Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Astm A320
Hochgeladen von
Achraf Boudaya0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten8 SeitenASTM-A320 details
Originaltitel
ASTM-A320
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenASTM-A320 details
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
1K Ansichten8 SeitenAstm A320
Hochgeladen von
Achraf BoudayaASTM-A320 details
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 8
r
aq Designation: A 320/A 320M — 94a (Reapproved 1995)"
An Arata Natonal Sandan
Standard Specification for
Alloy Steel Bolting Materials for Low-Temperature Service’
‘Ths andar is ised urder he ed desgtaton 32014 12104 he number inal ellowing the designation nde he eur
‘gal adept ox a he case of revise. the year of las iin A ruber panes cache yo of ls eae
‘supers epson iad an eter chung sine the last even apna,
‘hs standard hasbeen aponoved for ase by ages ofthe Depart of Defense, Comal th DoD Inder of Speicatons and
Sunda forte spec war of ue whch hat been aed bythe Deparment of Doone
1 Non—Keywords were alle in December 108
4, Scope
1.1 This specication? covers alloy steel bolting materials
for pressure vessels, valves, flanges, and fiings for low-
temperature service. The term “bolting material” a used inthis
specification covers rolled, forged, or strain hardened bars,
bolts, serews, studs, and stud bolts. The bars shall be hot”
wrought. The material may be farher processed by centeriess
nding or by cold drawing, Austenitie stainless steel may be
solution annealed or anneaied and strain-hardened
1.2 Several grades are covered, including both feritc and
austenitic stels designated L7, BB, etc, Selection will depend
on design, service conditions. mechanical properties, ant
low-temperature characteristics. The mechanical requirements
of Table 1 indicate the diameters for which the minimum
mechanical properties apply to the various grades and classes,
and Table 2 stipulates the requirements for Charpy impact
energy absorption. The manufacturer should determine thatthe
material can conform to these requirements before parts are
manufactured. For example, when Grade L43 is specified to
meet the Tabie 2 impact energy values at ~150°F [-101°C),
iditional restrictions (such as procuring a steel with lower P
and $ contents thin might normally be supplied) in the
chemical composition for AISI 4340 are likely to be required.
Nore 1—The committe formulating this specification fas included
Several grades material that have boen rather extensively used fo the
resent purpose. Other compositions will be considete for inclusion by
‘he commie trom time to time asthe need becomes apparent. User.
Should note that hardenabilty of some oF the grades mentioned oy
Festi the manimum size at which the requivedmectenical properties ate
inable
1.3 Nuts for use with this bolting material are covered in
Section 9 and the mut material shall be impact tested
14 Supplementary Requirements (S1, 82, and $3) of an
ptional nature are provided. They shall apply only when
"Ths pistons unde juste of ASTM Commitee A-1 on Si
Stes Sci and Relaed Alloys and the tect espns of Sobeommice
‘40122 om Vives, Figs Wot, and Fines Co High and Sarmonpleic
Reapers
Cent ction appraved lune 15, 1994 Pblihed Auge 1954 Orsi
Ioiea ab 4320-48. Lan prio eon A 32-98
or ASME Bote an Pes Vel Code aplication. se late Spcit
‘ation S320 Seton I Ha Cove
specitied in the inquiry, contract and order.
1.5 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units
and in SI units. However. unless the order specifies the
applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the mate~
"ial shall be furnished to inch-pound nits,
1.6 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
are to be regarded separately as standard, Within the text, the
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, cach system must
be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
‘wo systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi-
cation,
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards
A28/A 29M | Specification for Steel Bars, Carbon and
Alloy, Hot-Wrought and Cold-Finished, General Require-
ments for?
AI98IA 194M Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel
Nuts for Bolts for High-Pressure and High-Temperature
Service"
A276 Specification for Stainless and Hest-Resisting Steel
Bars and Shapes?
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
‘of Steel Produets*
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for
Chemical Analysis of Steel Products®
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Mateials*
E 566 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy-Curent) Sorting
of Ferrous Metals?
F 436 Specification for Hardened Steel Washers!
2.2 American National Standards Institute Standards:®
B18.2.1 Square and Hex Bolts and Screws
Annual Book of ASTM Sandan, Wo 01.08,
Aral Book of ASTM Stands, Wa 01.08
‘oval Book of ASTM Standard Val 1.98
"al Boot of ASTM Stade, Wal 08 BL
Amal Bask of ASTM Sudan, No 3.98
* ual Book of ASTM Stan, So 18.8
‘Aaa from American Nana Standards laste, 11 Wes 2nd St, 3th
Flor New York NY 1036
185
re
ih a 320/a 320M
TABLE 1 Wachanica! Requirements
Tersle vs Stengin BONGO pecan
et Teeatment sgn, ms iain OBIE adnegs
Class and Grade, Distr in mm wird wafers ‘so Am ae
TMPa) ose) rennin.
