Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reviewpacketcellsanswerkey
Hochgeladen von
api-2351605190 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
121 Ansichten7 SeitenCell is structural and functional unit of all living things, "building block" of life. List the three exceptions to the cell theory: chloroplast, mitochondria (self-duplicating) 4) Define organelle: tiny workers of the cell, discrete structure of a cell that has a specialized function. State two similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. A. Dna B. Cell membrane.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
reviewpacketcellsanswerkey
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCell is structural and functional unit of all living things, "building block" of life. List the three exceptions to the cell theory: chloroplast, mitochondria (self-duplicating) 4) Define organelle: tiny workers of the cell, discrete structure of a cell that has a specialized function. State two similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. A. Dna B. Cell membrane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
121 Ansichten7 SeitenReviewpacketcellsanswerkey
Hochgeladen von
api-235160519Cell is structural and functional unit of all living things, "building block" of life. List the three exceptions to the cell theory: chloroplast, mitochondria (self-duplicating) 4) Define organelle: tiny workers of the cell, discrete structure of a cell that has a specialized function. State two similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. A. Dna B. Cell membrane.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 7
Name:__________________________
Review Packet
Cell & Cell Transport
1) Define cell: structural and functional unit of all living things,
building block of life.
2) List the three statements to the cell theory:
A. The cell is the basic functional unit of all living things.
B. The cell is the basic structural unit of all living things.
C. All cells come from pre-existing cells.
3) List the three exceptions to the cell theory
A. Chloroplast, mitochondria (self-duplicating)
B. Origin of the first cell
C. viruses
4) Define organelle: tiny workers of the cell, discrete structure of a
cell that has a specialized function.
5) State two similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
A. dna
B. cell membrane
6) State two differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell.
A. eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles
B. Prokaryotic cells are smaller than eukaryotic cells. (1/10)
7) State the levels of organization from organellesorganism.
Organelles, cells, tissues, organs and organ systems, organism
Cell Structure and Function
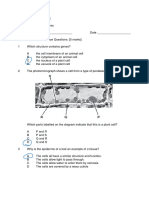
8) Label the organelles below. Is this a plant cell or an animal cell?
How do you know? Plant cell. Presence of a
cell wall, chloroplasts and central vacuole.
A: nucleus
B: cytoplasm (ribosome)
C: central vacuole
D: chloroplast
9) Briefly describe the function of each organelle:
A. Cell membrane: selectively permeable. Controls what
enters and exits the cell (simple one can, complex
molecules cant)
B. cytoplasm: site of metabolic reactions, contain organelles
C. Nucleus: contains dna, which carries genetic information
and instructions for protein synthesis
D. Nucleolus: site of ribosome synthesis
E. Nuclear envelope: Controls what enter/exits the nucleus
F. Endoplasmic reticulum: intracellular transport
G. Ribosome: site of protein synthesis
H. Mitochondria: production of ATP (site of cellular respiration)
I. Golgi bodies: receives, sorts and packages substances
J. Lysosomes: contains digestive enzymes, fuses with food
vacuole and digests food
K. Vacuoles: stores food,water and waste
L. Centrioles: appear to have a role in cell division
M. Contractile vacuole: water regulation organelle present in
unicellular organisms.
10)
Label the organelles below. Is this a plant cell or an animal
cell? How do you know? Animal cell. Presence of centrioles, no
cell wall
A: vacuole
B: mitochondria
C: ribosomes
D: cell membrane
Ribosomes synthesize proteins (enzymes); mitochondria requires
enzymes to convert glucose into ATP
Ribosomes require ATP (synthesized during respiration by
mitochondria) to synthesize proteins.
11)
What are four differences between plant and animal cells.
A. Cell wall (plant)
B. Chloroplast (plant)
C. Large central vacuole (plant)
D. Centrioles (animal)
12)
Briefly describe the functions of each organelle.
A. Chloroplast: site of photosynthesis( food making process in
plants)
B. Large central vacuole: stores water for photosynthesis
C. Cell wall: non living structure, composed of cellulose,
provides shape and protection.
Cell Membrane and Transport
13)
Label the diagram of the cell membrane.
14)
Define concentration gradient: difference among
concentration amounts
15)
Define Passive Transport: cellular transport, ATP is not
used, substances go from high to low concentration.
16)
List the three types of passive transport and briefly
describe them.
A. Diffusion: passive transport of molecules
B. Osmosis: passive transport of water across a cell
membrane
C. Facilitated diffusion: assistance by carrier proteins in
transporting substances across the cell membrane.
17)
What would happen to a cell placed in a hypotonic
environment? Draw a diagram to help explain your answer.
Water moves into the cell, because there is a
greater concentration of water outside the cell,
than inside.
18)
What would happen to a cell placed in a
hypertonic environment? Draw a diagram to help explain your
answer.
In a hypertonic environment, water
moves out of the cell, because there
is a greater concentration of water
inside the cell.
19)
What would happen to a cell placed in an isotonic
environment? Draw a diagram to help explain your answer. In a
isotonic environment, water concentration is equal inside the cell
and outside the cell.
20)
State the two basic differences between active transport
and passive transport.
A. In active transport, ATP is used and is not required in
passive transport.
B. In active transport, molecules go from low to high
concentration, in passive transport molecules go from high
to low.
21)
Two basic types of endocytosis are pinocytosis and
phagocytosis.
22)
State the basic difference between pinocytosis and
phagocytosis. Pinocytosis involves small dissolved
substances and phagocytosis-- involves large, undissolved
molecules.
23)
The flowing motion of the cytoplasm that transports
materials within the cell is called cyclosis.
24)
Review all concepts associated with Diffusion thru
Membrane!!!
