Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Edsc-304 Graphic Organizer - Main Idea Columns
Hochgeladen von
api-3007003760 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
90 Ansichten1 SeiteIdentify the main idea as well as the three supporting ideas for that main idea. Define, describe and provide reasoning for what the most basic, main and central idea is. Show how the supporting ideas all relate to each other.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
edsc-304 graphic organizer- main idea columns
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenIdentify the main idea as well as the three supporting ideas for that main idea. Define, describe and provide reasoning for what the most basic, main and central idea is. Show how the supporting ideas all relate to each other.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
90 Ansichten1 SeiteEdsc-304 Graphic Organizer - Main Idea Columns
Hochgeladen von
api-300700376Identify the main idea as well as the three supporting ideas for that main idea. Define, describe and provide reasoning for what the most basic, main and central idea is. Show how the supporting ideas all relate to each other.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
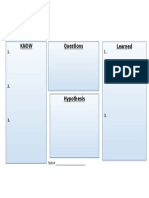
Name_____________________
Main Idea: Electromagnetism
As you read p. 556-630 in your Holt Physics textbook chapter for Electricity: Identify the main
idea as well as the three supporting ideas for that main idea. In the main idea box: define,
describe and provide reasoning for what the most basic, main and central idea is in this unit. In
each of the supporting idea boxes: define and describe as well as show how the supporting ideas
all relate to each other. There should be an equation for each supporting idea that ties to at
least one other idea. Then at the bottom of each supporting ideas box provide a completed
practice problem based on that idea as well. This activity is meant to help promote a more
intuitive understanding of how different concepts in the unit relate to one another. Hopefully,
after completion of this assignment, certain concepts will seem more understood as being
related than previously. Include some tie to MAGNETISM as well. The organizer shall be due by
the end of this week: Friday.
Electric Charge
All objects in the world are made up of an infinite amount of particles, which can be charged. Charge is
the property by which a particle is said to be affiliated in such a way as to have a preference of which
other source charges it would like to be near. The two different distinctions for charge are positive (eg:
positron) and negative (eg: electron). The symbol for charge is Q, and the units are Coulombs.
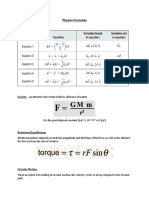
Electric Field (unit: V/m or N/C)
Electric Potential (unit: V)
Electric Current (unit: A)
The Electric Field is best defined
Electric Potential (also known
An electric current is defined to
as the ratio of voltage per
as Voltage) is defined as the
be the rate of change of electric
meter. Another definition of
Work per unit charge. It is best
charge. It is best understood as
the electric field is the force per
understood as the work
the ratio of charge per time.
charge ratio. The direction of
required to move a point
Similar to how a river of what is
the field is said to be in the
charge from one place to
made up of water molecules,
direction that would apply a
another. Another definition for
an electric current is simply a
force on a positive test charge.
electric potential is the product
flow of electric charge.
The electric field lines point
of the negative electric field
Conventionally the electric
radially outward from positive
with the distance. In many
current flows from positive to
to negative charges. E-fields are
ways, voltage is simply
negative, similar to how the
like the slope on a hillside,
describing different distance
electric field lines orient. The
whereas the voltage are the
points along an electric field.
most simple magnetic fields
various heights.
originate from simple currents.
= =
It is the ratio of volts per
=
=
resistance.
?
A
What is the work required to
= @ = B
What is the E-field on a 7 C
move a 20 C charge over 50 V?
How long does it take 1.50 C of
charge exerted under a 100 N
charge to pass in a 7 A wire?
force?
= = ()()
.
= =
= =
= .