~ Feriie Sele
Ta ree Te LL 785 105 © a
2vs(65) and uniee™ uenehed an ened 1 35
ire 28. 105 6 0
"4 10) ans uncer quenched ana tenoerod (080 1725)
um 100 20. 8 50 2a HB or
‘98 HRB
2568) ane unaer* usncned and engensd a EOF 1690) 880)
"e20°C) mon
u 8 105 16 50
1 es and uncer ‘uarenod an tempared vaso) 725) -
Gass 188,886, baw. BaP atid slvion vested = 3 cs BSB or
BAF, BB. BBLN, SEMEN. a sametere i515) 08) 96 HB
(lass TA BAA, BCA, BAMA, BOPA, ‘arise sokison vaste athe 78 o 8 50 12H ore”
‘BAA, BETA, BBLNA, nse conten ists) 176
Class 2 68, Bac, 89% BEF, B8T abide sition vest nd sin
arden
220) ar uncer us 100 2 85 321 Hors
(8604 reso) HRC
cover Sto (2040 25) nel 18 20 18 9 aerHB Oras
(es) isso) Re
ver 10 (85 10S ne "08 eS 2 35 aH ors
oT) Hac.
rer Fv to 1 4 1821 4 mer "ec 0 2 45 sei Horas
Fees) HRC
lace 2 Bone carbide sauion Yeats ae san
‘ardenee
24 20) ar unos 10 96 6 “6
ve 1855)
over 910 2010 25) et 00 20 20 “6
(em) 50)
lover 110 1 4[25 6 3, eS 5 2s “
)
ver #488115 (82 40 ne 20 2 30 45 se1Horas
20) 1385) HC.
7 These per dante ln ware etaaed one basis at hve war he lvgesl sues commonly avalabe hat conaony re speclicavon popeay ams Tay
arg no ita 25 absolute tts beyond whisn bong atonal coud na ange: be eared to the spectcaion
‘To mest te tans vequremants he Brn Morano sal ot bless tha 200 HB oF 98 HAS
© Closet products are rade fom soon sealed ate. Cass A pou arecokton eed ithe fnhod condition ler oroion resistance, nat treatments
tal or ehareing ss psi ropery and meet ne mochancsl pron requroments. Case ® products ee rave tm sowie ated mata hat has sok
ai hardened, Auer steel nthe sin hardened conden may ret show unto properies Irougrou ie ross secon, parlessanynstos ove et 20 ea
For sizes én (20 nm) in ameter ae smater,@ maxmuen nardnes o 241 HE (100 HA) is pemites.
TABLE 2_impact Energy Absorption Requirements AIAG B-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identification Tag. Appli-
‘Meira pac Van Miwa Inga Vas cation Standard!”
Sect spe, Rogrectorswerage | "Perea Ore
ca tach Seto Tree Specimen Ony oa
Species ND) ‘Seca 3. Ordering Information
seBeqpt® ~The inquiry and order for material under this specifica-
ews tion shall include the following as required to describe the
tous material adequately
— - 3.1.1 Specification designation latest issue, and analysis by
Tour io py” grade as selected from Table 3,
ioe rs 288) _ 3.1.2 Heat-treated condition (hati, for the austenitic stain
"See 82 51 rp amps less steels, solution treated (Class 1); solution treated after
finishing (Class 1A), and annealed- and strain-hardened (Class
2
B18.3 Hexagon Socket and Spline Socket Serews 3.1.3 Quantity (number of pieces or weight),
BI8.22.1 Plain Washers
23° AIAG Standard:
"Avail fom Autnuativ Industry Aston Group 24200 Lae, Suite 208
186
eee cll
\
Gh a szo/a 320m
414 Description of tems required (bars, bots, screws, oF
#27 pimensons (mse. gh of point, overall nth
finish, shape. and threads).
116 Nuts and washers. if required by purchaser, in accor
dance with Section 9
BLT End use,
318 Supplementary requirements, if any, and
3.19 Special requirements, in accordance with 4.3.1. 4.3.2.
433, 730104, HA. and 11
4, Materials and Manufacture
4.1 Process—The steel shalt be produced by any of the
TABLE 3. Chemical Requirements (Composition, %)*
following primary processes: open-hearth, basic-oxygen,
clectric-furmace. of vacuum-induction melting (VIM). The
primary melting may incorporate separate degassing or refin
ing. The molten steel may be Vacuum-treated prior to or during
pouring of the ingot. The basic oxygen process shall be limited.
to steels containing not over 6% chromium,
42 Discard—A sulficient discard shall be made to secure
Ireedom trom injurious piping and undue segregation.
