Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Analyser Rectifier Importance
Hochgeladen von
Srinivas RaghavanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Analyser Rectifier Importance
Hochgeladen von
Srinivas RaghavanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
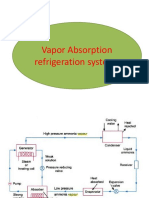
1. Analyzer.
When ammonia is vaporised in the generator, some water is also vaporised and will flow
into the condenser along with the ammonia vapours in the simple system. If these unwanted water
particles are not removed before entering into the condenser, they will enter into the expansion valve
where they freeze and choke the pipe line. In order to remove these unwanted particles flowing to
the condenser, an analyser is used. The analyser may be built as an integral part of the generator or
made as a separate piece of equipment. It consists of a series of trays mounted above the generator.
The strong solution from the absorber and the aqua from the rectifier are introduced at the top of the
analyser and flow downward over the trays and into the generator. In this way, considerable liquid
surface area is exposed to the vapour rising from the generator. The vapour is cooled and most of
the water vapour condenses, so that mainly ammonia vapour leaves the top of the analyzer. Since
the aqua is heated by the vapour, less external heat is required in the generator.
2. Rectifier. In case the water vapours are not completely removed in the analyzer, a closed type
vapour cooler called rectifier (also known as dehydrator) is used. It is generally water cooled and
may be of the double pipe, shell and coil or shell and tube type. Its function is to cool further the
ammonia vapours leaving the analyser so that the remaining water vapours are condensed. Thus,
only dry or anhydrous ammonia vapours flow to the condenser. The condensate from the rectifier is
returned to the top of the analyser by a drip return pipe.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hvac TrainingDokument33 SeitenHvac TrainingABHILASH THAKRENoch keine Bewertungen
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingVon EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Vapour AbsorptionDokument15 SeitenVapour AbsorptionSatheesh ChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deaerator Working Principle: What Is Deaeration?Dokument4 SeitenDeaerator Working Principle: What Is Deaeration?Freddy Mendoza CoronelNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEAERATORDokument14 SeitenDEAERATORHassan Faraz0% (1)
- Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemDokument26 SeitenVapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemRushikesh Dandagwhal100% (8)
- Fresh Water Generator On ShipsDokument19 SeitenFresh Water Generator On ShipsSheshraj VernekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemDokument27 SeitenVapour Absorption Refrigeration Systemvinayaka93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Condenser Functions of Condensers: Plant Maintenance Work and Service - PracticeDokument18 SeitenCondenser Functions of Condensers: Plant Maintenance Work and Service - PracticeTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine AuxillariesDokument139 SeitenTurbine AuxillariesAwez RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Condensers and EvaporatorsDokument32 SeitenPresentation On Condensers and Evaporatorsvipul sharma100% (1)
- Stator Water Cooling System - Stage-2Dokument12 SeitenStator Water Cooling System - Stage-2raghavendran raghuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler and Turbine For BOE ExamDokument71 SeitenBoiler and Turbine For BOE Examkeerthi dayarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Vapour Absorption RefrigeratorDokument5 SeitenStudy of Vapour Absorption RefrigeratorMohdQasimNoch keine Bewertungen
- VarsDokument25 SeitenVarsRuturaj UmaranikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2017Dokument3 SeitenRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2017chotumotu131111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Absorption SystemsDokument17 SeitenVapor Absorption SystemsTalibHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System WorkingDokument2 SeitenVapor Absorption Refrigeration System WorkingHamida HamidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air CDokument2 SeitenAir CHamida HamidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 RacDokument40 SeitenUnit 2 Racozair arshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rac, Module 3-NoteDokument81 SeitenRac, Module 3-NoteShan Mathews VettikuzhiyilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Conventional Refrigeration SystemsDokument21 SeitenNon-Conventional Refrigeration SystemsNishit ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.4 Three Fluid RefDokument3 Seiten3.4 Three Fluid RefShaik mahammad ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROLUX REFRIGERATOR (The Fluid Refrigerator)Dokument2 SeitenELECTROLUX REFRIGERATOR (The Fluid Refrigerator)Anonymous pKd6ekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemDokument19 SeitenVapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemchaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 RACDokument26 SeitenChapter 3 RACSameer AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapour AbsorptionDokument10 SeitenVapour Absorptiongayakwad12_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 PPSDokument6 SeitenLesson 2 PPSmarpelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Absorption Refrigeration CycleDokument11 SeitenVapor Absorption Refrigeration CycleUSHA PAWARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Test RigDokument7 SeitenVapour Absorption Refrigeration Test RigSwapnil DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Vapour Absorption Refrigeration System Working of Vapour Absorption Refrigeration System Components in Vapour AbsorDokument1 SeiteWhat Is Vapour Absorption Refrigeration System Working of Vapour Absorption Refrigeration System Components in Vapour Absordhoom 760Noch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Parts of BoilerDokument5 SeitenConstruction Parts of BoilerMdParbhezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil and Gas Separation System and Process: Unit-4Dokument18 SeitenOil and Gas Separation System and Process: Unit-4Rinkesh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning: Unit - 3Dokument30 SeitenRefrigeration and Air-Conditioning: Unit - 3SAATVIK JAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemDokument12 SeitenVapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemHarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- RACDokument3 SeitenRACneerajbhayal3456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat ExchangersDokument29 SeitenHeat ExchangerscooLkiD1412Noch keine Bewertungen
