to the government to
increase the sitting fee for directors from Rs 5,000 per sitting. But
she did not say what is the new fee that the bank wants to offer to
its directors.
48
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
49
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
NEWS ARTICLES ON COMMERCIAL PAPER
Banks investing in commercial paper instead of
lending directly
Gayatri Nayak & Saikat Das, ET Bureau Jul 2, 2015, 01.51AM IST
(Investment in commercial)
MUMBAI: Investment in commercial paper of firms instead of lending to them
directly is emerging as a prudent option for banks.
Banks' subscription of commercial paper has grown at a much quicker pace than
their core business of lending. This is helping them maintain the liquidity
coverage ratio, or LCR- a prudential requirement prescribed by the Reserve
Bank of India.
Commercial paper rates head for a 6% rate barrier
Gayatri Nayak, TNN Aug 28, 2002, 02.38am IST
MUMBAI: Commercial paper rates look set to flatten out at around six per cent.
Along with surging volumes, the primary CP market is also seeing yields fall by
the day.
And a new breed of investors liquid schemes of mutual funds are joining
the commercial paper chase in the markets. With a liquidity overhang in the
50
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
banking system, corporates are reducing their interest costs further by raising
short-term funds through the commercial paper (CP) route. As of August 15, the
total amount invested in commercial paper stood at Rs 9,148 crore.
COMMERCIAL PAPER
October 30, 2006
Money market rates remained steady but with a downward bias tracking the call
rates. Due to the festive season holiday, activities remained thin. Companies
borrowed funds through commercial papers in the range of 7.51-7.75%. Banks
raised short-term funds to meet up festive demand by issuing CDs. At the 91day treasury bills auction, RBI maintained the cut-off price at Rs 98.37 (yield
6.6462%). CREDENCE ANALYTICS INDIA PVT LTD.
India Ratings gives A+ rating to Mahindra Lifespace
Developers' Rs 150 crore commercial paper
Megha Mandavia, ET Bureau Sep 7, 2015, 03.02PM IST
MUMBAI: India Ratings assigned real estate firm Mahindra Lifespace
Developers' Rs 150 crore short-term unsecured commercial paper an 'A1+'
rating due to its strong brand name, long track record and diversified across
geography and ticket size, and strategic linkages with the parent firm.
'A+' rating means the rating agency expects the commercial paper to have
adequate degree of safety regarding timely servicing of financial obligations.
The purpose of the commercial paper is to refinance the company's existing
borrowings.
51
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
CONCLUSION
Short-term interest rate environment, credit rating and market
liquidity condition play an influential role in the Indian CP market
activity The empirical finding shows that CP issuance yield
depends on varying credit quality across the CPs issuers and
prevailing market liquidity. The short term risk premia also affect
CP issuances activity depending on spread between T-Bill yield and
CPs issuance rates. A rise in risk premia limits debt-paying capacity
of the company and hence compresses the market growth in CP
segment on account of rise in default probability. Credit rating and
market liquidity condition are the most persuading factors in CPs
market dynamics. Comfortable market liquidity makes availability
of funds easy in the open market at lower borrowing costs and
hence corporates prefer CPs route for borrowing their working
capital and vice versa. At present, Indian commercial paper market
is still in its nascent stage of evolution in terms of borrowing
activity.
52
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
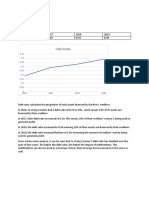
CP Issuances Business-wise Share (%) Profile
4
38
96
Non Financial
Financial
11
20
89
63
22
78
15
42
85
58
80
45
55
63
38
The business-wise CPs issuance profile points out a structural
change from non-financial companies - especially in power
generation, manufacturing, and automobile to financial (services)
companies. The plot shows a sharp decrease in NBFCs' share from
96% of total issuances to 24% in 2013-14. During the same period,
the share of financial (services) companies grew to 76% in 2013-14
from a meager 4% in 2004-05. Most of the financial companies are
either captive (subsidiaries of manufacturers) - or bank-related
financial companies - who are mostly dealing in equity market,
currency market and consumer financing space. However, taking an
analytical view, it is not a good signal for the Indian economy,
where financial/leasing companies are raising funds in the CP
market and investing in capital market mainly in the equity market
for arbitrage profiting which impedes the very basic purpose of
the CP market. Investigating the growth pattern of the Indian
commercial paper market, the paper finds that surplus domestic
liquidity and huge capital inflows during global financial crisis are
major catalysts for impressive growth in the CP market. The sharp
53
76
73
24
27
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
cut in policy rate along with huge liquidity injection by the RBI led
to surplus mode of liquidity in the market which prompted CP
issuers to borrow directly from the market due to easy accessibility
of funds at lower costs compared to higher bank lending rate. On
other end, investors were getting better shortterm return by parking
their funds in the CP market than LAF reverse repo window with
the RBI. This was the first time when the CPs issuers in India
tasted the benefits of taking the CP issuance route for meeting their
financing requirements. The average mid-issuance rate for CPs
during last six years hovered around the upper band of policy rate
corridor signaling natural preference of corporate borrowers for
CPs over bank credit which costs them additional 2% - 4% over the
bank rate depending on their credit rating.