Red Onion Osmosis Demonstration
1: Iodine
2: Iodine + Starch Blue Black
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2015nutrespexc ReviewpacketanswerkeyDokument6 Seiten2015nutrespexc Reviewpacketanswerkeyapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Pollution Climate Change TCDokument12 SeitenAir Pollution Climate Change TCapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feeding The World Health Toxicology 1545076398844 TCDokument11 SeitenFeeding The World Health Toxicology 1545076398844 TCapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Pollution Climate Change SCDokument11 SeitenAir Pollution Climate Change SCapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution Test 3/5 (Friday) Unit HW/Review Packet Due On Thursday (3/4) Labs (Biochemical Similarities, Beaks of Finches, Dichotomous Key)Dokument1 SeiteEvolution Test 3/5 (Friday) Unit HW/Review Packet Due On Thursday (3/4) Labs (Biochemical Similarities, Beaks of Finches, Dichotomous Key)api-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- RevewipacketanswerkeyrevisedDokument5 SeitenRevewipacketanswerkeyrevisedapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- ModerngeneticshwmillerDokument1 SeiteModerngeneticshwmillerapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecologyhwpacket 2015Dokument4 SeitenEcologyhwpacket 2015api-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015proteinsynthesishw PacketDokument7 Seiten2015proteinsynthesishw Packetapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review Packetmeiosisgeneticsanswerkey2015Dokument5 SeitenReview Packetmeiosisgeneticsanswerkey2015api-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis Lab 2Dokument4 SeitenMitosis Lab 2api-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Virtual LabsDokument4 SeitenPhotosynthesis Virtual Labsapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015pscrhw PacketDokument7 Seiten2015pscrhw Packetapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit4 Human Impact MillerDokument1 SeiteUnit4 Human Impact Millerapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecologyreviewsheet2 Answer KeyDokument6 SeitenEcologyreviewsheet2 Answer Keyapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit3ecologymillerhw SheetDokument1 SeiteUnit3ecologymillerhw Sheetapi-235160519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 3 CellsDokument7 Seiten3 CellsCaviles, Jasmin S.Noch keine Bewertungen
- A. B. C. D.: E. Schleiden and SchwannDokument22 SeitenA. B. C. D.: E. Schleiden and SchwannBatuhan TuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fundamental Unit of Life To Improvement in Food Resources ChaptersDokument104 SeitenThe Fundamental Unit of Life To Improvement in Food Resources ChaptersSARANSH oPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDokument2 SeitenCell - The Unit of LifeMega No01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Session 2 ANAPHY LecDokument9 SeitenSession 2 ANAPHY LecMaria Jub MangrubanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 7 - Quarter 2 - Week 4 Learning Activity SheetDokument4 SeitenScience 7 - Quarter 2 - Week 4 Learning Activity SheetTricia BrunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cell - Structure, Function, Diagram and TypDokument11 SeitenAnimal Cell - Structure, Function, Diagram and TypKolade YousuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell PartsDokument28 SeitenCell PartsArim ArimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Cell BiologyDokument111 Seiten03 Cell BiologyPrincess Noreen SavellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles ReviewDokument19 SeitenCell Organelles ReviewJelin VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology - The Cellular Level of OrganizationDokument11 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology - The Cellular Level of OrganizationChristina MarkwartNoch keine Bewertungen
- B GENERAL BIOLOGY I Q1M2.2 Learner-Copy Final LayoutDokument33 SeitenB GENERAL BIOLOGY I Q1M2.2 Learner-Copy Final LayoutLiennar Naikh100% (1)
- School Cell Analogy PpointDokument14 SeitenSchool Cell Analogy Ppointapi-265180883Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 5Dokument18 SeitenNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 5Pratham GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationDokument6 SeitenTopic 3 - Cellular Level of OrganizationAdeyinka OluyoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Fundamental Unit of LifeDokument31 Seiten1 - Fundamental Unit of Lifevivek tripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat Cell TheoryDokument3 SeitenReferat Cell TheoryVictor AndoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CityDokument3 SeitenCell Cityapi-305324654Noch keine Bewertungen
- Golgi Apparatus Class LectureDokument9 SeitenGolgi Apparatus Class Lectureapi-224849525Noch keine Bewertungen
- St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDokument6 SeitenSt. Paul College of Ilocos SurRica machells DaydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology and GeneticsDokument54 SeitenCell Biology and Geneticspnguyen810Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-1 (Cell and Enzymes) - 1Dokument3 SeitenChapter-1 (Cell and Enzymes) - 1ToXicNoch keine Bewertungen
- 62 F 5 B 6 B 93 e 3 F 3Dokument3 Seiten62 F 5 B 6 B 93 e 3 F 3HC GamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centrioles, Centrosomes, and CiliaDokument16 SeitenCentrioles, Centrosomes, and Ciliathebrotherhood2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- O. Tauri: 3-D Ultrastructure Of: Electron Cryotomography of An Entire Eukaryotic CellDokument14 SeitenO. Tauri: 3-D Ultrastructure Of: Electron Cryotomography of An Entire Eukaryotic CellMARIA ANGGIE CANTIKA DEWANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Biology - Cell CycleDokument11 SeitenUnit 5 Biology - Cell CycleLisa Bavaro0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology in SHS Bulk Vesicular Transport ReviewerDokument30 SeitenBiology in SHS Bulk Vesicular Transport ReviewershengNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO411 Cell Biology: AssignmentDokument7 SeitenBIO411 Cell Biology: AssignmentNur AqillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Growth and DivisionDokument15 SeitenCell Growth and DivisionJohn Lester BerdinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cohort 2 - Group 5 - Class 9 - 25 Aug - Hindi - Science EM - Maths EMDokument3 SeitenCohort 2 - Group 5 - Class 9 - 25 Aug - Hindi - Science EM - Maths EMIasam Groups'sNoch keine Bewertungen