4.3 Heat Treament
a - Steels
\aerenion 7 i
e770 aun 8. 76,u79 u uw
ove MU BU vou we
Giomimaoyaieum Carbon Ceorsars Tae Givarmon” Nal Grom
(WSI140, 4842 0° Malyodarum Moyoaoren ‘Mojodenum Mayécerure
rade a) (ars 4037) wisi) ser "ast Lom Caren Boron
Produc Proaich Prodaat Prod Proaict Prowse
Ange, SION. Range, VATHON. Range, VERSION. ange, VanstOn’% Range, VANSIONX gag, verses
Swe Owe Grew rt Ore
Or ter? ie ers Under od
Soom 002 002 085m 038.092 0a8- 008 10a ue
a0 oa oa ‘03 o-
Mangaese oe 900 070. aca os ook go 003 ate g
390 00 (3 vo
Prospons, 00s 005 0036 ods © 008s oas ss as «msm
Sutimax 0040 0008040 once 0a ons nae 00s 49 oom” 008s
stean Or 0c” ots. ode s= ones” ons. aes ae
035 03s 036 as 035 930
Net 04o- 0318-05,
070 200
005 pe ons oat og? 03
“0 Deo 090
002 oz. one ons ome zt ome ene
030 25 030 030
001
_ _ _ ‘2000
‘asian Sow, Cease 1, TA ara bP _
36,888 Corry
Ursiaoieed 18 Cooma Nike ai Type 308)
Ti 1 Grom wa AS THEOL
Prost Vator,
Procuctvaraten
ange —Pae Perse %
" (em naar ese Over or reer
orcas Dae 001 over 008 01 ovr
Manganese, max 200 008 ove 200 004 over
Prose, ous 2010 ower ones D010 ever
Sune max a0 0005 oe 030 2.005 ever
Scan 00 0.05 over 100 B05 over
Neat A010. on 90-130 ors
roman tee-zo0 020 170-190 020
(Corum + tartan 10 carton 005 unser
4 a s20/a 320m
TABLE 3 Continued
iv sr, ara 5PBaPA ce sem, Baen
vguotond 3 $8 cremumi0Nioe |
sabes 18 chemin “Sharma ah Added Sur tn An Soren 9
Goose eke (I Type 321) Neket AS Type 306 with ype se) Type. Se) MOST AS Type |
‘enc ea)
ea J east Front Frese
ven veo vee § vere version
ranges nse 2 rarons AS ages Sage
, ee MO og Derg MS eee Maat
oe e's tio? Mh
Dos Ociowr G08 Ov ow OTS ddl ow O18 ‘Odi owe Oae ;
20) doer 207 Snore 200 Gonomr 200 Otome | Soe
Goss doidawr 0045 Satan 899 Gotoom dso Soom obs Oates |
tai mar Sousa O05 mar dtmsom 018.mn Onwi” OGk.mx OBIDere Ofsemex oases ||
$00" teow 500°" Oaserer tao” Gos too Gos tan gana
an eG te aoe tap, :
120 o4s so ONS oo 10 100 149 08 1
we ve v0 wo
190 020 190 08 0020 130 (020 sao 020 ‘
20 010 '
S00
045; oaunder a
in ~ Rae St ae oo :
Identification Symbot __ _____ BBL. BALA _ _ ‘BSMLN, BEMLNA I
: Urspizes 1 Geer Nowa wih Nkopen—~ Urvabiaed 19 Crema 10 Wek Wayaapan wah
jee aS Tpe Sea wn etc xt) ‘ivogen (SI Tye stew van estar taka
Product Variation, % Product Varaion, & ‘
Rooyen ST forge —ecetvaraen S|
ee Over oF Under ‘ne Over oF Under ® :
xton ax 2090 0005 or cow 5 ow é
Nergorese, max 200 Sonor 200 0010 oe
rospors. max oes D010 ome aus 210 om
Soke man Soae soos oer a0 008 ove ‘
Stone tae Sosewen on 205 om |e
Now Boros ons ‘ebro a5 13
Srorien t0'200 a0 0-100 22
wjecone Sonnto 210
Noten ain-oxe on aioe
“Tre nina addton of B.S, Te, ond Pb ot pelied orca! fr Grade BF. whch searaun spacing and ere
2 Proaet anand dotarmratons sornetmes vary om te spect kets om rages At shown m te tables, The sever Gotorrintons of any vc
loment a heat ey rt vary bn above an blow he spots ange
For te L7M grace, «minum carbon content 0.28 hs peril [roves thatthe requ tense propertes ire metin the secon sts nied the use AS
4130 0 a4 alowed
Clas 1 ae mace rom schvion-realc mata. Css 1A product (BBA, BACA, BBA, BBPA, BAA, end BETA) are sokutorteated i De fhod cnstion. hss | 0
2 posts we toon ene and wronrsoee :
|
4.3.1 The bolting mterial shall be allowed to cool 10 room order, material shall be solution tested in the finished condi:
temperature aftr rolling of forging. Grades L7.L7A, L7B, tion: material so treated is described a Class UA t
L7C. LIM, 143.1, 70,71, U72, and L73 shal be reheated 4.3.2. When increased mechanical propentie are desired, the |
tv above the upper ertial temperature and liquid quenched austenitic bolting matenals shall be solution annealed ond | T
ain! tempered, Grades BS, BSC. BRM, BST, BEF BSP, BSLLN, strain handened if specified in the purchase order: material 30. | fi
ang BSMLN shall receive a carbide solution eatment, Prod: treated is ientiied as Class A
cis made trom such material are deseribed as Class 1. This 4.3.3 If scale-free bight finish is eequired this shall be
shall consist of holding the material fora salicient tine at a specified inthe purchase ones
temperature at which the chromium carbide will go into 4.3.4 For L7M bolting, the final heat weatment, which may |
solution and then cooling in air or ina Higuid medium a rate be the tempering or stess-rlieving operation conducted st | €
sufficient t prevent repreciptation of the carbide. Material 1150°F (620°C) minimum, shall he done after machining or |
thus treated is described as Class 1. specified in the parchaxe rolling ofthe threads
va
ec ccclUl
,
i) a s20/a 320M
‘5, Chemical Composition,
5.1 Heat Analysis—An analysis of each heal of steel shall
tbe made by the manulacturer 1 determine the percentages of
the elements specified in Table 3. This analysis shall be made
from a (est ingot taken during the pouring of the heat. The
chemical composition thus determined shall he reported to the
purchaser or the purchaser's representative, and shall conform
to the requirements prescribed in Table 3.
5.2 Product Anaivsis—An analysis may be made by the
purchaser from samples representing the bolting material, ‘The
chemical composition thus determined shall conform to the
requirements prescribed in Table 3
53 The steel shall not contain an unspecified clement for
the ordered grade to the extent that the steel conforms to the
requisements of another grade for which that element is a
specified element. Furthermore, clements present in concentra-
tions greater than 0.75 weighupercent shall be reported.
‘Chemical analysis shall be performed in accordance with Test
Methods A 75
6.1 Tensile Properties:
6.1.1 The material shall conform to the requirements as to
tensile properties prescribed in Table 1 at room temperature
ater heat treatment (see 4.3.1).
6.1.2 Number af Tests
6.12.1 For heat-treated bars, one tension test and one
impact test consisting of three specimens shall be made tor
cach diameter of each heat represented in each tempering
charge. In the continuous type treatment, a charge shall he
defined as 6000 Tb [2700 ke},
6.1.2.2 For studs, bolts, screws, cte., one tension test and.
fone set of three impact specimens shall be made for each
diameter of each heat involved in the lot. Each lot shall consist
ofthe following:
‘lamate ne
Lot Sie hal
10] ae under
ver 30) 301 445 ne
(ver 34 5 2 465), et
Over? ses}
1500 (580) er racon mere
4500 [2040 acten threct
{500 2700] 9 ration here?
6.1.2.3 Tension und impact tests are not required to be made
fon bolts, screws, studs, oF stud bolts which are fabricated from
heat-treated bars furnished in accordance with the requirements
of this specification and tested in accordance with 6.1.21
brovided they are not given a subsequent heat treatment
6.1.3 Test Specimens—Tension test specimens taken trom
finished bolts, screws. studs, or stud bolts shall be machined to
the form and dimensions and shall be taken from positions
shown in Annex A3 on Steel Fasteners, paragraph A3.2.1.7 of
Test Methods and Definitions A 370, ‘Tension test specimens
from bar stock are covered by Test Methods and Definitions
A370 in Annex AL, “Steel Bar Products.”
6.1.4 Test Method —Tension tesis shall be made in accor
dance with Test Methods and Detinitions A 370 including
Speed of testing in the scetion on Testing Apparatus. nd
Operations, on speed of testing, and the parts of Annex A3,
“Steel Fasteners.” applicable to machined test specimens.
6.2 Impact Properties
6.2.1 Requirements
6.2.1.1 Material of Grades L7. LTA, L7B, L7C, LIM, LA3,,
170, L714, L72, and L73 shall show a minimam impact energy
absorption of 20 ft Ib¢ [27 J] and of Grade Lia minimum
impact energy absorption of 40 tt - lef {54 J} at the test
temperature when tested by the procedure specified in the
applicable portions of Sections 19 to 28 of Test Methods and
Definitions A 370, The temperature of the coolant used for
chilling the test specimens shall be controlled within +3°F
[15°C]. Impact tests are not required for catbide solution
{reated or strain hardened Grades BS, BRE, BSP, BSM, BRT.
BLN, and BSMLN for temperatures above -325°F |-200°C}
for carbide solution treated Grades BS, BSP, BSC, and B8LN
above ~425°F [-255°C]: for all ferritic and austenitic steel
‘grades of bolting “sn. (12.5 mm) and smaller in diameter. All
‘ther material furnished under this specification shall be tested.
Test temperatures for ferritic grades are listed in Table 4
Exceptions to this requirement are permissible, and the impact,
tests may be made al specified temperatures diferent than
those shown in Table 4, provided the test temperature is at least
as low as the intended service temperature and the bolting is
suitably marked to identify the reported test temperature. When,
impact testing is required for austenitic grades, test critena
shall be agreed upon between the supplier and purchaser.
6.2.1.2 The impact test requirements for standard and sub-
size Charpy test specimens are prescribed in Table 2
6.2.2 Number of Tess:
6.2.2.1 The test requirements for heat-treated bars are given
in 6121
6.2.2.2 For test requirements on studs, bolts, screws, etc
see 6.1.2.2 and 6.1.2
6.2.2.5 Impact tests are not required to be made on heat-
treated bars, bolis, serews. studs, and stud bolts in, (125
mm} and under in diameter.
6.2.3 Test Specimens:
6.2.3.1 The impact test specimen shall have the form and
dimensions shown in Fig. 10 of Test Methods and Definitions
A.370 for the Charpy V-notch specimen, Type A. The notch
shall be located on the test specimen surface which most
closely approaches « radial direction. The base of the notch
shall be as nearly as practicable perpendicular to the surface of
the bat.
6.2.3.2 For sections 1 in. [25 mm] or less in diameter, test
specimens shall be taken atthe axis; for sections aver I in. [25
mm} in diameter, midway between the axis and the suriace
6.3 Hardness Requirements:
6.31 The hardness shall conform to the requirements pre-
scribed in Table 1 with testing performed in accordance with
‘Test Methods and Definitions A 370,
6.3.2 The maximum hardness of Grade L7M shall be 235
HB or 99 HRB (conversion in accordance with Table 2B of
TABLE 4 Recommended Test Temperature for Stock
©
Tne, ire, a Ta
U.t7a, LB, 7, Sor
va, ar
AGH
ew.
‘Gh a 320/A 320M
‘Test Methods and Definitions A 370). Minimum hardness shall
not be less than 200 HB or 93 HRB. Conformance 10 this
hardness shall be ensured by testing the hardness of each stud
oF bolt by Brinel! or Rockwell B methods as described in the
sections on Brinell Test, Portable Hardness Test, and Rockwell
Test of Test Methods and Detiaitions A 370,
6.3.2.1 The use of 100% electromagnetic testing for hard-
ress a8 an alternative to 100 % indentation hardness testing is
Permissible when qualified by sampling using indentation
hardness testing. Each lot tested for hardness electromagnet
cally shall be 100 % examined in accordance with Practice
566, Following electromagnetic testing for hardness, a ran-
dom sample of a minimum of 100 pieces in each purchase lot
(as defined in 6.1.2.2) shall be tested by indentation hardness
methods. All samples must meet hardness requirements. to
Permit acceptance of the lot. If any one sample is outside of the
specified maximum or minimum hardness, the lot shall be
rejected and either reprocessed and resampled. or tested 100%
by indentation hardness methods
6.3.2.2 In the event a controversy exists relative to min
‘mum strength, tension tests shall prevail over hardness read.
ings. Products which have been tested and found acceptable
shall have a line under the grade symbol
6.3.2.3 Surface preparation for indentation hardness testing
shall be im accordance with Test Methods E 18. Harness tests
shall be performed on the end of the bolt of stud. When this
impractical, the hardness test shall be performed elsewhere.
7. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
7.1 Bolts, serevis, studs, and stud bolts shall be pointed and
shall have 2 workmanlike finish. Points shall be flat and
chamfered or rounded at option of the manufacturer. Length of
points on studs and stud bolts shall be not less than one nor
‘more than two complete threads as measured from the extreme
fend parallel to the axis. Length of studs and stud bolts shall be
measured from first thread to first thread.
7.2 Standard permissible variations for dimensions of bars
shull be as prescribed in Tuble 5. Aside from the tolerances
given in Table 5, additional tolerances for the basic materials
are given in Specifications 29/ 29M and A 276,
7.3 Bolt heads shall be in accordance with the dimensions of
ANSI BI8.2.L. Unless otherwise specified in the purchase
order, the Heavy Hex Screws Series should be used, except the
TABLE 5 Permissible Variations in Size of Hot-Rolled ars
Ouro
Spetid Sze Semis oe
i cy Unser
Salehar acer 0008" 013 as
Over eto ve(t, et 00D B18 8008
ver Tato Wel) inet 0007 BIB 3007
Over sete aiz2l inet 0.008020 3.008
Over ato 151.06 0008-073 300 O23 DON O33
Queries wiza].me_ 9010025901) O25 DIS Oe
(2.rei Oon 928 de! O98 DoIe oat
Ours utors[ss} O12 050 D012 Gad DOW OMe
Overt Seto 1 (98h nd 0918 9:98 oo aa O62 O58
Ore 15102 (seh inc oe BaD 040 0023 Ose
Qui 22 ies iped vs O79 Od 0.09 O88
190
‘maximum body diameter and radius of fillet may be the same
as for the Heavy Hex Bolt Series. Sucket-head fasteners shall
be im accordance with ANSI BI8.3.
8. Retests
8.1 If the results of the mechanical tests of any test lot do
not conform to the requirements specified, the manufacturer
may retreat such lot not more than twice, in which ease two
additional tension tests and one additional impact test consis
ing of three specimens shall be made from such fot, all of
which shall conform to the requirements specified.
9, Nuts and Washers
9.1 Bolts, studs. and stud bolls of Grades L7, L7A, L7B,
LIC. L43. L170, L7I. L72, and L73 shall be equipped with
ferritic alloy nuts conforming to Grade 4 or Grade 7 of
Specification A 194/A 194M or a grade of steel similar to the
studs, Gride 7M nuts at a hardness not exceeding 235 HB (or
equivalent) shall be used with Grade L7M bolts, studs, and stud
bolts. All nut materials, including those which may be supplied
under Specification A 194/A 194M, shall be subject t0 the
impact requirements of this specification in the following
‘manner: impact tests shall be made on test specimens taken
tom the bar or plate from the heat of steel used tor manufac.
(uring the nuts, and heat teaied with the nut blanks.
9.2 Bois. studs, and stud bolts of Grades B8, B8C, BST,
BSP, BSF. BSM, BSLN, and BEMLN shall be equipped with
saustenitic alloy nuts conforming to Grades 8, 8C. ST, 8F. 8M,
SLN, and 8MLN for Specification A 194/4 194M
‘are not required tor Grades 8F. $M, 87. and SMLN for
temperatures above ~325°F [~200°C] and for Grades 8. 8B, 8C,
tnd SLN above ~425°F [255°C]
93°F the purchaser requires nuts with a Charpy impact
energy absorption of mot less than 20 ft - Wot [27 J] at
temperatures below ~150°F [100°C], he may require that the
‘nuts conform to Grades 8, 8C, 8M, BP, 8T, 8E, SLN, or SMLN.
of Specification A 194/4 194M,
9.4 Washers for use with ferrtie steel boltin
to Specification F 436,
9.5 Washers for use with austenitic steel bolting. shall be
made of austenitic steel as agreed upon between the manufac
turer and purchaser.
9.6 Washer dimensions shall be in accordance with require:
‘ments of ANSI B18.22.1, unless otherwise specified in the
purchase order.
10. Threads
10.1 Al alloy steel bolts, studs, and stud bolts, unless
otherwise specified, shall be threaded in accordance with ANSI
BI.1, Class 2A fit sizes 1 in. (25 mm] and smaller in diameter
with the Coarse Thread Series, and 1% in, [29 mm] and larger
in diameter with the 8 Pitch Thread Series.
10.2 Where practical, all threads shall be formed after heat
teament. Class 1A. Grades BSA, BSCA, BSMA, BSPA,
BSFA, BETA, BSLNA. and BSMLNA are to be solution:
teated in the finished condition.
11, Inspeeti
HA The inspector representing the purchaser shall have
free entry, at all times while work on the contract of the
shall conform
Ty
81
i
ee
8
Si
ic
eer
yr
b
f
i
4
1
‘ib a s20/a 320m
purchaser is being performed, to all parts of the manufacturer's
works that concem the manufacture of the material ordered
‘The manufacturer shall afford the inspector all reasonable
facilities to satisfy hirm that the material is being furnished in
accordance with this specification. All tests (except product
analysis} and inspection shall be made at the place of manu
facture prior 0 shipment, unless otherwise specified, and shall
bbe so conducted as not to interfere unnecessarily with the
operation of the works,
12, Rejection and Rehearing
121 Rejection:
12.1.1 Unless otherwise specitied in the order, any rejection
based on tests made in accordance with 5,2 shall be reported to
the manufacturer within 30 days from the receipt of samples by
the purchaser.
12.1.2 Material that shows defects subsequent to its accep-
lance at the manufacturer's works shall be rejected. and the
manufacturer shall be notified.
122 Rehearing —Samples tested in accordance with 3.2
that represent rejected material shall be preserved for 2 weeks
from the date of the test report. In case of dissatisfaction with
the results of the tests, the manufacturer may make claim for a
rehearing within thar time
13. Certification
13.1 When agreed upon in writing between the manufac
turer and the purchaser, a certification that the material von-
farms to the requirements of this specification shall be the basis
of acceptance of the material. Otherwise, the manufacturer
Shall report to the purchaser or the purchaser's representative
the results of the chemical analyses and mechanical tests made
in accordance with the specification. The specification desig
tation included on test reports shall include year of issue and
revision letter, if any
1. Product Marking
14.4 Grade and manufacturer's symbols shall be applied to
‘oe end of studs x in. {10 mm) in diameter and larger and to
the heads of bolts Yin. [6 mm in diameter and larger (If the
available area is inadequate, the grade symbol may be marked
fon one end and the manufacturer's identification symbol
‘marked on the other end.) The identification symbol shall be as
shown in Table 3. In the case of Class 2, Grades B8, BSC.
8M, BSP. BSF, and BST strain hardened as provided in Table
1.4 Tine shall be stumped under the grade symbol in order to
distinguish it from Class | and Class 1A bolting which has not
been strain hardened. In the case of Class 1A. the marking
BRA. BSCA, B8MA. BRPA. BEFA, BSTA, BSLNA. and
BSMLNA identifies the material as being in the solution
treated condition in the finished state, Grade L7M which has
been 100 i evaluated in conformance with this specification,
shall have a Tine under the grade symbol to distinguish ic from
LIM prexluced to previous revisions not requiring 100%
hardness testing
14.2 For bolting materials, including threuded bars, that are
furnished bundled and tagged or boxed, the tags and boxes
shali carry the grade symbol for the material identification and
the manufacturer's identification mark or name
14.3 Nuts fom materials that have been impact tested shall
be marked with the leer “L’
14.4 For purposes of identification marking, the manufac:
turer is considered the organization that certifies the fastener
Was manufactured, sampled, tested, and inspected in accor,
dunce with the specification and the results have been deter.
‘mined to meet the requirements of this specification.
14.5 Bar Coding—In addition to the requirements in 14.1,
14.2. 14.3, and 144, bar coding is acceptable as a supplemen.
lary identification method. Bar coding should be consistent
with AIAG Standard B-5 02.00. [used on small items, the bat
code may be applied to the box or a substantially applied tag
15. Keywords
15.1 additional elements: austenitic stainless steel: bolts
Mecl; chromium-molybdenum steel: fasteners—steel; mark
ings on fitings: nickel-chromium-molybuenum alloy steels
Pressure vessel service; stainless steel bolting material: starting
material stel bars—alloy; steel bolting material: steel flanges.
Steel valves: temperature service apphieations—low
SUPPLEMENTARY REQUIREMENTS.
The following supplementary requirements shall apply only when specified by the purchaser in the
inguiry, contract, and order
S1. Impact Propertis
1.1 When impact properties are desired for austenitic steel
frades exempt from (esting under 6.2.1, test shall be made as
‘greed between the manufacturer and the purchaser
82. Marking
S21 Grade and manufacturer's identification symbols shall
be applied to one end of studs and to the heads of holts of all
Sizes. (If the available area is inadequate, the grade symbol
‘may be marked on one eng and the manufacturer's identitiew:
Won symbot marked on the other end.) For bolts and studs
smaller than Yin. (6 mm] in diameter and for 4 in. 16 mm)
suds requiring more than a total of three syinbols. the marking
shall be a matter of agreement hetween the purchaser and
manufacturer,
83. Lateral Expansion
S3.1 When lateral expansion measurements. for ferttic
Meels are required in addition to the energy absorption require:
‘ments of 6.2.1.1. the minimum vilue for each specimen of a set
must be 01S in, [038 mm). The test temperature shall be
specified by the purchaser and agreed upon by the producer
191
NGS
ay.
en
dade
{ha 32070 320m
Not Si—Grades 17, 7A. L7B will generally have diieulty meeting
the minimum vatae at ~150°F [
APPENDIX
(Nonmandatory Information)
x
XL.) Stain hardening is the increase in strength and
hardness that results from plastic deformation below the
recrystallization temperature (cold work). This effect is pro-
duced in austenitic stainless steels by reducing oversized bars
fof wire to the desired final size by cold drawing or other
process, The degree of strain hardening achievable in any alloy
is limited by its strain hardening characteristics. In addition, the
amount of strain hardening that can be produced is further
limited by the variables of the process, such asthe total amount
of cross-section reduction, die angle and bar size. In large
diameter bars, for example, plastic deformation will occur
principally in the outer regions of the bar, so thatthe increased
strength and hardness due (o strain hardening is achieved
predominantly near the surface of the bar. That is, the smaller
the bar, the greater the penetration of strain hardening,
STRAIN HARDENING OF AUSTENITIC STEELS
X12 Thus, the mechanical properties of a given strain
hhardened fastener are dependent not just on the alloy, but also
‘on the size of bar from which itis machined. The minimum bar
size that can he used, however, is established by the configu.
ration of the fastener, so that the configuration can affect the
strength of the fastener,
X1.3_ For example, a stud of a particular alloy and size may
bbe machined from a smaller diameter bar than a bolt of the
same alloy and size because a larger diameter bar is required to
accommodate the head of the holt. The stud, therefore, is likely
to be stronger than the same size bolt in a given alloy
‘The American Society for Tsing ané Matera aks no postion respecting tho vakdy of any patent igh assariedn conscton
win any tom mortoned i dh etanaaré. Unrs f tvssandard ar expressly assed ha delrmnaton of ha val O ary au
Daten rin. and the nsk oie of sch ts, 9 ently tre own responsibly
Tie stands uti fo rvision at any ime bythe response tnatnica commited mutt bo ravioned aver fe year and
itnchrense, eter eaporvador mincann Your commen are ed ater revs of hs standad or for aceon tae
‘anu shuld te adresse ASTM reacurters. Your comnts wal csv carat corsiteaon a. hoe oe expanse
{aomseal commute, wich You may aera you lel fa your comments Mave na ecewee a Ya Pearing YOu Sheu ake Yur
‘tons ten tho ASTA Commies on Standard 100 vr Harbor Divo, Wet Conshohocken PA 19428
192
