Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
LANE, BLIGH & Khosla Theories
Hochgeladen von
Lo0oVveOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LANE, BLIGH & Khosla Theories
Hochgeladen von
Lo0oVveCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
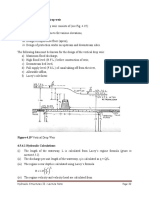
Blighs creep theory:(1) according to the theory of percolating water creeps the outline of the base of foundation of
structure.
(2) hydraulic slope or gradient is constant throughout the impervious length of apron.
(3) head or energy is lost as per collating water creeps along the base profile of weir & sub soil.
(4) loss of head is proportional to length of travelling of creeping water.
Limitations: Bligh made no distinction between horizontal and vert creep length. Loss of head is
considered proportional to the creep length which in actual is not so. The idea of ext gradient has
not been considered.
Lanes Weighted Creep theory: it is the modification of BCT. In Blighs theor there is no
distinction between horizontal and vertical path of percolation. In lanes theory vertical path of
percolation is given more weightage L=B+3(2d1+2d2+2d3)
Khoslas theory:(1) the inner faces of sheet piles and horizontal creep are much effective than outer faces of sheet
piles.
(2) intermediate pile if shorter than the outer one was in effective (3) actual measurement of
pressure with the help of pipes inserted on the floor of siphon did not show any similarity with
pressure calculated by Blighs theory .
(4) the flow below hydraulic structure is governed by Laplace equation Kx d 2/dx2 + Ky
d2/dy2 + Kz d2/dz2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Functions of Subgrade, Subbase & Base CourseDokument1 SeiteFunctions of Subgrade, Subbase & Base CourseLo0oVve90% (10)
- Pavement Analysis & DesignDokument11 SeitenPavement Analysis & DesignLo0oVve100% (1)
- Types of EarthdamsDokument21 SeitenTypes of EarthdamsDilipKumarAkkaladeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastering: CEMENT PLASTERING: For Brick Masonry 18mm Thick, (1:6) Plaster in Two Layers MayDokument4 SeitenPlastering: CEMENT PLASTERING: For Brick Masonry 18mm Thick, (1:6) Plaster in Two Layers MayLo0oVve100% (1)
- Chapter-4 Design of Weirs On Permeable Foundation PDFDokument15 SeitenChapter-4 Design of Weirs On Permeable Foundation PDFFekadu Wub80% (5)
- Chapter 2 2 GroynesDokument20 SeitenChapter 2 2 GroynesGetahun Tadesse100% (1)
- 11 - Theories of Seepage and Design of Weirs and BarragesDokument90 Seiten11 - Theories of Seepage and Design of Weirs and BarragesYIBELTAL EBABU100% (1)
- Hydraulic Structure - 2 Chapter-4Dokument43 SeitenHydraulic Structure - 2 Chapter-4Debela Kebede Kera100% (1)
- Embankment Dam (HE 621)Dokument280 SeitenEmbankment Dam (HE 621)Otoma Orkaido100% (1)
- Stabilization and Rectification of RiversDokument50 SeitenStabilization and Rectification of RiversCharles Bong50% (2)
- Chapter4 - Surface Irrigation NewDokument28 SeitenChapter4 - Surface Irrigation NewMūssā Mūhābā ZēĒthiopiāNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch. 5 - Stream Gauging PDFDokument38 SeitenCh. 5 - Stream Gauging PDFviedos liker100% (1)
- Orientation Buildings: Maximum Ventilation and Natural Light in All Climatic Conditions. ItDokument6 SeitenOrientation Buildings: Maximum Ventilation and Natural Light in All Climatic Conditions. ItLo0oVve100% (1)
- Wrie Iii Prepared By: Yassin Y. Dam Engineering II ExercisesDokument6 SeitenWrie Iii Prepared By: Yassin Y. Dam Engineering II ExercisesWalterHu100% (1)
- 02 - 2 Design of Weir and Barrage PDFDokument50 Seiten02 - 2 Design of Weir and Barrage PDFzelalemniguse100% (1)
- Chapter 4 PART 2Dokument14 SeitenChapter 4 PART 2Fetene Nigussie75% (8)
- Chapter 3 Earth Dam 2020Dokument61 SeitenChapter 3 Earth Dam 2020Ali ahmed100% (1)
- Chapter 2 B 1 Arch ButressDokument19 SeitenChapter 2 B 1 Arch ButressYasin Mohamed BulqaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Vertical Drop Weir PG, Example, 2020Dokument9 SeitenDesign of Vertical Drop Weir PG, Example, 2020zelalemniguse75% (4)
- Canal Module and EscapeDokument31 SeitenCanal Module and EscapeShubham Garg100% (1)
- Design of Weirs and BarragesDokument42 SeitenDesign of Weirs and BarragesDivyaSlp100% (2)
- Head and Cross RegulatorsDokument14 SeitenHead and Cross RegulatorsSaphal Lamichhane78% (9)
- Site SelectionDokument12 SeitenSite Selectionsuchendra singh100% (1)
- Blighs TheoryDokument5 SeitenBlighs TheoryAnde Bhanu100% (1)
- Chapter 8Dokument16 SeitenChapter 8Mohit Kumar RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bligh'S Theory and Khoslas'S TheoryDokument60 SeitenBligh'S Theory and Khoslas'S Theorychukkala sridhar0% (1)