- TE-A-19 SanGFket Tekade (CIA 4)Dokument10 SeitenTE-A-19 SanGFket Tekade (CIA 4)jojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6200 Area - Urea Plant: Process OverviewDokument8 Seiten6200 Area - Urea Plant: Process OverviewtreyzzztylerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Marine Engineering TechnologyDokument7 SeitenUniversiti Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Marine Engineering TechnologyHafizuddin RazakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibd TankDokument2 SeitenIbd Tankjasmeet_5563Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 To Study VASDokument5 Seiten2 To Study VASAnand GujaratiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Condensers PDFDokument29 SeitenCondensers PDFsandhya100% (1)
- Absorption Refrigeration SystemDokument4 SeitenAbsorption Refrigeration SystemFrancisco ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 34 Boiler AccessoriesDokument21 Seiten34 Boiler AccessoriesSwaraj TodankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaporation AssignmentDokument11 SeitenEvaporation AssignmentFazal JalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fresh Water Production Plants 1 DMOE2002Dokument16 SeitenFresh Water Production Plants 1 DMOE2002Yohannes DennisNoch keine Bewertungen
- TesfayDokument29 SeitenTesfayfisahabirhane16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ppe Steam CondenserDokument27 SeitenPpe Steam CondenserNilesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slug CatcherDokument3 SeitenSlug Catcherwkhan_55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review of Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemDokument7 SeitenLiterature Review of Vapour Absorption Refrigeration SystemnqdpuhxgfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionDokument7 SeitenSteam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaporator AccessoriesDokument21 SeitenEvaporator AccessoriesgrittyptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Absorption Refrigeration System: Technical DescriptionDokument6 SeitenVapor Absorption Refrigeration System: Technical Descriptionbilal buttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automobile Ac by Utilising Waste Heat & GasesDokument18 SeitenAutomobile Ac by Utilising Waste Heat & Gasesraveesh11150% (2)
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit V Refrigeration and Airconditioning Support NotesDokument9 SeitenBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit V Refrigeration and Airconditioning Support NotesA.R. Pradeep Kumar100% (1)
- Condenser Efficiency EngineeringDokument9 SeitenCondenser Efficiency Engineeringโอม ปามาติกะ100% (2)
- Steam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionDokument7 SeitenSteam Separator and Steam Trap Are Almost Same in FunctionTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Condenser: Me 420 - Me Laboratory 2Dokument74 SeitenSteam Condenser: Me 420 - Me Laboratory 2daanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Plumbing Repairs for the Home and FarmsteadVon EverandSimple Plumbing Repairs for the Home and FarmsteadNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Much Hope Should We Have For BiofuelsDokument15 SeitenHow Much Hope Should We Have For BiofuelsSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Performance Evaluation of A Dual-Circuit Thermal Energy Storage Module For Air ConditionersDokument12 SeitenDesign and Performance Evaluation of A Dual-Circuit Thermal Energy Storage Module For Air ConditionersSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impacts of Stormwater Pipe Materials and Pipe Repairs On Stormwater Quality: A ReviewDokument13 SeitenImpacts of Stormwater Pipe Materials and Pipe Repairs On Stormwater Quality: A ReviewSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biofuels Versus Food Production - Does Biofuels Production Increase Food PricesDokument7 SeitenBiofuels Versus Food Production - Does Biofuels Production Increase Food PricesSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dividing Indian Air Force Would Be Regrettable. Balakot Was Demonstration of Will and SkillDokument4 SeitenDividing Indian Air Force Would Be Regrettable. Balakot Was Demonstration of Will and SkillSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fellowship DetailsDokument1 SeiteFellowship DetailsSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoroastrianism in IndiaDokument3 SeitenZoroastrianism in IndiaSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11acwe Zhi - LiuDokument9 Seiten11acwe Zhi - LiuSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics and Maximum Entropy Production in The Earth SystemDokument25 SeitenNonequilibrium Thermodynamics and Maximum Entropy Production in The Earth SystemSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aptitude Problems On Trains3 (WWW - Students3k.com)Dokument6 SeitenAptitude Problems On Trains3 (WWW - Students3k.com)Srinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 1 Engineering Drawing Internal Exam Date: 2-11-15 Write Two Questions From The Given Internal Choice TIME: 1 HourDokument3 SeitenSet 1 Engineering Drawing Internal Exam Date: 2-11-15 Write Two Questions From The Given Internal Choice TIME: 1 HourSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can Chinese Companies Live Up To Investor ExpectationsDokument7 SeitenCan Chinese Companies Live Up To Investor ExpectationsSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 IPOs Axed at The Last Minute Since January 2011 - The Economic TimesDokument3 Seiten15 IPOs Axed at The Last Minute Since January 2011 - The Economic TimesSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 Days After Victory, Mamata Banerjee's Administration Discovers A 35-Yr Worth To-Do List - The Economic TimesDokument2 Seiten30 Days After Victory, Mamata Banerjee's Administration Discovers A 35-Yr Worth To-Do List - The Economic TimesSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ii Mid FM&HMDokument8 SeitenIi Mid FM&HMSrinivas RaghavanNoch keine Bewertungen