Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
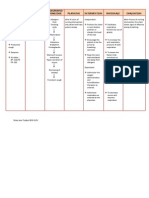
Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Evaluation
Hochgeladen von
Jay Depakakibo GallardoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Evaluation
Hochgeladen von
Jay Depakakibo GallardoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing
Diagnosis
Impaired Gas
Exchange secondary
to ventilation and
perfusion inequality;
Related to retained
secretions as
Evidence by
Tachycardia,
Tachypnea, crackles,
wheezing and
cyanosis.
Objectives
Short Term:
Nursing Diagnosis
Rationale
Evaluation
Independent:
Short Term:
Within 15 mins of
duty, Difficulty of
breathing will be
lessened.
Long Term:
After 1 day of
Nursing
Intervention pt.
Will demonstrate
improvement in
ventilation and
adequate
oxygenation within
Normal limits and
having absence
symptoms of
respiratory Distress
Elevate the head of the
bed 45 degrees or Semi
fowlers position.
It maximized lung
expansion thus sustain
open Airway
Advised patient to keep
calm During the
episodes of breathing
difficulty
To prevent aggravating
of the disease.
Encouraged deep
controlled breathing
exercise.
It promotes optimal
chest expansion.
Dependent:
Low Flow O2 inhalation
via Nasal Cannula as
ordered by Physician.
Administer Nebulizer as
Ordered by Physician
Administer AntiInflammatory agents as
ordered.
To Promote the O2
need of the patient.
(Giving of High Flow O2
may remove the
Hypoxic Drive- leading
to Increased
Hypoventilation,
Respiratory
Decompression and
worsening the
Respiratory Acidosis.
It Smoothen Smooth
Muscles cells of the
respiratory tract
causing smooth muscle
relaxation.
Patient Verbalized
Medyo naka ginhawa na
ako
Goal Partially Met.
Long Term:
Patient demonstrate
improvement in
ventilation and
adequate oxygenation
within Normal Limits
and absence symptoms
of respiratory Distress.
Decreased use of
Accessory Muscles
when Breathing,
absence of Nasal
Flaring, and Decreased
Respiratory Rate.
These are used to
suppressed airway
inflammation and
reduce asthma
symptoms. It blocks
late response to inhaled
allergens and reduce
Bronchial Hyper
responsiveness.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Nursing Care Plan: COPDDokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan: COPDneuronurse88% (32)
- Nursing Care Plan - CAP-MRDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan - CAP-MRCarmela Mabel Ansay Principe100% (3)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenAsthma Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis92% (24)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDokument79 SeitenChest PhysiotherapyRabab Ahmed100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument1 SeiteNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceImation DataNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument11 SeitenNCPRyan Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanCamille Serrano100% (1)
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Nyimas FatimahDokument61 SeitenPulmonary Rehabilitation: Nyimas FatimahNur akilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BronchiectasisDokument40 SeitenBronchiectasisyana jaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Basic Concept of Emergency Nursing Nursing With Case of FailureDokument5 SeitenNursing Care Basic Concept of Emergency Nursing Nursing With Case of Failurejamil aldasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteCues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationemrithNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Kochs2Dokument2 SeitenNCP Kochs2Ava VierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument22 SeitenImpaired Gas ExchangecheenapberberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Disease and AnaesthesiaDokument8 SeitenRespiratory Disease and AnaesthesiaReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pleural Effusion NCPsDokument7 SeitenPleural Effusion NCPsJaja Nagallo100% (2)
- Decreased Lung Compliance (Dispensability) Associated With Pleural Effusion and Accumulation of Fluid in The Pulmonary Interstitium and AlveoliDokument2 SeitenDecreased Lung Compliance (Dispensability) Associated With Pleural Effusion and Accumulation of Fluid in The Pulmonary Interstitium and AlveoliSatra SabbuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodmarc Corpuz BaranganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDokument8 Seiten1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bronchitis Nursing Care PlanDokument8 SeitenBronchitis Nursing Care PlanBryan NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PneumoniaDokument12 SeitenPneumoniaRola Miranda Guiang-ManaliliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNEUMONIADokument24 SeitenPNEUMONIAwheeyycoldandhot55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ncp'sDokument8 SeitenNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiotherapy Management in Icu Patients: Dr.S.Ramachandran MPTDokument37 SeitenPhysiotherapy Management in Icu Patients: Dr.S.Ramachandran MPTvaishnaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 118 SDL#1 - Orcullo 4NFDokument5 SeitenNCM 118 SDL#1 - Orcullo 4NFGerelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP CopdDokument2 SeitenNCP CopdJane Umali TulabotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implemented Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues: Goal: Goal Partially MetDokument3 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implemented Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues: Goal: Goal Partially MetzysheaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDokument2 SeitenNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument8 Seiten1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceEsel Mae DinamlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeDokument2 SeitenNCP Ineffective Gas ExchangeRez ApegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tolleno (Pneumonia ER)Dokument4 SeitenTolleno (Pneumonia ER)Hannah TollenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenTuberculosis Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceCyrus De Asis86% (36)