= . /
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TeachingAboutEnergy (RobinMillar)Dokument20 SeitenTeachingAboutEnergy (RobinMillar)RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 ModuleDokument49 SeitenGrade 8 ModuleJuan Miguel Sapad AlpañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guides and Introductions To Tutorials: Electricity 1Dokument12 SeitenStudy Guides and Introductions To Tutorials: Electricity 1Cher TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set Theory ThesisDokument5 SeitenSet Theory ThesisTracy Hill100% (1)
- Annotated Bibliography Assignment-NSS 2015Dokument3 SeitenAnnotated Bibliography Assignment-NSS 2015Hyung Joo AhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Statement Dark MatterDokument7 SeitenThesis Statement Dark Mattersoniasancheznewyork100% (2)
- ESL acommendationsDokument7 SeitenESL acommendations3slearning3Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 - Module 22: Magnetic Property of AtomsDokument19 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 1 Quarter 2 - Module 22: Magnetic Property of AtomsLovely MalejanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admmodule s11 12ps Iiia 1Dokument24 SeitenAdmmodule s11 12ps Iiia 1George AbreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TH Phy NatureDokument14 SeitenTH Phy NaturenchandrasekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minh 1Dokument7 SeitenMinh 1api-551486913Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1A Gases: Its Properties and The Kinetic Molecular TheoryDokument16 SeitenScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1A Gases: Its Properties and The Kinetic Molecular TheoryMei RaidenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 Sci8 Mod6Dokument24 SeitenQ1 Sci8 Mod6Regine Rafer EscalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesizing Information: Step-by-Step Instructions For LearnersDokument3 SeitenSynthesizing Information: Step-by-Step Instructions For LearnersRomelSorianoLadislao100% (1)
- Isaacs Storm Thesis StatementDokument5 SeitenIsaacs Storm Thesis Statementafcnomlaq100% (2)
- Towards A Research-Informed Teaching Sequence For EnergyDokument24 SeitenTowards A Research-Informed Teaching Sequence For Energyivan talonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellanalogyassignmentDokument2 SeitenCellanalogyassignmentapi-238210606Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Theory of Neural ComputationDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To The Theory of Neural ComputationLuthier91Noch keine Bewertungen
- HeidiprotocolrevisedDokument13 SeitenHeidiprotocolrevisedapi-302772510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Educ602 Learning PlanDokument20 SeitenEduc602 Learning Planapi-261868573Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDokument7 SeitenDigital Unit Plan Templateapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q2M1Dokument23 SeitenQ2M1Jesus GombaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science Q2 Week 6 SLM 7Dokument15 SeitenPhysical Science Q2 Week 6 SLM 7Romel Bayaban33% (3)
- Q2M3Dokument22 SeitenQ2M3Sophia Jhayne AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Lesson - CircuitsDokument9 SeitenScience Lesson - Circuitsapi-280467536Noch keine Bewertungen
- #4) Body Paragraphs: University of Arkansas 1Dokument6 Seiten#4) Body Paragraphs: University of Arkansas 1IvetNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 2Dokument14 SeitenGeneral Physics 2Frances Ayanna QueddengNoch keine Bewertungen
- STE Electronics10 Q1 Mod2 Relationship-of-Basic Quantities Vargas-FlorizelDokument19 SeitenSTE Electronics10 Q1 Mod2 Relationship-of-Basic Quantities Vargas-FlorizelApril EspiñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 6 Factors Affecting The Strength of ElectromagnetDokument20 SeitenScience: Quarter 3 - Module 6 Factors Affecting The Strength of ElectromagnetMaria Bettina Francesca Bartolome100% (10)
- STE Grade 10 Electronics Q1 Module 6Dokument21 SeitenSTE Grade 10 Electronics Q1 Module 6harry timbol100% (1)
- Organizing Supporting Statements with ConnectivesDokument3 SeitenOrganizing Supporting Statements with ConnectivesFatima JabeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Authoritative WritingDokument22 SeitenAuthoritative Writinglatest Lekhesh sNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDITED STE Electronics Q1M6 ApoderadoCorazon SMNHSDokument29 SeitenEDITED STE Electronics Q1M6 ApoderadoCorazon SMNHSwetlog lolololim100% (1)
