Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Coordinate System and Dimensioning
Hochgeladen von
laurenjia0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten1 SeiteCoordinate System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCoordinate System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten1 SeiteCoordinate System and Dimensioning
Hochgeladen von
laurenjiaCoordinate System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
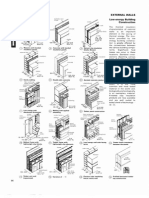
COORDINATE SYSTEM AND
evan: DIMENSIONING
veo Modular Arrangements in Building Practice
co ‘The units for the modular arrangement are M = 100mm for
itera 30 | the basic module and 3M ~ 300mm, 6M = 600mm, and
: 32M = 1200mm, for the multi-modules, The limited
sera aesnesuninaee multiples of the proferced numerical series are generated in
ani this way. The coordinate dimensions - theoretical standard
vee dimensions ~ are, ideally, generated from these. These
limitations are the result of functional, constructional and
economic factors.)
In addition, thore aro standardised, non-modular
extending dimensions, |= 25mm, 50mm and 75mm, @.g., for
‘matching and overlapping connection of components,
‘The coordinate system in practical usage
Usina rules of combination. different sizes af companante
can also be arranged within a modular coordinate system.
6
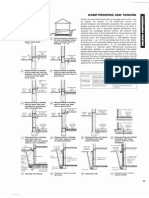
With the help of calculations with numerical groups (e.9.
Pythagoras) or by factorisation (e.g. continued fractions,
non-rectangular components can algo be arranged within a
modular coordinate systom. » Q) + @)
By constructing polygonal traverses (e.g. triangular,
rectangular, pentagonal and the halves of the same), the so
called ‘round! building structures can be devised
Using modular arrangements, technical areas such a8 th
for structural engineering, electrotechnology, transport
‘Enample application, sloping Compensating measure on ation, which are dependent on each other from a
oot © wom ‘geometrical and dimensional viewpoint, can be combined,
ttt ®
© Modu neygonat averse (@) Example te kao of echic eing mar erngeents
potvgnal waves te ple
35
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- How To Design Vertical Sand DrainsDokument10 SeitenHow To Design Vertical Sand DrainslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Waste ManagementDokument9 SeitenPlastic Waste ManagementlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Loading Dock System GuideDokument38 SeitenLoading Dock System Guideberolyan06Noch keine Bewertungen
- US EPA Air Quality IndexDokument1 SeiteUS EPA Air Quality IndexlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Properties & UsageDokument4 SeitenAluminium Properties & UsagelaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Ozone Is FormedDokument1 SeiteHow Ozone Is FormedlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Design of Slender Reinforced Concrete Structural WallsDokument6 SeitenSeismic Design of Slender Reinforced Concrete Structural WallssaharuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- River ManagementDokument10 SeitenRiver ManagementlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment Excitation and Measurement of Beam MobilityDokument21 SeitenMoment Excitation and Measurement of Beam MobilitylaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roman BuildingsDokument15 SeitenRoman BuildingslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confidentiality PolicyDokument3 SeitenConfidentiality PolicylaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annex 7Dokument3 SeitenAnnex 7viswa santhi tungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire DetectionDokument1 SeiteFire DetectionlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAAQSDokument1 SeiteNAAQSlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roof StructuresDokument3 SeitenRoof StructureslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchoolDokument7 SeitenSchoollaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Services ConnectionsDokument1 SeiteServices ConnectionslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture TheatresDokument4 SeitenLecture TheatreslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation DuctDokument1 SeiteVentilation DuctlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chimneys and FluesDokument1 SeiteChimneys and FlueslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Site DrainageDokument3 SeitenBuilding Site DrainagelaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masonry BondsDokument1 SeiteMasonry BondslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction ManagementDokument4 SeitenConstruction ManagementlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- External WallsDokument1 SeiteExternal WallslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthworks and Foundation StructuresDokument1 SeiteEarthworks and Foundation StructureslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Construction Techniques and FormsDokument1 SeiteModern Construction Techniques and FormslaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damp-Proofing and TankingDokument3 SeitenDamp-Proofing and TankinglaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Building SiteDokument1 SeiteThe Building SitelaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building DesignDokument2 SeitenBuilding DesignlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design MethodDokument1 SeiteDesign MethodlaurenjiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)