- Design Principles For Sarda Type and Straight Glacis FallDokument12 SeitenDesign Principles For Sarda Type and Straight Glacis Fallshweta0% (1)
- Worksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5Dokument14 SeitenWorksheet - 143760187HS-II, TUTORIAL ON CH-5A MusaverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Gravity DamsDokument35 Seiten7 Gravity Damskishing0905100% (1)
- Final Exam Dam Engineering 18-12-2020 PDFDokument11 SeitenFinal Exam Dam Engineering 18-12-2020 PDFBaba ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Question (Hydraulic Structures)Dokument5 SeitenModel Question (Hydraulic Structures)Debanjan Banerjee71% (7)
- Phreatic Line PDFDokument21 SeitenPhreatic Line PDFshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diversion Head WorksDokument48 SeitenDiversion Head Worksprashanthreddyh100% (4)
- Canal OutletsDokument32 SeitenCanal OutletsAhmed Hassan83% (6)
- Culvert Design - WEEK 4 LECTURE NOTESDokument31 SeitenCulvert Design - WEEK 4 LECTURE NOTESDammy Taiwo-AbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture#1 Guide BankDokument34 SeitenLecture#1 Guide BankManamno Beza100% (1)
- Chapter-3: Hydraulic Jump and Its Practical ApplicationsDokument26 SeitenChapter-3: Hydraulic Jump and Its Practical ApplicationsahsansaddiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10CV65 - Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design - Drawing Question BankDokument6 Seiten10CV65 - Hydraulic Structures and Irrigation Design - Drawing Question BankMr. Y. RajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- External and Internal Stability of Soil WallsDokument4 SeitenExternal and Internal Stability of Soil WallsManilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WRI7 - 8 - 9 - Hydrograph Analysis, Unit Hydrograph, S-Hydrograph, Numerical ProblemsDokument13 SeitenWRI7 - 8 - 9 - Hydrograph Analysis, Unit Hydrograph, S-Hydrograph, Numerical ProblemsmustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four 4. Irrigation Canals and DesignDokument8 SeitenChapter Four 4. Irrigation Canals and DesignBrooke AbebeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ Ahe U6Dokument3 SeitenMCQ Ahe U6Abhijeeth Nagaraj100% (1)
- CHAPTER - 2 Stresses in PavementDokument49 SeitenCHAPTER - 2 Stresses in PavementHaile GuebreMariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- HS Chapter 4Dokument28 SeitenHS Chapter 4Akli Ale Man100% (3)
- Design of Irrigation StructuresDokument21 SeitenDesign of Irrigation StructuresJames K. KirahukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- محاضرات تصاميم السدود-كورس اول-1995205249Dokument132 Seitenمحاضرات تصاميم السدود-كورس اول-1995205249khellaf cherif100% (3)
- Hydraulic Structure II AssignmentDokument6 SeitenHydraulic Structure II Assignmentmasre1742100% (1)
- HW Engineering I Work Out ProblemsDokument4 SeitenHW Engineering I Work Out ProblemsHaile GuebreMariam100% (1)
- Chap6-10 - KhoslaDokument46 SeitenChap6-10 - KhoslaDarya Memon79% (28)
- Water Resources Engineering - Section 1: A. B. C. D. EDokument15 SeitenWater Resources Engineering - Section 1: A. B. C. D. EajaydevmalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unesco 1979Dokument53 SeitenUnesco 1979pleyvaze100% (1)
- CH 5 Cross DrinageDokument40 SeitenCH 5 Cross DrinageAbuye HDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Resources Engineering-IIDokument8 SeitenWater Resources Engineering-IICharan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Jump PDFDokument24 SeitenHydraulic Jump PDFJebone Stein Web Juarbal100% (1)
- Chapter 4 WcuDokument29 SeitenChapter 4 WcuKuba100% (3)
- Wier On Permeable FoundationDokument34 SeitenWier On Permeable FoundationMahmoud I. MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weir On Pevious FoundationDokument27 SeitenWeir On Pevious FoundationAlexdorwinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seepage TheoryDokument18 SeitenSeepage TheoryRadu BriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16btceng061 (Shivansh Tiwari)Dokument12 Seiten16btceng061 (Shivansh Tiwari)indu kant dwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- دياناDokument46 SeitenدياناMuhaimen MadridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Seepage TheoriesDokument60 SeitenChapter 4 Seepage Theoriesmimahmoud100% (1)
- Design of Hydraulic Structures: B.Tech Civil Credit Hours: 03Dokument13 SeitenDesign of Hydraulic Structures: B.Tech Civil Credit Hours: 03Suleman FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barrage Lec3 Students 2017Dokument12 SeitenBarrage Lec3 Students 2017Top5 foryouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Flexible & Rigid PavementsDokument2 SeitenDifference Between Flexible & Rigid PavementsLo0oVve100% (2)