- SCI8 Q1M3 Lolomboy NHSDokument32 SeitenSCI8 Q1M3 Lolomboy NHSAivie PastranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Ambitions On A Finite PlanetDokument465 SeitenHuman Ambitions On A Finite PlanetdltanevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitational Potential EnergyDokument14 SeitenGravitational Potential EnergyKezzy ZiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Teaching Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenMicro Teaching Lesson Planmanthasha100% (1)
- Unit PlanDokument9 SeitenUnit Planapi-393524677Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 8 3Q Module 3Dokument22 SeitenSCIENCE 8 3Q Module 3Bing Sepe Culajao100% (2)
- Theme Synthesis Teaching Assignment: Conclusion About Theme in Your Presentation/EssayDokument2 SeitenTheme Synthesis Teaching Assignment: Conclusion About Theme in Your Presentation/Essaykal51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Mass Research PaperDokument7 SeitenAtomic Mass Research Papertozvnfvnd100% (1)
- Physical Science Module 9Dokument28 SeitenPhysical Science Module 9Leiryza Capanayan100% (3)
- Science: Self-Learning ModuleDokument16 SeitenScience: Self-Learning ModuleMei RaidenNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeneralPhysics12_Q3_ver4_Mod2_Electric-Potential-version4Dokument19 SeitenGeneralPhysics12_Q3_ver4_Mod2_Electric-Potential-version4belloheideliza2Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1-3aDokument17 SeitenGeneral Physics 1-3aAshley Loyola GarnicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENCHEM1 12 Q1 WEEK6 MELC21 MOD Aguite Lovella FINAL Sherwin Jay PalaspasDokument21 SeitenGENCHEM1 12 Q1 WEEK6 MELC21 MOD Aguite Lovella FINAL Sherwin Jay Palaspaswencylle casilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro to Squishy CircuitsDokument7 SeitenIntro to Squishy CircuitsianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1, Week 1 - Module1: Postulates of The Cell TheoryDokument55 SeitenGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1, Week 1 - Module1: Postulates of The Cell TheoryCoulline DamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Essays With An OutlineDokument2 SeitenWriting Essays With An OutlineErikNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Universitext) Stephen Bruce Sontz (Auth.) - Principal Bundles - The Classical Case-Springer International Publishing (2015)Dokument285 Seiten(Universitext) Stephen Bruce Sontz (Auth.) - Principal Bundles - The Classical Case-Springer International Publishing (2015)Eduardo UrsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read 550 Bda Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenRead 550 Bda Lesson Planapi-404203709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics (1STQ-M1)Dokument23 SeitenElectronics (1STQ-M1)lj emadem100% (1)
- Forms of EnergyDokument6 SeitenForms of Energyapi-279793282Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Statement Going GreenDokument8 SeitenThesis Statement Going GreenPaperWritersOnlineUK100% (2)
- Envi Sci - Module 2, Unit 3Dokument5 SeitenEnvi Sci - Module 2, Unit 3Roshin TejeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text As Connected DiscourseDokument14 SeitenText As Connected DiscourseWecenyekeylanes GemcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- ct9 Ilm1Dokument13 Seitenct9 Ilm1heart MUNOZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Theory of Neural ComputationDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To The Theory of Neural ComputationJon Arnold GreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction to Probability: A Concise Exploration of Core ConceptsVon EverandAn Introduction to Probability: A Concise Exploration of Core ConceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Unit Plan TemplateDokument7 SeitenDigital Unit Plan Templateapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and CircuitsDokument11 SeitenElectricity and Circuitsapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 304-Guided NotesDokument2 SeitenEdsc 304-Guided Notesapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 304 - Electric Cart RubricDokument1 SeiteEdsc 304 - Electric Cart Rubricapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 442c-Teaching Philosophy MatrixDokument3 SeitenEdsc 442c-Teaching Philosophy Matrixapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc-304 Graphic Organizer - Main Idea Columns BlankDokument2 SeitenEdsc-304 Graphic Organizer - Main Idea Columns Blankapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 304-Webercise ElectricityDokument3 SeitenEdsc 304-Webercise Electricityapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Why Study MomentumDokument3 SeitenWhy Study Momentumapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 304-Main and Supporting Ideas GoDokument2 SeitenEdsc 304-Main and Supporting Ideas Goapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Argumentation EpDokument1 SeiteArgumentation Epapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ep