- © 2009 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All World Rights ReservedDokument24 Seiten© 2009 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. All World Rights Reservedachsan tudhonnnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP SDokument8 SeitenNCP SMarvie CadenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alteration in OxygenDokument8 SeitenAlteration in OxygenBb RabbitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competencymr McdougalcopdDokument17 SeitenCompetencymr Mcdougalcopdmac_rymrt7569Noch keine Bewertungen
- Obstructive DisordersDokument23 SeitenObstructive DisordersMartha ChaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary Physical Therapy RevDokument11 SeitenPulmonary Physical Therapy Revpearl042008100% (2)
- AssessmentDokument2 SeitenAssessmentJim StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP TBDokument6 SeitenNCP TBGrhace Aquino100% (3)
- PT in ICUDokument38 SeitenPT in ICUArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPEugine Elizabeth Pilarca PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Chapter 20 (Oct 16th)Dokument2 SeitenCase Study Chapter 20 (Oct 16th)Anz MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Assignment ON: Bronchial HygieneDokument12 SeitenAn Assignment ON: Bronchial Hygienesoniya joseph100% (1)
- 13.acute Respiratory FailureDokument34 Seiten13.acute Respiratory Failurekarim hassan100% (1)
- Case Pres - PneumoniaDokument39 SeitenCase Pres - Pneumoniafortunelobster100% (1)
- Region 1 Medical Center: Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Planning / Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenRegion 1 Medical Center: Assesment Nursing Diagnosis Planning / Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationGlaiza Mae MasaoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For PneumoniaDokument3 SeitenNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- Nursing ManagementDokument4 SeitenNursing ManagementjeponieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For PneumoniaDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan For PneumoniaJonas Galeos100% (2)
- Chest TraumaDokument5 SeitenChest TraumaRyrey Abraham PacamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing ManagementDokument16 SeitenNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch50 NCP IneffAirClear 1395-1396Dokument2 SeitenCh50 NCP IneffAirClear 1395-1396Caress Mae Gubaton CabudoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument9 SeitenNCPEjie Boy Isaga67% (3)
- Case Study COPDDokument6 SeitenCase Study COPDpallavNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Baby DDokument3 SeitenNCP Baby DYna LafuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseVon EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandAspiration Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- COPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanVon EverandCOPD Diet: A Beginner's 3-Week Step-by-Step Guide to Managing COPD Symptoms, With Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 058 Registered Nurse MED LES 9 1Dokument8 Seiten058 Registered Nurse MED LES 9 1Jay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument20 SeitenNursing Care PlanZamranosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Additives Essay PDFDokument2 SeitenFood Additives Essay PDFJay Depakakibo Gallardo100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Diagnosis Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Diagnosis Rationale EvaluationJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRAND NAME: Prilosec, Zegerid: GENERIC NAME: Omeprazole, Omeprazole/sodium BicarbonateDokument2 SeitenBRAND NAME: Prilosec, Zegerid: GENERIC NAME: Omeprazole, Omeprazole/sodium BicarbonateJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program DescriptionDokument15 SeitenProgram DescriptionJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Following Formulas Need To BeDokument10 SeitenThe Following Formulas Need To BeJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Registrants Are Advised To Observe The Following StepsDokument1 SeiteInitial Registrants Are Advised To Observe The Following StepsJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume MGustiloDokument3 SeitenResume MGustiloJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Calculation of IV Flow Rate2Dokument12 Seiten5 Calculation of IV Flow Rate2Jay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric IV TherapyDokument30 SeitenPediatric IV TherapyJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument2 SeitenDrugsJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labor Delivery Nursing 1209267990824369 9Dokument72 SeitenLabor Delivery Nursing 1209267990824369 9Jay Depakakibo Gallardo100% (1)
- What Is Basic IV Therapy TrainingDokument6 SeitenWhat Is Basic IV Therapy TrainingJay Depakakibo GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen