Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Module 4
Hochgeladen von
api-291246438Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Module 4
Hochgeladen von
api-291246438Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
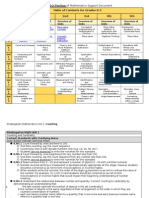
Grade 3, Module 4
Core Focus
Reading and writing four-digit numbers
Locating four-digit numbers on a number line, working with place value, comparing,
and ordering
Reviewing fraction concepts using the area model
Writing fractions as words, common fractions, and relating fraction words and symbols
Numbers in Base-Ten
Once base-10 place value is understood for numbers up to several hundreds,
students know just about everything necessary to work with large numbers.
In this module, students extend their understanding of one-, two-, and three-digit
numbers to four-digit numbers.
4.5
Read house numbers,
videogame scores or highway
signs to practice saying threeand four-digit numbers.
Reinforce place-value
language by asking, How
many thousands, hundreds,
tens, and ones?
Working with Place Value of Four-Digit Numbers
How many blocks are in each
place of this number picture?
When possible, demonstrate
how amounts are written out
in words.
Write the number on this expander.
How do you read
the number?
In this lesson, students use base-10 blocks and numeral expanders to increase
or decrease numbers by 10 or 100.
Essential base-10 concepts are practiced by locating numbers on a number line;
comparing and ordering numbers; and working with place value using mathematical
language: thousands, hundreds, tens and ones.
4.6
Ideas for Home
If four-digit numbers seem
easy for your child, nd larger
numbers millions, billions, or
even trillions e.g. by looking
for and reading how many
hits a website has received.
Glossary
A place-value chart is used to
record large quantities in their
place values.
Comparing and Ordering Four-Digit Numbers
How can you figure out which number is greater?
Th
Which place would you look at first to mark the numbers on this number line?
2,000
3,000
ORIGO Education.
In this lesson, students use a number line and place-value strategy to
compare and order four-digit numbers.
Ones
A numeral expander
shows how each position
in a number represents a
designated place value.
6
1
120815
Grade 3, Module 4
Fractions
Fractions are often challenging for students, but they are very important in daily life
and they provide essential understanding for later work with decimals, algebra, and
other advanced mathematics.
In Grades K2, students explored their understanding of one-half, one-third, and
one-fourth in sets of objects and in geometric shapes. This module includes a
fraction review using sets of objects.
4.8
Ideas for Home
Notice fractions in
kitchen measures, e.g.
1
Compare a 2 cup our to a
whole cup; 41 tablespoon to
1 tablespoon, etc.
Look at an analog clock
together and notice the
half, (30 minutes), quarter
(15 minutes), and third
(20 minutes).
Reviewing Fractions
Luis borrowed 6 books from the library.
One-half of them were adventure stories.
What does one-half mean?
How many of the books were adventure stories?
Glossary
One-third of the books were about
science experiments.
What does one-third mean?
How many of the books were about
science experiments?
The bottom number of a
fraction is the denominator,
the total number of equal
parts in the whole.
A fraction is a number that
describes an amount that has
been split into equal parts.
What special name is used for numbers
like one-half and one-third?
In this lesson, students review the naming of fractions.
As in Grades 1 and 2, the area model continues to represent the fractions
by naming the relationship between the shaded area and the total area.
The top number is the
numerator, the count of equal
parts considered.
parts of
equal parts
4.11
The dark gray shows 4 parts
out of 6 equal parts.
Writing Common Fractions
Trina is covering a rectangle
with pattern blocks.
The same fractional amount
can look dierent. Ask your
child why all of the shaded
areas below equal . (In an
area model, the equal shaded
portions of the region count
as the fractional amount,
not the number of pieces.
What fraction of the rectangle has she covered so far?
Write a numeral to show the number
of parts that are covered and a numeral
to show the number of equal parts.
parts of
equal parts
The numeral on the top is called the numerator.
The numeral on the bottom is called the denominator.
In this lesson, students write common fractions using numbers.Three shaded
parts out of eight equal parts is written 3 .
ORIGO Education.
In Grade 3, fraction models extend beyond area models to number lines and are
described using numeric symbols. The number line will be introduced to represent
relative position of fractions in future modules.