Text StudyDokument1 SeiteEp Text Studyapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc-Graphic Organizer KQHLDokument1 SeiteEdsc-Graphic Organizer KQHLapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 442c-Modeling Lesson 1Dokument10 SeitenEdsc 442c-Modeling Lesson 1api-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc Evaluation 2-Lesson PlanDokument6 SeitenEdsc Evaluation 2-Lesson Planapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 442c-Ep Inquiry ActivityDokument2 SeitenEdsc 442c-Ep Inquiry Activityapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc 442c-Lesson Plan For InquiryDokument10 SeitenEdsc 442c-Lesson Plan For Inquiryapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edsc-Epistemic Text LessonDokument7 SeitenEdsc-Epistemic Text Lessonapi-300700376Noch keine Bewertungen
- Building Utilities 2: Casulla, Cristine T. Bs in Architecture 3 University of LuzonDokument20 SeitenBuilding Utilities 2: Casulla, Cristine T. Bs in Architecture 3 University of LuzonEreca NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test # 12.1 Physics-Ii: Superb in EducationDokument8 SeitenTest # 12.1 Physics-Ii: Superb in EducationKamran AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS Module 4 WorksheetsDokument14 SeitenPHYS Module 4 WorksheetsPrathmesh Sinha100% (2)
- George Van Tassel - The Council of Seven LightsDokument44 SeitenGeorge Van Tassel - The Council of Seven Lightsanon-193720100% (7)
- Physics FormulasDokument20 SeitenPhysics Formulasbrandon100% (1)
- Cutler-Hammer: Learning Module 2: Fundamentals of ElectricityDokument39 SeitenCutler-Hammer: Learning Module 2: Fundamentals of ElectricityobeNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 Science 3RD QTRDokument4 SeitenG8 Science 3RD QTRFlorita LagramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Tests Electrical Potential Energy PDFDokument9 SeitenPractice Tests Electrical Potential Energy PDFFirdausia Rahma Putri100% (2)
- Test Bank For A Concise Introduction To Logic 13th EditionDokument36 SeitenTest Bank For A Concise Introduction To Logic 13th Editionsarong.luxateslkm100% (41)
- Electricity Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenElectricity Lesson Planapi-278394742Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics (Theory) PDFDokument43 SeitenElectrostatics (Theory) PDFKisna guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ligand Field Theory. Cotton PDFDokument12 SeitenLigand Field Theory. Cotton PDFIngrid Rincón Valdivieso0% (1)
- 169 P3 Sol PDFDokument11 Seiten169 P3 Sol PDFEmanuel Martínez FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unil Ecch 26 MagnetismDokument72 SeitenUnil Ecch 26 Magnetismeviegonzalez211Noch keine Bewertungen
- Harold Aspden - The Physics of CreationDokument276 SeitenHarold Aspden - The Physics of Creationtrashbox1368100% (2)
- 9 Science Structure of AtomDokument8 Seiten9 Science Structure of AtomAjay AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23Dokument22 SeitenChapter 23hasanaltifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Forces and Fields Exam 1 ReviewDokument4 SeitenElectric Forces and Fields Exam 1 ReviewBob TheBuilderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1962 Fallout Shelter DesignDokument218 Seiten1962 Fallout Shelter DesignLouie_popwhatski100% (1)
- Pinch Effect in ConductorsDokument5 SeitenPinch Effect in ConductorsabhiknitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Igor Douven, AbductionDokument27 SeitenIgor Douven, AbductionakansrlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Theory I-LEC Mohamed MegahedDokument137 SeitenCircuit Theory I-LEC Mohamed MegahedHussien HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDokument43 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Currentdata teamNoch keine Bewertungen
- LLNL TR 411183Dokument35 SeitenLLNL TR 411183alaincharoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 1-2 PhysicsDokument42 SeitenForm 1-2 PhysicsRuvimbo NhongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom Models: From Democritus To Modern ModelDokument77 SeitenAtom Models: From Democritus To Modern ModelLance Iverson MeganoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics WikibooksDokument401 SeitenElectronics WikibooksBrent Michel FarmerNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Physics) R Gupta's Popular Master Guide 2022Dokument150 Seiten(Physics) R Gupta's Popular Master Guide 2022beniiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy sources and formsDokument13 SeitenEnergy sources and formsDERRICK LIM XIN LER MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gadaad Helnii Negdcen Shalgalt EnglishDokument17 SeitenGadaad Helnii Negdcen Shalgalt EnglishzoloolearnNoch keine Bewertungen