There is need for further studies to carry out similar study for a
longer time period. This would allow better generalizations across
the board for similar CP issues. A similar study should also be
carried out on relationship between firms performance and
Treasury bills and commercial paper performance in India.
Comparable studies should also be carried-out to establish the
effect on commercial paper yield by other short term debt
instruments like bank overdrafts or even long term debt instruments
like corporate bonds in India.
Equivalently, studies on how other key factors bear effect on
commercial paper should be conducted to establish their extent, for
instance there is need to establish how Central Bank Rate, bank
interest rates and inflation levels influence commercial paper yield.
The commercial paper market has long been viewed as a bastion of
high liquidity and low risk. But twice during the financial crisis of
54
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
20082009, the commercial paper market nearly dried up and
ceased being perceived as a safe haven. Major interventions by the
Federal Reserve, including large outright purchases of commercial
paper, were eventually used to support both issuers of and investors
in commercial paper. Even though the commercial paper market
has experienced disruptions in the past, the financial crisis of 2008
2009 was by far the largest decline in the commercial paper market,
and in contrast to previous turbulent episodes, it mostly affected
commercial paper issued by financial institutions. This crisis has
also shown that the Federal Reserve is likely to respond
aggressively to such a sudden decline of the commercial paper
market. In fact, the scale of the Federal Reserves response was
unprecedentedincluding a blanket guarantee of money market
investment
worth $3 trillion and direct purchases of commercial paper of up to
$370 billion.
Such large-scale market interventions raise concerns about future
moral hazard of commercial paper issuers, independent of whether
these guarantees will remain implicit or not. Financial regulation
will need to address the negative incentives generated by the
expectation of future government interventions, either by directly
regulating the risk of commercial paper issuers or by charging
issuers or investors for the insurance provided by the government.
I CONCLUDE
Commercial paper is an important money market security. By making
this project I learn about the features, advantages and disadvantages
of the commercial paper. The main point is that
55
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
It is usually issued by reputed companies
It is done for meeting urgent short term needs
The usual period to issue is 180 days.
It is always sold at discount and is redeemable at its face value
The maturity period is from 3 to 6 months
Minimum size of commercial paper is 25 lacs.
It provides the exit option to the investors to quit the investment.
It is quick and cost effective way of raising working capital.
Studying commercial paper I come to know about how big companies
meet their capital needs.
References:
Acharya, Viral, and Philipp Schnabl.
Downing,2009.
Chris, and Stephen Oliner. 2007.The
Term Structure of Commercial Paper Rates.
Do Global Banks Spread GlobalJournal
Imbalances?
The
Case of 83(1):
Assetof Financial
Economics,
5986.
Fabozzi, Frank, and Steven Mann. 2005. The
Backed Commercial Paper duringHandbook
the Financial
200709.
of FixedCrisis
Income of
Securities.
McGrawHill Professionals.
http://imf.org/external/np/res/seminars/2009/arc/pdf/acharya.pdf.
Acharya, Viral ,
Philipp Schnabl,
Gustav o Suarez.
Securitization
without Risk
Books:Advance financial
arrangement By Dr. M.A.
Kohok (Page No. 40 to
46)Financial Market &
Instruments Journal:Source : (http://www.scribd.com/)
http://www.scribd.com/doc/95
823767/Commercial-Papers
56
and
2009.
Project report for- Commercial paper as
a money market instrument-2015-2016
Transfer.http://www.richmondfed.org/conferences_and_events/research/2
009/pdf/suarez_paper.pdf.