2
120815
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 6 Standard MathDokument96 Seiten6 Standard Mathtaaniakhan11100% (1)
- Chapter 12 PracticeDokument96 SeitenChapter 12 PracticeDavid VundiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Maths Primary School NSWDokument37 SeitenSyllabus For Maths Primary School NSWexhaustedcactusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Module 3Dokument502 SeitenMath Module 3peppylepepper50% (2)
- Fractions UnitDokument6 SeitenFractions Unitapi-284232017100% (1)
- Math Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeVon EverandMath Fluency Activities for K–2 Teachers: Fun Classroom Games That Teach Basic Math Facts, Promote Number Sense, and Create Engaging and Meaningful PracticeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Parent Tip SheetDokument2 SeitenEureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Parent Tip Sheetapi-326893495Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 t1 Unit 1Dokument5 SeitenYear 5 t1 Unit 1api-267136654Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Multiplication and Division Practice - Ages 8-11’ eBookVon EverandElementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Multiplication and Division Practice - Ages 8-11’ eBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.place Value Routine 4th Grade Lesson PlanDokument3 Seiten4.place Value Routine 4th Grade Lesson PlanNessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Programming Bolwarra Ps - Year 5Dokument54 SeitenMaths Programming Bolwarra Ps - Year 5api-267136654Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Program Proforma Yr 3 T2 - S TOONEYDokument36 SeitenMaths Program Proforma Yr 3 T2 - S TOONEYS TANCRED100% (3)
- Grade 4 Unit Map 4Dokument10 SeitenGrade 4 Unit Map 4api-264363149Noch keine Bewertungen
- Primary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) – Maths - Publications Guide – Ages 5-7’ eBookVon EverandPrimary School ‘KS1 (Key Stage 1) – Maths - Publications Guide – Ages 5-7’ eBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 t1 Unit 6Dokument10 SeitenYear 5 t1 Unit 6api-267136654Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths the Wacky Way for Students...By a Student: From Foundation up to Higher Level GcseVon EverandMaths the Wacky Way for Students...By a Student: From Foundation up to Higher Level GcseNoch keine Bewertungen
- T 60Dokument2 SeitenT 60Sharyn RynNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 3 4samplcominedacadem13Dokument4 Seiten2 3 4samplcominedacadem13mian zeeshan ullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 Parent TipsDokument2 SeitenModule 6 Parent Tipsapi-298601310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Parentguide Math 5Dokument6 SeitenParentguide Math 5api-255198155Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: DecimalsDokument5 SeitenMathematics: DecimalsKashishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numeracy PlannerDokument17 SeitenNumeracy Plannerapi-298019214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Program Proforma Yr 4 T2-S TOONEYDokument43 SeitenMaths Program Proforma Yr 4 T2-S TOONEYS TANCREDNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractionsunitDokument5 SeitenFractionsunitapi-222745762Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3, Module 1: 1 Ten 5 Ones 3 Hundreds 6 Ones 7 Hundreds 3 TensDokument2 SeitenGrade 3, Module 1: 1 Ten 5 Ones 3 Hundreds 6 Ones 7 Hundreds 3 Tensapi-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Program Profrma S1 Yr1 T2-S TooneyDokument31 SeitenMaths Program Profrma S1 Yr1 T2-S TooneyS TANCREDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Topic: Place Value, Fractions & Decimals Subject(s) : Math Grade(s) : 4 Designer(s) Samantha Miller Understanding by DesignDokument12 SeitenDesign Topic: Place Value, Fractions & Decimals Subject(s) : Math Grade(s) : 4 Designer(s) Samantha Miller Understanding by Designapi-369706033Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Enhancement Program On Mathematics 2018 - Elementary LevelDokument23 SeitenSummer Enhancement Program On Mathematics 2018 - Elementary LevelAnthony Feraer Balatar Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 4 - ESC 14Dokument5 SeitenActivity 4 - ESC 14Elvira CuestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Program Proforma Yr 2 t1Dokument27 SeitenMathematics Program Proforma Yr 2 t1S TANCRED100% (2)
- g4 m1 Full ModuleDokument256 Seiteng4 m1 Full ModuleKe HebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2Dokument6 SeitenWeek 2Ritah NantezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- G3-M4-Ta VfinalnewsletterDokument1 SeiteG3-M4-Ta Vfinalnewsletterapi-261399250Noch keine Bewertungen
