Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Questions Page 469
Hochgeladen von
api-299641879Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Questions Page 469
Hochgeladen von
api-299641879Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Questions page 469 #s 1-11
1. What is the purpose of mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is to precisely separate the two copies of the
genetic information and place them in two separate nuclei in
preparation for the formation of two complete daughter cells with
identical genetic information.
2. Explain why the DNA that makes up two sister chromatids is
identical.
New DNA is copied directly from existing DNA to make identical copies.
It is critical that the DNA in the sister chromatids be identical so that
each daughter cell carries the same information as the parent cell
3. How can mutations lead to changes in the cell cycle?
If a mutation occurs in a gene that controls cell division, the cell cycle
might be altered. For example, a normal gene might turn off the
process of cell division after injured tissue has been repaired. A
mutation could occur in that gene and the cell division process would
continue indefinitely.
4. A person notices a dark spot on their skin this dark spot turns
out to be skin cancer. What could have caused the start of the
skin cancer tumour and has was mitosis and cell division of
these cells affected?
Skin cancer has been linked to exposure to ultraviolet radiation from
the Sun. Ultraviolet radiation can cause a mutation in a gene that
controls the cell cycle causing uncontrolled cell division. As cells
accumulate, they form a tumour on the skin.
5. How would a cure for skin cancer possibly work to stop the
occurrence of skin tumours?
A cure for skin cancer might be a drug that would recognize and
destroy all skin cancer while having no effect on healthy cells
6. Summarize each phase of mitosis. Use sketches to illustrate
your explanations.
Sketches can be similar to those in Figure 14.7 on page 464 in the text
book.
Prophase
-
Chromatin condenses into short, thick chromosomes forming an Xshape
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear
Centrioles migrate to opposite poles of the cell and spindle fibres
form
Metaphase
-
Spindle fibres from each pole attach to the centromere of each
chromosome and push the chromosomes to the equator of the cell
Anaphase
-
Centromeres divide and the spindle fibres pull the chromatids (now
chromosomes) to the opposite poles of the cell
Telophase
-
Chromosomes begin to uncoil and become chromatin
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus reform
7. In what areas of a plant would mitosis occur most frequently?
Explain why.
The most rapidly dividing cells in plants are in the root tip, shoot tips,
and buds. Therefore mitosis will be occurring most frequently in these
parts of the plant.
8. At what time of the year would mitosis in a plant occur most
frequently? Explain why.
In the temperate regions of the world such as Canada, plant growth
and therefore mitosis occur most frequently in the spring and summer
months.
9. What would happen to chromosome number in a cell if that cell
does not go through S phase of the cell cycle?
If a cell did not go through S phase, no new DNA would be synthesized
and therefore there would be only one copy of each chromosome.
During mitosis, the single chromosomes would randomly migrate to
the daughter cells. Since neither daughter cell would contain a full
complement of genetic information, they would not be viable and
would die.
10.
Why is the process of cytokinesis necessary to ensure the
normal functioning of a cell?
Cytokinesis is the separation of the cytoplasm and the completion of a
membrane (in plants, a membrane and cell wall) around each daughter
cell. If cytokinesis did not occur, the parent cell would contain two,
identical nuclei. The cell would probably be viable but there would be
no new cells.
11.
Explain why different kinds of cells in the body might live
for different lengths of time.