Akerlof, George. 1970. The Market for Lemons Quality
Uncertainty and the Market
. 1995
57
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Study of Government SecuritiesDokument37 SeitenStudy of Government Securitiesswapnil2288Noch keine Bewertungen
- Securitization of Assets File 2Dokument24 SeitenSecuritization of Assets File 2khush preet100% (1)
- RBI Act 1934 NDokument42 SeitenRBI Act 1934 NRohit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documentos Comerciales en InglesDokument46 SeitenDocumentos Comerciales en InglesMiguel100% (3)
- Mercial PaperDokument39 SeitenMercial PaperArjun Khunt100% (1)
- Commercial PaperDokument12 SeitenCommercial Paperjaideep92naikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial PaperDokument6 SeitenCommercial PapervmktptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debt MarketDokument104 SeitenDebt MarketOmkar Rohekar100% (1)
- SecuritizationDokument39 SeitenSecuritizationSakshi GuravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depository SystemDokument38 SeitenDepository SystemTarun SehgalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial Paper: (Industrial Paper, Finance Paper, Corporate Paper)Dokument27 SeitenCommercial Paper: (Industrial Paper, Finance Paper, Corporate Paper)shivakumar N100% (1)
- Project On Commercial PaperDokument23 SeitenProject On Commercial PaperSuryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commercial PaperDokument20 SeitenCommercial PaperHarsh TharianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Act, 1938Dokument101 SeitenInsurance Act, 1938dodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation For Commercial Paper 2019Dokument14 SeitenPresentation For Commercial Paper 2019Shahmeer Waqar Malik50% (2)
- Currency ConvertibilityDokument37 SeitenCurrency Convertibilitylavkush_khannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Deposits Offered by BanksDokument6 SeitenTypes of Deposits Offered by Banksfarhana nasreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foreign Remittance of DBBLDokument57 SeitenForeign Remittance of DBBLtariqul21100% (1)
- Commercial Bills MaktDokument18 SeitenCommercial Bills MaktHaresh Kansara100% (1)
- Project by BrincyDokument64 SeitenProject by BrincyJeeva VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRM in Private BanksDokument27 SeitenCRM in Private BanksManuKingKaushik67% (3)
- Merchant BankingDokument86 SeitenMerchant Bankingmehroze0% (1)
- Private Sector BanksDokument3 SeitenPrivate Sector BanksBalaji GajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Debt MarketDokument32 SeitenIndian Debt MarketProfessorAsim Kumar Mishra0% (1)
- Relationship Between Banker and CustomerDokument10 SeitenRelationship Between Banker and Customerswagat098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Financial InclusionDokument42 SeitenIntroduction To Financial InclusionshreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP 5 Acceptance of Deposits-UnlockedDokument38 SeitenCP 5 Acceptance of Deposits-UnlockedKarthik Imperious100% (1)
- Banker and CustomerDokument23 SeitenBanker and CustomerAnkan Pattanayak100% (1)
- ChapterDokument78 SeitenChaptershaannivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deposit IntroductionDokument6 SeitenDeposit Introductionmohomed100% (2)
- Presentation On Financial InstrumentsDokument20 SeitenPresentation On Financial InstrumentsMehak BhallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merchant BankingDokument27 SeitenMerchant Bankingapi-3865133100% (13)
- Revocable Letter of Credit Can Be Revoked Without The Consent of TheDokument3 SeitenRevocable Letter of Credit Can Be Revoked Without The Consent of ThePankaj ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BankingDokument168 SeitenBankingVaishnav Kumar100% (1)
- Credit Markets1Dokument45 SeitenCredit Markets1David Raju GollapudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yes BankDokument24 SeitenYes Banktrisanka banikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debt SecuritizationDokument20 SeitenDebt SecuritizationSandeep KulshresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Fund FlowDokument11 SeitenSynopsis Fund FlowBala SudhakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Consumer Loan Services System of IDLCDokument51 SeitenReport On Consumer Loan Services System of IDLCisraatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bankers Book Evidence Act 1891 - PPT - 11.4.2020Dokument52 SeitenBankers Book Evidence Act 1891 - PPT - 11.4.2020Rajamohan MuthusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Banking LatestDokument189 SeitenUniversal Banking LatestSony Bhagchandani50% (2)
- A Study On Various Deposit Schemes, Retail Banking and Internet Banking With Reference To Syndicate BankDokument67 SeitenA Study On Various Deposit Schemes, Retail Banking and Internet Banking With Reference To Syndicate BanklalsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFPB ManualDokument171 SeitenCFPB ManualveereshchiremathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project For Print Out of Fullerton IndiaDokument51 SeitenFinal Project For Print Out of Fullerton IndiaVinay Bairagi100% (1)
- Bill DiscountingDokument21 SeitenBill DiscountingsrinaathmNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICICI Vehical LoanDokument49 SeitenICICI Vehical Loanjagdish80% (5)
- Introduction To Commercial PaperDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Commercial PaperBhoomi AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debenture and BondDokument7 SeitenDebenture and BondPiesie AmponsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury ManagementDokument10 SeitenTreasury Managementrakeshrakesh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Loan NewDokument8 SeitenConsumer Loan NewDave3818Noch keine Bewertungen