- Observation 3 Math Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenObservation 3 Math Lesson Planapi-336922068Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 4Dokument2 SeitenMod 4api-268594130Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Program s2 Yr4 t1Dokument35 SeitenMaths Program s2 Yr4 t1S TANCREDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Program s3 Yr 6 t1Dokument37 SeitenMaths Program s3 Yr 6 t1S TANCREDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Program Proforma S1 Yr 2T2-S TOONEY 2Dokument32 SeitenMaths Program Proforma S1 Yr 2T2-S TOONEY 2S TANCRED100% (3)
- Maths Program Profrma s1 Yr1 t2Dokument31 SeitenMaths Program Profrma s1 Yr1 t2api-237136245Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bridges 3rd Grade Unit 4Dokument2 SeitenBridges 3rd Grade Unit 4api-289263859Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Eed6Dokument22 SeitenModule 2 Eed6Laika EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Eed9Dokument22 SeitenModule 1 Eed9Laika EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Unit PlanDokument6 SeitenMini Unit Planapi-636515442Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Fractions: Name: Tom Blanchard Grade Level Learning Objective(s)Dokument4 SeitenComparing Fractions: Name: Tom Blanchard Grade Level Learning Objective(s)api-285360604Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Chapter/Title:: Smallest Greatest 1-Digit 0 9 2-Digit 10 99 3-Digit 100 999 4-Digit 1,000 9,999Dokument2 SeitenUnit Chapter/Title:: Smallest Greatest 1-Digit 0 9 2-Digit 10 99 3-Digit 100 999 4-Digit 1,000 9,999Mallika Bekal VijeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGDokument8 SeitenEdtpa Lesson Plan Guide LPGapi-679722171Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Mapping AssignmentDokument4 SeitenCurriculum Mapping Assignmentapi-487823106Noch keine Bewertungen
- Numeration-Rational Numbers Math 4 Alston: Design Topic Subject(s) Grade(s) Designer(s) Understanding by DesignDokument4 SeitenNumeration-Rational Numbers Math 4 Alston: Design Topic Subject(s) Grade(s) Designer(s) Understanding by Designapi-282674907Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Parent TipsDokument2 SeitenModule 1 Parent Tipsapi-298601310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unitplank12 IhernandezDokument8 SeitenUnitplank12 Ihernandezapi-378876175Noch keine Bewertungen
- Division - Lesson 1Dokument4 SeitenDivision - Lesson 1magicklaxonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Program Proforma Es1 t1Dokument20 SeitenMathematics Program Proforma Es1 t1S TANCRED100% (3)
- Math LP Dec 8-12, 2014Dokument10 SeitenMath LP Dec 8-12, 2014Tasia Starling ScruggsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Food Is For SharingDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan Food Is For Sharingapi-284493101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Te 801 Project 2Dokument13 SeitenTe 801 Project 2api-404347657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daughtry Leslie Lesson-Plan-1q7ta8uDokument7 SeitenDaughtry Leslie Lesson-Plan-1q7ta8uAkayo BeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan FractionsDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan FractionsJonathan RobinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- k-2 Support Document - Word - 2Dokument74 Seitenk-2 Support Document - Word - 2api-290854496100% (1)
- Shonna Roberts Math 5e Lesson Plan FinalDokument4 SeitenShonna Roberts Math 5e Lesson Plan Finalapi-549210273Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Publications Guide - Ages 8-11’ eBookVon EverandElementary School ‘Grades 3, 4 & 5: Math – Publications Guide - Ages 8-11’ eBookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 9Dokument2 SeitenMod 9api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 7Dokument2 SeitenMod 7api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- CostumeguidelinesDokument1 SeiteCostumeguidelinesapi-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 8Dokument2 SeitenMod 8api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5Dokument2 SeitenModule 5api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6Dokument2 SeitenModule 6api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- ScheduleDokument1 SeiteScheduleapi-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3Dokument2 SeitenModule 3api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 3, Module 1: 1 Ten 5 Ones 3 Hundreds 6 Ones 7 