The cells in the lining of the stomach are exposed strong acid and cells
on the lining of the intestine are exposed to digestive enzymes. All of
these cells are exposed to mechanical motion. Blood cells are exposed
to mechanical motion through small vessels and high pressure in the
heart. Skin cells are subject to stretching, pressure, and abrasions. All
of these cells die relatively rapidly and must be replaced. In contrast,
neurons in the brain and spinal cord are protected by the bones of the
skull and spinal column and therefore most of them survive for the life
of the individual.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Parts of The Male Reproductive System TestesDokument24 SeitenParts of The Male Reproductive System Testesapi-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 NotesDokument22 SeitenPart 1 Notesapi-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Questions Page 480Dokument3 SeitenQuestions Page 480api-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
- EggvsspermanswerkeyDokument2 SeitenEggvsspermanswerkeyapi-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
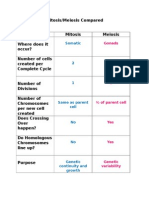
- Mitosis/Meiosis Compared: SomaticDokument2 SeitenMitosis/Meiosis Compared: Somaticapi-299641879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Effects of Formic Acid Administration in The Drinking Water On Production Performance, Egg Quality and Immune System in Layers During Hot SeasonDokument6 SeitenEffects of Formic Acid Administration in The Drinking Water On Production Performance, Egg Quality and Immune System in Layers During Hot Seasonahmed galalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics of RetinoblastomaDokument5 SeitenGenetics of RetinoblastomadesmawitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory System:: BloodDokument101 SeitenThe Circulatory System:: BloodAntonio MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MANGO ReferenceDokument15 SeitenMANGO ReferenceN S Arun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIORESTEC 2023 PosterDokument1 SeiteBIORESTEC 2023 PosterSebastian MariangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Follow The Physiology Formula Lactic AcidosisDokument59 SeitenFollow The Physiology Formula Lactic AcidosisFlorin VavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodegradation of Phenol by Pseudomonas PDFDokument8 SeitenBiodegradation of Phenol by Pseudomonas PDFKelly RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life ScienceDokument25 SeitenEarth and Life ScienceJonathan MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna, Rna, Dan Protein 1Dokument26 SeitenDna, Rna, Dan Protein 1R yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contemporary Chemical Approaches For Green and Sustainable Drugs 1St Edition Torok M Ed Full ChapterDokument51 SeitenContemporary Chemical Approaches For Green and Sustainable Drugs 1St Edition Torok M Ed Full Chapterjohn.mclarty382100% (15)
- Biotechnology Patenting in India and Related IssuesDokument22 SeitenBiotechnology Patenting in India and Related IssuesShruti KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDokument3 SeitenBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKambaska Kumar BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 3 Experiment No: 6Dokument2 SeitenPaper 3 Experiment No: 6Asha AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsDokument17 Seiten7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsTheresa IzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NC-AhR Diminishes The Efficacy of Chemotherapy Via Suppressing STING Dependent Type-I Interferon in Bladder CancerDokument17 SeitenNC-AhR Diminishes The Efficacy of Chemotherapy Via Suppressing STING Dependent Type-I Interferon in Bladder Cancerzhe zhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological KingdomsDokument2 SeitenBiological KingdomsValeria GrijalvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tobacco Etch Virus Protease: A Shortcut Across BiotechnologiesDokument16 SeitenTobacco Etch Virus Protease: A Shortcut Across BiotechnologiesNhật ThiệnNoch keine Bewertungen
- EB3225 Chapter 1 - Overview of Industrial MicrobiologyDokument43 SeitenEB3225 Chapter 1 - Overview of Industrial MicrobiologyPatricia Jayshree Samuel JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- IchthyosisDokument154 SeitenIchthyosisprajnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahasa Inggris WajibDokument19 SeitenBahasa Inggris WajibIta PuspitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sustained Release Drug FormulationDokument14 SeitenSustained Release Drug Formulationapi-3750955100% (5)
- Andrographis Paniculata A Review ofDokument12 SeitenAndrographis Paniculata A Review oftio_bsNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of HIVDokument4 SeitenHistory of HIVHyrum KamandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Primary Structure of The Saccharmoces Cerevisiae Gene For ADH1 - Bennetzen & Hall 1981 PDFDokument9 SeitenThe Primary Structure of The Saccharmoces Cerevisiae Gene For ADH1 - Bennetzen & Hall 1981 PDFMeidayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatoprotective Activity of Ocimum Americanum L LDokument7 SeitenHepatoprotective Activity of Ocimum Americanum L LNurul Rachman NasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis PDFDokument30 SeitenMitosis PDFPankaj MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gel Electrophoresis Lesson PlanDokument8 SeitenGel Electrophoresis Lesson Planapi-215898557Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 13 Study Guide - Phylum ChordataDokument6 SeitenModule 13 Study Guide - Phylum Chordataapi-233817991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument19 SeitenLab 6nur athilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeast Cellular Respiration Labfin-2Dokument7 SeitenYeast Cellular Respiration Labfin-2Nabeel UddinNoch keine Bewertungen