- Negotiable InstrumentsDokument11 SeitenNegotiable InstrumentsMahesh ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer FinanceDokument36 SeitenConsumer FinanceAditya0% (1)
- Prospectus TypesDokument2 SeitenProspectus Typesarti guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Regulation and Deposit InsuranceDokument7 SeitenBank Regulation and Deposit InsuranceZainur NadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Retail BankingDokument3 SeitenAssignment Retail BankingSNEHA MARIYAM VARGHESE SIM 16-18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Depository SystemDokument33 SeitenDepository SystemjasminalkaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking MaterialDokument87 SeitenBanking Materialmuttu&moonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government Securities MarketDokument11 SeitenGovernment Securities MarketVikasDalal100% (2)
- International Liquidity & International ReservesDokument17 SeitenInternational Liquidity & International ReservesPrabu ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Operations In Turkey and Contemporary Sovereign Treasury ManagementVon EverandTreasury Operations In Turkey and Contemporary Sovereign Treasury ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constitution of the State of Minnesota — 1876 VersionVon EverandConstitution of the State of Minnesota — 1876 VersionNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDS Certificate PDFDokument2 SeitenTDS Certificate PDFSoumyabrata BhattacharyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application FormDokument5 SeitenApplication FormJagadeesh SuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 7Dokument27 SeitenChap 7Joanne Chau100% (1)
- Ulep - Uneven Cash PaymentsDokument4 SeitenUlep - Uneven Cash PaymentsNoel BajadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relic Spotter Inc. CaseDokument9 SeitenRelic Spotter Inc. CaseC DonisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Information Technology (It) On Banking Sector: Madhushree L. M., Revathi Radhakrishnan, & P. S. AithalDokument8 SeitenImpact of Information Technology (It) On Banking Sector: Madhushree L. M., Revathi Radhakrishnan, & P. S. Aithaltushar vatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narasimham Committee ReportDokument4 SeitenNarasimham Committee ReportSumit MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- There Are 10 Principals That Form The Foundation of Financial ManagementDokument6 SeitenThere Are 10 Principals That Form The Foundation of Financial ManagementRoopini RavindranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Income TaxDokument15 SeitenIncome TaxZayed Mohammad JohnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz - iCPA PDFDokument14 SeitenQuiz - iCPA PDFCharlotte Canabang AmmadangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bitcoin - Review of LiteratureDokument27 SeitenBitcoin - Review of LiteratureNeha ChhabdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Personal FinanceDokument39 SeitenManaging Personal FinanceBeverly EroyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 2Dokument3 SeitenDocument 2Un Konown Do'erNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leases - Practice QuestionsDokument18 SeitenLeases - Practice Questionsosama saleemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial AccountingDokument103 SeitenFinancial AccountingDaniel HunksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fu Wang Ceramic Debt Management RatioDokument4 SeitenFu Wang Ceramic Debt Management RatioMd Abil KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Android Hacker-S HandbookDokument2 SeitenAndroid Hacker-S HandbookJack LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interest Rate Derivatives Beginners ModuleDokument70 SeitenInterest Rate Derivatives Beginners ModuleKarthick100% (1)
- Uncle Eric Books Lesson PlansDokument6 SeitenUncle Eric Books Lesson PlansMelanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniwersytet Jagielloński Jagiellońskie Centrum JęzykoweDokument9 SeitenUniwersytet Jagielloński Jagiellońskie Centrum JęzykoweVân TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Penghitungan Pajak PenghasilanDokument13 SeitenContoh Penghitungan Pajak PenghasilantorangsiagianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monthly Summary of Mortgage Activities For The Period Ending April 2019Dokument17 SeitenMonthly Summary of Mortgage Activities For The Period Ending April 2019Nico Gillo ObejeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch23 Statement of Cash FlowsDokument90 Seitench23 Statement of Cash FlowsIma ListyaningrumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 581616893-BMO-Bank-Statement-Tina Vennessa MullinsDokument3 Seiten581616893-BMO-Bank-Statement-Tina Vennessa MullinsAlex NeziNoch keine Bewertungen
- RE 01 03 Office Acquisition Case StudyDokument3 SeitenRE 01 03 Office Acquisition Case StudyAnonymous bf1cFDuepPNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOFM - Assignment 1: Instruction: Last Date of Submission of Assignment Is 31 March 2015Dokument2 SeitenFOFM - Assignment 1: Instruction: Last Date of Submission of Assignment Is 31 March 2015Shekhar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOREX Practical - Assign - 1 - 2020Dokument5 SeitenFOREX Practical - Assign - 1 - 2020prideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Financial StatementsDokument36 SeitenUnderstanding Financial StatementsDurga PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept - Note - Implementation - of - RuPay - qSPARC - Based - NCMC v2.1Dokument43 SeitenConcept - Note - Implementation - of - RuPay - qSPARC - Based - NCMC v2.1Luiz Fernando Galdino DubielaNoch keine Bewertungen