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Series LFII Residential Concealed Pendent Sprinklers, Flat Plate 4.2 K-FactorDokument4 SeitenSeries LFII Residential Concealed Pendent Sprinklers, Flat Plate 4.2 K-FactorAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series LFII Residential Horizontal Sidewall Sprinklers 4.2 K-FactorDokument8 SeitenSeries LFII Residential Horizontal Sidewall Sprinklers 4.2 K-FactorAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series LFII Residential Flush Pendent Sprinklers 4.2 K-FactorDokument8 SeitenSeries LFII Residential Flush Pendent Sprinklers 4.2 K-FactorAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sprinkler Spray Patterns Refer To The General Description Section Before Applying The Spray Pattern DataDokument38 SeitenSprinkler Spray Patterns Refer To The General Description Section Before Applying The Spray Pattern DataAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series LFII Residential, NFPA 13 Optimized Horizontal Sidewall Sprinklers 5.6 K-FactorDokument6 SeitenSeries LFII Residential, NFPA 13 Optimized Horizontal Sidewall Sprinklers 5.6 K-FactorAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model G2 Sprinkler Guard, Model WS-2 Shield, and Model WSG-2 Sprinkler Guard With Shield Series ELO-231, ELO-231B, and ELO-231FRB SprinklersDokument4 SeitenModel G2 Sprinkler Guard, Model WS-2 Shield, and Model WSG-2 Sprinkler Guard With Shield Series ELO-231, ELO-231B, and ELO-231FRB SprinklersAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model G1 & G4 Sprinkler Guards Model G1/S1 & G4/S3 Guards With Shields Series TY-B, TY-FRB, TY-L, and TY-FRL SprinklersDokument4 SeitenModel G1 & G4 Sprinkler Guards Model G1/S1 & G4/S3 Guards With Shields Series TY-B, TY-FRB, TY-L, and TY-FRL SprinklersAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jotashield Flex: Technical Data SheetDokument3 SeitenJotashield Flex: Technical Data SheetAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installer Warning!!! Read The Following Cautions Before Handling or Installing Your SprinklersDokument4 SeitenInstaller Warning!!! Read The Following Cautions Before Handling or Installing Your SprinklersAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series LFII Residential Pendent Sprinklers 4.9 K-Factor: Technical Services: Tel: (800) 381-9312 / Fax: (800) 791-5500Dokument8 SeitenSeries LFII Residential Pendent Sprinklers 4.9 K-Factor: Technical Services: Tel: (800) 381-9312 / Fax: (800) 791-5500Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Style 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 Recessed Escutcheons & Protective Paint Caps For Automatic Sprinkler Recessed InstallationDokument4 SeitenStyle 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 Recessed Escutcheons & Protective Paint Caps For Automatic Sprinkler Recessed InstallationAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flyer TycoDokument8 SeitenFlyer TycoAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
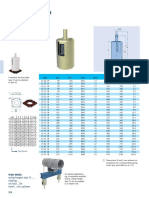
- Spring Hangers Type 25Dokument1 SeiteSpring Hangers Type 25Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snubbers Type 31Dokument1 SeiteSnubbers Type 31Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jotun Essence Easy Clean Matt: Technical Data SheetDokument3 SeitenJotun Essence Easy Clean Matt: Technical Data SheetAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jotashield Extreme: Technical Data SheetDokument3 SeitenJotashield Extreme: Technical Data SheetAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esab Pipeweld 6010R: Classifications: ApprovalsDokument1 SeiteEsab Pipeweld 6010R: Classifications: ApprovalsAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classifications: Approvals:: Typical Tensile PropertiesDokument1 SeiteClassifications: Approvals:: Typical Tensile PropertiesAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classifications: Approvals:: Typical Tensile PropertiesDokument1 SeiteClassifications: Approvals:: Typical Tensile PropertiesAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical Tensile Properties: Classifications: Welding Current: Diffusible Hydrogen: Alloy Type: Coating TypeDokument1 SeiteTypical Tensile Properties: Classifications: Welding Current: Diffusible Hydrogen: Alloy Type: Coating TypeAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld-On Brackets Type 35Dokument1 SeiteWeld-On Brackets Type 35Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snubbers Type 30Dokument1 SeiteSnubbers Type 30Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid Struts Type 39Dokument1 SeiteRigid Struts Type 39Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
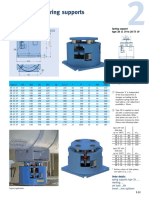
- ANVIL PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS ContinuedDokument1 SeiteANVIL PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS ContinuedAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring Supports Type 29Dokument1 SeiteSpring Supports Type 29Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
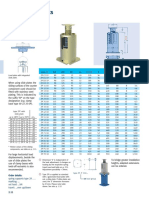
- Heavy Duty Spring Supports Type 28Dokument1 SeiteHeavy Duty Spring Supports Type 28Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring Hangers Type 21Dokument1 SeiteSpring Hangers Type 21Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANVIL PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS (CTD)Dokument1 SeiteANVIL PIPE HANGERS & SUPPORTS (CTD)Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anvil Pipe Hangers & SupportsDokument1 SeiteAnvil Pipe Hangers & SupportsAchraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heavy Duty Spring Hangers Type 22Dokument1 SeiteHeavy Duty Spring Hangers Type 22Achraf BoudayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)