Hundreds 3 TensDokument2 SeitenGrade 3, Module 1: 1 Ten 5 Ones 3 Hundreds 6 Ones 7 Hundreds 3 Tensapi-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument2 SeitenModule 2api-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Economy RulesDokument2 SeitenClassroom Economy Rulesapi-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class EconomyDokument2 SeitenClass Economyapi-291246438Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Mid Term Exam InstructionsDokument1 SeiteCBSE Mid Term Exam InstructionsSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Readiness ChecklistDokument2 SeitenClassroom Readiness ChecklistRonan-Gayle Monserate MarcialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Teacher SurveyDokument3 SeitenMath Teacher Surveyapi-465284190Noch keine Bewertungen
- AO1.2 - Poster EssayDokument5 SeitenAO1.2 - Poster EssayHeart EspineliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edte301 FrameofreferenceDokument3 SeitenEdte301 Frameofreferenceapi-344542334Noch keine Bewertungen
- English - Intervention Remediation Plan For The Identified Learning GapsDokument5 SeitenEnglish - Intervention Remediation Plan For The Identified Learning GapsArtbie A. SamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agnes GreyDokument165 SeitenAgnes GreyLaura Elena ApetroaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengembangan Modul Pendidikan Seks Untuk Anak Usia Dini (4-6 TAHUN)Dokument9 SeitenPengembangan Modul Pendidikan Seks Untuk Anak Usia Dini (4-6 TAHUN)Novianti PuspitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psumt Newsletter FallDokument3 SeitenPsumt Newsletter Fallapi-251592269Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/12 February/March 2022Dokument17 SeitenCambridge International AS Level: English General Paper 8021/12 February/March 2022shwetarameshiyer7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Passed 5104 13 21MELCS Baguio Roles of Theater EdtDokument89 SeitenPassed 5104 13 21MELCS Baguio Roles of Theater EdtChristopher David OlivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plenaristas León 2022xDokument6 SeitenPlenaristas León 2022xGloria MontielNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lincoln University: International Graduate Admission Application and Acceptance InformationDokument7 SeitenThe Lincoln University: International Graduate Admission Application and Acceptance Informationapi-281064364Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae: EducationDokument3 SeitenCurriculum Vitae: EducationSomSreyTouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.4 Sample Trust DeedDokument13 Seiten5.4 Sample Trust DeedSunil Kumar100% (3)
- CENTRE FOR TEACHING EXCELLENCE Self-Directed Learning A Four-Step ProcessDokument4 SeitenCENTRE FOR TEACHING EXCELLENCE Self-Directed Learning A Four-Step ProcessDRADRIGA PATRICKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/12 October/November 2021Dokument3 SeitenCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/12 October/November 2021For Gaming0% (1)
- MFR Assignment 3 Front SheetdDokument8 SeitenMFR Assignment 3 Front SheetdSyed Imam BakharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jared M. Hansen: 1803 Anna ST Bellevue, NE 68005 Phone: C: (402) 709-1615 H: (402) 293-1565Dokument2 SeitenJared M. Hansen: 1803 Anna ST Bellevue, NE 68005 Phone: C: (402) 709-1615 H: (402) 293-1565dcfan402Noch keine Bewertungen
- QF EheaDokument200 SeitenQF Eheajose_dias_58Noch keine Bewertungen
- Website Cover LetterDokument1 SeiteWebsite Cover Letterapi-488518650Noch keine Bewertungen
- TCS PassagesDokument91 SeitenTCS PassagesRachanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011-12 Handbook For WebsiteDokument56 Seiten2011-12 Handbook For WebsiteIresh VelanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theories of Congruent Communication by Haim GinottDokument11 SeitenTheories of Congruent Communication by Haim GinottAdam AriffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof R Krishna Report On Credit Related Issues Under SGSYDokument135 SeitenProf R Krishna Report On Credit Related Issues Under SGSYRakesh ChutiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specimen Copy of Answer BookDokument2 SeitenSpecimen Copy of Answer BookMegha SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optional Exams 2019-20: Smt. Sulochanadevi Singhania SchoolDokument1 SeiteOptional Exams 2019-20: Smt. Sulochanadevi Singhania SchoolRamanand YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Math GAS Daily Lesson LogDokument5 SeitenGen Math GAS Daily Lesson Logjun del rosario100% (2)